Ascending & Descending Tracts Flashcards
(50 cards)
Nuclei
Clusters of neuronal cell bodies within the CNS
Ganglia
Collection of neuronal cell bodies outside the CNS e.g. dorsal root ganglia
Grey matter
Areas occupied by neuronal cell bodies
White matter
Dense collections of myelinated fibres
Nerves
Bundles of axons covered by CT sheath -> PNS
Tracts
Funiculus
Fasciculus
Bundles of axons in the CNS
e.g. ascending and descending tracts
How does the CNS communicate with peripheral body structures
Where do they travel
Through pathways
They conduct either sensory or motor info
Pathways travel through the white matter of the brainstem and/or the spinal cord as they connect various CNS regions with cranial and spinal nerves
Principal fibre tracts of spinal cord (composite)

How do ascending and descending tracts differ in their naming convention
ASCENDING - “spino…” as they’re carrying impulses from pain, tactile, thermal, muscle and joint receptors
DESCENDING - “cortico…” as they carry motor info from the cerebral cortex and brainstem
Precentral gyrus
Primary motor cortex

Post-central gyrus
Primary somatosensory cortex

What do the superior peduncles connect
The midbrain to cerebellum, allowing info to travel from spinal cord to cerebellum
SUPERIOR
MIDDLE
INFERIOR

What are pathways composed of
Paired tracts
How many neurons are involved in SENSORY pathways
3
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
S ≈ 3
How many neurons are there in motor pathways
2
Upper motor neuron
Lower motor neuron
Located in ventral horn of grey matter (vent of car)

Name the main descending spinal tract
To distinguish posterior from anterior (spinal cord) -
H of grey matter reaches posterior aspect of SC
Anterior median sulcus

Where would an upper motor neuron be located
Cell body located either within the cerebral cortex or a nucleus within the brainstem
Where would a lower motor neuron usually be located
Within the anterior grey matter of the spinal cord or within a brainstem cranial nerve nucleus
Where do motor neurons usually decussate
At the medulla

What tract is responsible for the conscious control of muscle
The corticospinal tract/pyramidal pathway
Originates in the cerebral cortex
Axons descend through the internal capsule, enter the cerebral peduncles and form descending motor tracts

What do the corticospinal tracts form
A thick pair of anterior bulges in the medulla
- PYRAMIDS

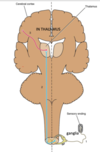
DECUSSATION of corticospinal tracts

Pathway of the lateral corticospinal tracts
What do these tracts control
Decussate within the pyramids of the medulla and then form the lateral corticospinal tracts in the lateral funciuli of the spinal cord
Axons of the lower motor neurons innervate skeletal muscles that control skilled movements in the limbs

Pathway of the anterior corticospinal tracts
What do these tracts innervate
The tracts descend the spinal cord in the anterior white funiculi
Axons decussate and synapse either with interneurons or lower motor neurons in the anterior grey matter of the spinal cord
Axons of the lower motor neurons innervate axial skeletal muscle






















