Hand Movement Flashcards
(26 cards)
Which bones does the radiocarpal joint connect? [3]
What type of joint is it? [1]
scaphoid & lunate to radius not the ulna
condyloid joint extension and flexion and ulnar and radial devaitation (side to side)

which direction is extension and flexion of the thumb?
which direction is adductio and abduction of thumb?
what is oppositon of the thumb?

what is 1-5?

1 = flexion
2 = extension
3 = adbuction
4 = adduction
5 = oppostion

anterior compartment in the forarm is innervated by which nerves?
posterior comparment in the formarm is innervated by which nerve?
what type of movemement occurs from anterior and posterior compartments?
anterior compartment in the forarm is innervated by which nerves
- **ulnar and median nerves
- flexion
- pronation !!**
posterior comparment in the formarm is innervated by which nerve?
- **radial nerve
- extension
- supinators !!**
muscles of the superficial layer of forearm:
names? [4]
where do they run from / to?
muscles of the superficial layer of forearm:
- Pronator teres (pronates the arm)
- Flexor carpi radialis (flexes the wrist)
- Palmaris longus (small muscle)
- Flexor carpi ulnaris (flexes the wrist)
(Pass Fail Pass Fail)
muscles of the superficial layer do not extend into the digits so they act to
- **flex the wrist
- pronate the arm**

which muscle is this?

palamaris longus
which superficial forearm muscle is this?

palmaris longus
Which is the muscle of intermediate layer of forearm?
Where does it run to from the medial epidcondyle?
What movements does it cause? [3]
which is the muscle of intermediate layer of forearm?
* flexor digitorum superficialis
where does it run to from the medial epidcondyle?
* middle phalanx
Movements:
- flexes the wrist
- flexes the MCP
- flexes the PIP
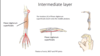
What are deep layer muscles of the forarm? [3] where run to ? what movements?
flexor digitorum profundus:
- makes way to fingers and distal phalanx !
- causes flexion of the wrist, MCP, PIP and DIP joints
flexor pollicis longus
- forearm to distal phalanx of thumb
- thumb flexion
pronator quadratus
- between ulnar and radius
- initiates pronation of the forearm

what is the synovial sheath and what is its role?
what is synovial sheath held in place by?
what is the synovial sheath and what is its role?
surrounds the flexor digitorum superficialis & flexor digitorum profundus to reduce friction of those tendons rubbing together.
what is synovial sheath held in place by?
surrounded by fibrous digital tendon sheath

what are ganglion cysts?
- synovial sheath is filled with fluid - get accumulation of fluid = lump

Pronation of the forearm is undertaken by pronator quadratus (deep layer) and pronator teres muscle (superficial layer).
which of these is the main muscle involved in pronation and which assists pronation?
pronator quadratus (deep layer): main
pronator teres muscle (superficial layer): assists
what is the carpal tunnel?
what is the layer at the top called?
which nerve runs through?
- At the base of the palm of the hand, there is a groove/tunnel through which 9 flexor tendons pass.
- Across the top is the flexor retinaculum (thickening of the deep fascia)
- median nerve runs through the carpal tunnel

what is carpal tunnel syndrome caused by?
what does it present as? a) short term? b) long term?
compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel (oedema, reptitive strain)
presents as:
i) short term: numbness of tingling of first 3.5 digits
ii) long term muscle wasting away

which tendons are from muscles A & B?
which joints of the fingers are these muscles acting on?

A= **flexor digitorum profundus:** all the way to distal phalanx. **PIP &** **DIP flex** B = **flexor digitorum superficialis:** middle phalanx. **PIP flex**

name the muscles of the posterior compartent that run laterally and what movements they permit

Brachioradialis: humurus –> radius: only flexes the elbow (as doesnt cross wrist)
extensor carpi radialis longus: extend and adbuct the wrist
extensor carpi radialis brevis: extend and adbuct the wrist

what do these tendons from these muscles cause movement of? [3]

what do these tendons from these muscles cause movement of the thumb !!
abductor pollicis longus: abducts thumb
extensor pollicis longus & brevis: extend thumb

What are the borders of the anatomical snuffbox? [3]
abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis longus & extensor pollicis brevis

what movements do each of the following cause?

extensor digitorum: **extends MCP, DIP and PIP joints** extensor carpi ulnaris (runs to carpals on ulnar side) extensor indices (runs to index finger)

Which muscle causes supination of arm? [1

thenar eminence
hypothenar eminence
lumbricals and interossei
_thenar eminence: t_henar muscles act on the thumb, and are at the base of the thumb. They adduct, oppose, abduct and flex. They are mainly there for opposition: abduction, flexion, opposition to move the thumb and make it opposable
Hypothenar muscles act on the little finger. Abductor digiti minimi allows us to abduct the little finger, yet the hypothenar muscles act as a cushion so we can actually hold an object
lumbricals and interossei: act in digits 2-5


lumbricals: flex MCP
dorsal interrossei: abduct fingers (DAB)
palmar interrossei adduct the fingers (PAD)

fyi








