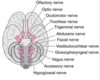
Cranial Nerves Flashcards
Oh, Oh, Oh, To Touch And Feel Very Good Velvet, Ah Heaven
CN I - Olfactory
CN II - Optic
CN III - Oculomotor
CN IV - Trochlear
CN V - Trigeminal
CN VI - Abducent
CN VII - Facial
CN VIII - Vestibulocochlear
CN IX - Glosspharyngeal
CN X - Vagus
CN XI - Accessory
CN XII - Hypoglossal
Some Say Money Matters, But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter Most
CN I - Sensory (Olfactory)
CN II - Sensory (Optic)
CN III - Motor (Oculomotor)
CN IV - Motor (Trochlear)
CN V - Both (Trigeminal)
CN VI - Motor (Abducent)
CN VII - Both (Facial)
CN VIII - Sensory (Vesitbulocochlear)
CN IX - Both (Glossopharyngeal)
CN X - Both (Vagus)
CN XI - Motor (Accessory)
CN XII - Motor (Hypoglossal)
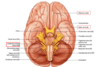
Gross anatomy photo of CNs

Sensory & Motor CN nuclei

Define olfactory bulb
Bundles of olfactory nerve fibres pass through cribriform plate of ethmoid bone

Where do olfactory tracts run
In olfactory sulcus
Olfactory tracts extend from olfactory bulb
What does the olfactory sulcus divide into
Medial and lateral olfactory striae
What happens if there is unilateral olfactory loss (anosmia)
Patient is often unaware of loss as contralateral olfaction can compensate

What does the optic nerve (CN II) do
What is its path
Optic nerve fibres obtain info from photoreceptors in retina
Optic nerve accesses optic cavity via optic canal
- unites with opposite optic nerve forming optic chiasm
- optic tract to lateral geniculate nuclei of thalamus
Where does the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) exit
Exits brainstem at PONTOMEDULLARY junction (at cerebellopontine angle)
Function of vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
Vestibular - maintain balance (vertigo)
Cochlear - conducts nerve impulses concerned with sound from organ of Corti in cochlea

Where do the olfactory, optic, facial and vestibulocochlear nerves exit the cranial cavity
Olfactory - foramina of cribriform plate
Optic - optic canal
Facial & vestibulocochlear - internal auditory meatus

Openings in the cranium

What happens as the auditory pathways enter the brainstem
Info crosses at multiple levels
What is common about the oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV) and abducent (CN VI) nerves
Travel in same part of the brain to innervate the muscles of the eye
In what direction do CN XI and XII travel
Towards the neck
Where does the oculomotor nerve arise
Describe its path
Where does it exit the cranium
Emerges on anterior surface of the brainstem - between pons and midbrain, in INTERPEDUNCULAR FOSSA
Usually passes between posterior cerebral artery and superior cerebellar artery
Exits skull via superior orbital fissure

Differentiate between the 2 nuclei of the oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Main oculomotor nucleus - supplies most of the extrinsic muscles of the eye
Accessory PS nucleus (Adenger-Westphal nucleus) - ciliary ganglion for pupillary light reflex

Name the foramen in the cranium that the oculomotor nerve passes through
Superior orbital fissure
Describe the path of the trochlear nerve (CN IV)
What is noteworthy about this nerve
What does it innervateM
Most fragile of the cranial nerves
Emerges from posterior surface of midbrain, from inferior caliculi
Passes through the superior orbital fissure
Innervates the superior oblique muscle of the eye
Describe the path of the abducent nerve
What does it innervate
What foramen of the cranium does it pass through
Emerges in groove between lower pons and medulla
Enters orbit through superior orbital fissure
Supplies lateral rectus muscle of eyeball
What do the occulomotr, trochlear, ophthalmic and abducent nerves have in common
All traverse the cavernous sinus to exit skull via superior orbital fissure

Specific function of trochlear nerve
Turns eye downwards and laterally
Specific function of abducent nerve
Abducts the eye laterally in horizontal direction























