Pyramidal tract lesion signs Flashcards
Define
corticospinal tract
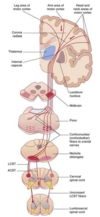
corticospinal tract
is a white matter motor pathway that carries efferent information from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord.
It is responsible for the voluntary movements of the limbs and trunk
corticospinal tract starting at the cerebral cortex that terminates on lower motor neurons and interneurons in the spinal cord

- Acute stage lesions*
- Name 3:*
Flaccid pararlysis (a neurological condition characterized by weakness or paralysis and reduced muscle tone without other obvious cause
-This abnormal condition may be caused by disease or by trauma affecting the nerves associated with the involved muscles.)
Areflexia (muscles don’t respond to stimuli) Hypotonia (decreased muscle tone)
Chronic stage lesions
Name 5:
- Increased reflex = hyperreflexia
- Increased muscle tone = hypertonic
- Areflexia = no muscular response to stimuli
- Extensor toe response (positive Babinski sign)
- Reduction or loss of superficial abdominal and cremasteric reflexs
- <u><em> Clouns </em></u> is involuntary and rhythmic muscle contractions caused by a permanent lesion in descending motor neurons. Resulting in uncontrollable, rhythmic, shaking movements found at the ankle, patella, triceps surae, wrist, jaw, biceps brachii.
Cortico-spinal tract Pathway
- 1st neuron starts from motor cortex in frontal lobe
- corona radiata come together at posterior internal capsule fibers
- fibers decussate at point of distal medulla
- then fibres cross forming lateral corticospinal tract (ipsilateral) and Anterior corticospinal tract
- Only to synapse in anterior horn of spinal cord —>
–> 2nd neuron (LMN) going to periphery
Pyramidal tract lesion signs of
UMN (Central motor neuron lesion)
Name:
- 1st sign of acute UMN lesion = paresis
- later (chronic) signs: ↑tone, spastic paralysis, clonus,
hyperreflexia, pyramidal signs - pyramidal signs: Babinski sign, Hoffman sign
- others: bowel & bladder dysfunction, sexual dysfunction
Pyramidal tract lesion signs of
LMN (Peripheral motor neuron lesion)
Name:
- ↓tone, flaccid paralysis, hyporeflexia,
*NO pyramidal signs
- atrophy (nutritional stimulus goes through peripheral nerve)
*Preferential innervation of pyramidal tracts: wrist extensor, forearm supinator, foot extensor
- if there’s a pyramidal tract lesion those movements will be weak!

