Ankle and Foot Flashcards
tibia and fibula articulate with which bone? [1]
tibia and fibula articulate with which bone? [1]
talus

which bones do inversion / eversion movements of foot come from? [1]
which bones do inversion / eversion movements of foot come from? [1]
sub talus bones.


which movements does the ankle joint mainly permit? [2]
which movements does the ankle joint mainly permit? [1]
dorsiflexion & plantarflexion
v small amount of wobble !!
neutral position of foot (on floor), is technically:
plantarflexion
dorisflexion
neutral position of foot (on floor), is technically:
plantarflexion
dorisflexion


talus is wider or thinner anteriorly?
which side is shorter - medial or lateral malleolus?
talus is wider anteriorly
- more stable in dorsiflexion than plantar flexion
which side is shorter: medial malleolus
-more stable ineversion that inversion
which is more stable:
- plantar flexion
- dorsi flexion
- eversion
- inversion
which is more stable:
- plantar flexion
- *- dorsi flexion**
- eversion
- *- inversion**
which ligament structure stabilises the medial side of ankle? [1]
what does ^ attach to? [3]
what movement does it prevent? [1]
which ligament structure stabilises the medial side of ankle? [1]
medial / deltoid ligament
what does ^ attach to? [3]
medial malleoulus of tibia
calcaneus
navicular
what movement does it prevent? [1]
prevents subluxion
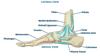
which 3 ligaments make the the lateral ligament? [3]
which are they clinically significant? [1]
which 3 ligaments make the the lateral ligament? [3]
anterior talofibular
posterior talofibular
calcaneofibular
which are they clinically significant? [1]
because theyre seperate structures - really likely to tear: lateral collateral ligament tear

what type of injury is this to ankle?
inversion
eversion
which ligaments would be damaged here? [1]

what type of injury is this to ankle?
inversion
eversion
which ligaments would be damaged here? [1]
lateral ligaments!!
dorsiflexion and toe extension:
- innervated by which nerve?
- which muscles? [3]
- which compartment of leg? [1]
eversion:
- innervated by which nerve?
- which muscles? [2]
- which compartment of leg? [1]
dorsiflexion and toe extension:
- innervated by which nerve: deep branch of common peroneal nerve
- which muscles: **tibialis anterior, E. digitorum longus and E. hallicus longus
- anterior compartment**
eversion
- innervated by which nerve: superficial branch of common peroneal
- which muscles: fibularis longus and fibularis brevis
- lateral compartment



fyi

plantarflexion:
which muscles do this ? - of superficial plexor and deep muscles
**plantarflexion:
superficial plexors:**
- gastrocnemius
- soleus
- plantaris
- *deep muscles: toe flexion**
- flexor digitorum longus
- flexor hallucis longus
- tibialis posterior - also does foot inversion

which muscles of leg cause foot inversion? [2]
which muscles of leg cause foot inversion? [2]
tibialis posterior - deep posterior compatment
tibialis anterior - anterior comparment




tibial nerve


toe flexion !
tibial nerve

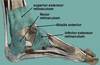
what are the flexor and extensor retinacula?
where found?
what are the flexor and extensor retinacula?
tendon sheath that hold tendons in place as enter foot
where found?
see photo

which structures pass under the flxor retincula? [2]
which structures pass under the extensor retincula? [2]
which structures pass under the flxor retincula? [2]
tibial nerve
posterior tibial artery
which structures pass under the extensor retincula? [2]
deep peroneal nerve (fibular nerve)
anterior tibial artery

what is arrow pointing to?

extensor reticulum



which muscles cause inversion of foot? [2]
which muscles cause eversion of foot? [2]
which muscles cause inversion of foot? [2]
tibialis anterior
tibialis posterior
which muscles cause eversion of foot? [2]
peroneus longus
peroneus brevis

which ligaments of foot get stretched out when foot planted, sot that when you take a step, release energy and help lift off?
a) medial side [1]
b) lateral side [2]
which ligaments of foot get stretched out when foot planted, sot that when you take a step, release energy and help lift off?
a) medial side: spring ligament
b) lateral side: long and short plantar ligaments

what type of movement are the muscles in leg for?
what type of movement are intrinsic muscles of the foot for?
what type of movement are the muscles in leg for?
propulsion & power grr
what type of movement are intrinsic muscles of the foot for?
precise movements - constantly contracting and relaxing to respond to dynamic changes
3-4 layers
explain the arches of the foot? [3]
medial longitudinal arch:
- open footprin side: middle of foot isnt it
- contact with ground: big toe & calcaneous
- resilient due to large no. of bones
lateral longitudinal arch:
- flatter
- less bones
- talus transmits body weight through it - weight not central though - either goes forward or backwards
transverse arch:
not a true arch - maintained by some mscles and ligaments as longuitnial arches
- bony fit is particularly good

where is weight distribution in foot?
found in medial & longitudinal arch - not the transverse arch !!

what maintains the longitduinal arches? [2]
dynamic support
- muscle contracts as when required
- muscle tendons insert into apex of arches - when muscles contracts, pulls apex up & counteract body weight
- includes intrinsic muscles
passive support
- constant & ongoing support
- due to shape of bones: allows them to interlock


what are bunions (aka Hallux Valgus)?
movement of great toe towards the 2nd toes
inherited or acquired



