Brainstem Flashcards
(51 cards)
Sagittal section through the brainstem

Name the structures of the prosencephalon (forebrain)
Telencephalon - cerebral hemispheres/cerebrum
Diencephalon - between brain
Name the 3 structures of the rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
Metencephalon - pons
Myelencephalon - medulla
Metencephalon - roof portion (cerebellum)
*** NOTE: hindbrain does not include midbrain
What structures surround the brainstem
Brainstem lies anterior to cerebellum
Superiorly, continuous with the diencephalon
Medulla is continuous with the spinal cord
What structure is bulbar palsy associated with
Medulla
Function of brainstem
- Vital role in basic attention, arousal & consciousness
- Passes information between the spinal-cord and the cerebrum
- located in an area near bony protrusions, making it vulnerable to damage during trauma
- cranial nerve exit points
What cranial nerves arise from the brainstem
CN 3-12

Sagittal section through the brain

Coronal section through brain & brainstem
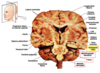
What feature tells you that you’re in the brainstem specifically the midbrain
Substantia nigra
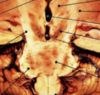
Name the structures on the posterior aspect of the brainstem

Posterior aspect of the brainstem

Where does the tegmentum lie
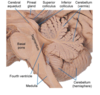
Locations of the pyramid, tegmentum and tectum of the
- medulla
- pons
- midbrain

What features define the anterior surface of the midbrain
- Interpeduncular fossa - deep depression in the midline
- Cerebral peduncles
- Posterior perforated substance - small BVs perforate floor
- Oculomotor nerve emerges from groove on medial side

What features define the posterior surface of the midbrain
Superior & inferior colliculi (corpora quadrigemina)
Trochlear nerve emerges below inferior colliculi

What are superior colliculi responsible for
Visual centres for visual reflexes
What are inferior colliculi responsible for
Lower auditory centres
What are the internal structures of the midbrain
Cerebral peduncles
Crus cerebri - descending axonal tracts
Cerebral aqueduct

How is the cerebral peduncle divided
By pigmented substantia nigra
ANTERIOR - crus cerebri
POSTERIOR - tegmentum

What are crus cerebri
Descending axonal tracts
Structure of cerebral aqueduct
What lies posterior to the cerebral aqueduct
Lined by ependymal cells
Surrounded by central grey matter - periaqueductal grey
TECTUM lies posterior to cerebral aqueduct
What is the superior colliculi
What is the function of the SC
- Large nucleus of grey matter
- Part of visual system
- Afferent corticotectal fibres from visual cortex - occipital lobe and frontal eye field of frontal lobe
- Controls eye movement

What defining feature lies at the level of the superior colliculi
RED NUCLEUS
- Grey matter mass between cerebral aqueduct and substantia nigra
- Redish hue due to iron containing pigment in cytoplasm of neurons
- Fibres pass to spinal cord via rubrospinal tract
- Motor control





















