Neurovascular of Lower Limb Flashcards
where does the aorta bifuricate into common iliac artery?
- L1
- L2
- L3
- L4
- L5
where does the aorta bifuricate into common iliac artery?
- L1
- L2
- L3
- *- L4**
- L5
1-4?
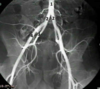
1 - aorta
2 - common iliac artery
3 - interal iliac artery
4 - external iliac artery
which three arteries branch off the internal iliac artery? [3]
which out of ^^ are medial compartment of thigh?
which out of ^^ are posterior compartment of thigh?
from which artery does the superior gluteal artery arise from? [1]
internal iliac artery –> superior gluteal artery
internal iliac artery –> inferior gluteal artery
internal iliac artery –> obturator artery
superior & inferior gluteal: posterior region
obturator: medial region
superior and inferior gluteal artery relate to which muscle? [1]
superior and inferior gluteal artery relate to which muscle? [1]
piriformis !

where does external iliac artery –> femoral artery? [1]
where do u palpate for femoral artery? [1]
where does external iliac artery –> femoral artery? [1]
at inguinal ligament
where do u palpate for femoral artery? [1]
mid inguinal point
which artery is commonly used to gain access to abdominal aorta?
- descending aorta
- femoral artery
- hepatic artery proper
- common iliac artery
which artery is commonly used to gain access to abdominal aorta?
- descending aorta
- *- femoral artery**
- hepatic artery proper
- common iliac artery
what are the three borders of the femoral triangle? [3]
which structures do we find in femoral triangle? [3] - correct order pls from lateral- medial
what are the three borders of the femoral triangle? [3]
inguinal ligament
sartoria
adductor longus
which structures do we find in femoral triangle? [3] - correct order pls !!
femoral nerve, artery, vein

what is the first branch of the femoral artery?
what does ^ lead into? [2]
what are the branches of the femoral artery?
femoral artery –> profunda femoris: –> medial circumflex femoral artery
femoral artery –> profunda femoris: –> lateral circumflex femoral artery
both supply the head of the femur


at what stage does femoral artery –> popliteal artery? [1]
at what stage does femoral artery –> popliteal artery? [1]
after going through the adductor hiatus

popliteal artery divides into ? [2]
popliteal artery divides into ? [2]
- *- posterior tibial artery - gives off fibular artery laterally
- anterior tibial artery**
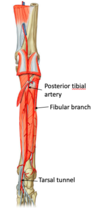
which artery
antierior tibial artery –> which artery?
antierior tibial artery –> dorsalis postieror artery
dorsalis pedis pulse can be found lateral to which tendon? [1]
dorsalis pedis pulse can be found lateral to which tendon? [1]
extensor hallucis longus (big toe tendon)
superficial veins of legs?
what do they drain into?
small / short saphenous vein –> popliteal vein
great saphenous vein –> femoral vein

why do superficial veins at greatest risk of varicous? [2]
why do superficial veins at greatest risk of varicous? [2]
- **outside of fascia - less muscle compression
- further to run / agaisnt gravity**

dorsalis pedis artery

arcuate artery
all nerves from the lower limb come from where? [1]
all nerves from the lower limb come from where? [1]
lumbosacral plexus !!
label the correct dermatomes xox

S1 - small toe AND base of most of foot - STAND ON S1 !

how do u remember dermatomes of lower limb? L3-L5 & S1-S4?
L3: knees
L4: down to the floor
L5: big toe
S1: stand on S1
S2: lie on
S3: sit on
S4: wipe

whats a myotome?
same as dermatome - but for motor movement
lumbosacral plexus:
which major nerves come from the lumbar plexus? [3] what are nerve roots?
which major nerves come from the lumbar plexus? [3]
femoral nerve: L2, L3, L4
obturator nerve: L2, L3, L4
lateral cut. nerve of thigh: L2 & l3
femoral nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
what movement does this cause? [2]
main muscles of anterior [3]
femoral nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
anterior
what movement does this cause? [2]
flex hip
extend knee
main muscles for ^?
quadriceps
sartoruis
iliopsoas
what can damage femoral nerve? [3] basic understanding x
what would damage to femoral nerve cause? movement wise xo
what can damage femoral nerve? [3]
•Compression – from treatment for congenital hip dysplasia
•Pelvic fractures
•Anterior hip dislocations (very very rare)
what would damage to femoral nerve cause?
- paralysis of quadriceps
- sensory loss to anterior thigh
obturaror nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
what movement does this cause? [1]
main muscles of this? [1]
- *obturaror** nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
- *medial compartment**
what movement does this cause? [1]
adduction of thigh
main muscles of this? [1]
adductors
lateral cutaenous nerve occurs from which Vert levels? [2]
what is role? [1]
lateral cutaenous nerve occurs from which Vert levels? [2]
L2 & L3
what is role? [1]
sensory innervation to lateral aspect of thigh

which three nerves arise from sacral plexus? [3]
which three nerves arise from sacral plexus? [3]
•Sciatic nerve (Tibial and common peroneal nerves)
•Superior gluteal nerve
•Inferior gluteal nerve
sciatic nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
what movement does this cause? [2]
main muscles of this compartment [3]
sciatic nerve provides motor supply to which compartment of thigh? [1]
posterior compartment
what movement does this cause? [2]
extend hip
flex knee
main muscles of this compartment [3]
•Semitendinosus
•Semimembranosus
Biceps femoris (long head
what are the 3 muscles compartments of the leg (knee - foot)
what are the muscle movements each compartment do?
Posterior compartment of leg:
- two compartments of postior? [2]
- innervation? [1]
- movement? [2]
- blood supply? [1]
Posterior compartment of leg:
- two comparments: superficial & deep
- innervation: tibial nerve
- movement: plantar flexion, flexion of digits
- blood supply: posterior tibial artery
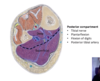
what are these posterior superficial muscles? [3]
what do they all insert onto?
movement?

all insert onto: achilles tendon - plantar flexion !!!!




plantaris muscle

gastrocnemius muscle
posterior dep compartment:
innervation?
movement? [2]
blood supply?
posterior dep compartment:
innervation: tibial nerve
movement: plantar flexion, flexion of digits
blood supply: posterior tibial artery

anterior leg compartment:
innervation?
movement? [2]
blood supply?
anterior leg compartment:
innervation: deep peroneal nerve
movement: dorsiflexion, extension of digits
blood supply: anterior tibial artery
lateral leg compartment:
innervation?
movement?
blood supply?
lateral leg compartment:
innervation: superficial peroneal nerve
movement: eversion
blood supply: fibular artery
which nerves provide sensory innervation to the image? [2]
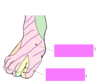
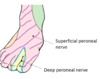
fracture to the neck of the fibula can cause damage to which nerve?
- sciatic nerve
- posterior tibial nerve
- anterior tibial nerve
- superficial peroneal nerve
- common peroneal nerve
why?
fracture to the neck of the fibula can cause damage to which nerve?
- sciatic nerve
- posterior tibial nerve
- anterior tibial nerve
- superficial peroneal nerve
- *- common peroneal nerve**
wraps around the neck of the fibula - vulnerable to fracture !

what happens when u get damage to common peroneal nerve? [1]
why? [2]
what happens when u get damage to common peroneal nerve? [1]
foot drop
why? [2]
provides innervation to anterior and lateral compartment of leg - only innervation is to the posterior - unnaposed plantar flexion
damage to sciatic nerve is characterised by? [3]
oFoot drop
oWasting of hamstrings, calf muscles and dorsiflexors
oLoss of Achilles reflex


what do Gluteus Medius and Minimus do when walking?
Gluteus Medius and Minimus contract to cause hip stabilisation & keep pelvis in alignment
a postive trendelenburg test is likely to occur from damage to which nerve?
superior gluteal nerve
inferior gluteal nerve
femoral nerve
common peroneal nerve
superficial peroneal nerve
a postive trendelenburg test is likely to occur from damage to which nerve?
superior gluteal nerve
inferior gluteal nerve
femoral nerve
common peroneal nerve
superficial peroneal nerve

A ! - least risk of neurovascular damage
which nerve would you be likely to hit if you did IM in D?
- sciatic nerve
- posterior tibial nerve
- anterior tibial nerve
- superficial peroneal nerve
- common peroneal nerve
which nerve would you be likely to hit if you did IM in D?
- *- sciatic nerve**
- posterior tibial nerve
- anterior tibial nerve
- superficial peroneal nerve
- common peroneal nerve


