:) Flashcards
(45 cards)
which is this muscle?
innervation?
movement [2]

which is this muscle: sartorius
innervation: femoral nerve
movement [2]: flexes hip AND knee
what are the 3 different muscles that insert at the medial aspect of the knee? [3]
which compartment are they all originally from? [3]
what is name for this meetin of three muscles? [3]
- Sartorius - anterior
- Gracilis - medial
- Semitendinosus - posterior
= pes anserinus !!

what are the 3 articulations of knee joint? [3]
which is bone is not part of the knee joint? !!! [1]
what are the 3 articulations of knee joint? [3]
–lateral femoral and tibial condyles with corresponding meniscus
–medial femoral and tibial condyles with corresponding meniscus
–patella and femur
fibula not part of knee joint!!
what are the 3 articulations of knee joint? [3]
which is bone is not part of the knee joint? !!! [1]
what are the 3 articulations of knee joint? [3]
–lateral femoral and tibial condyles with corresponding meniscus
–medial femoral and tibial condyles with corresponding meniscus
–patella and femur
fibula not part of knee joint!!
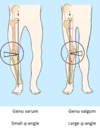
what is the Q line?
where is at a line between? [2]
what s the angle in men? (compared to vertical) [1]
whats the angle in women? (compared to vertical) [1]
Q line: asis –> centre of patella
what s the angle in men: 14 degress
whats the angle in women: 17 degrees

whats it called when have a small q angle?
whats it called when you have a large q angle?
which condyle does this cause increased presssure on for small q [1] / large q [1]?
whats it called when have a small q angle: genu varum - medial condyle
whats it called when you have a large q angle: genu valgum - lateral condyle

whats it called when have a small q angle?
whats it called when you have a large q angle?
which condyle does this cause increased presssure on for small q [1] / large q [1]?
whats it called when have a small q angle: genu varum - medial condyle
whats it called when you have a large q angle: genu valgum - lateral condyle


what is a sesamoid bone? [1]
what is a sesamoid bone: bone that develops in ligament


reflex test of patella: tests which nerve? [1] & which spinal segments[1]
reflex test of patella: tests femoral nerve and spinal segments L2-L4
causes contraction of quads
what are the names of the collateral ligaments of knee? [1]
how do they differ? [1]
which one is more prone to damage? [1]
what are the names of the collateral ligaments of knee? [2]
medial/ tibial collateral ligament & fibula collateral ligament
how do they differ? [1]
- *fibula collateral ligament:** seperate to the knee capsule
- *tibial collateral ligament:** part of the knee capsule
which one is more prone to damage? [1]
tibial collateral ligament bc if damage the knee it also damages the ligament


what is the role of the cruciate ligaments?
connecting the tibia and the femur to prevent displacement of the tibia relative to the femur
what is the medial menisci attached to [2] (anteriorly / posteriorly)
what is the lateral menisici attached to? [1]
what is the medial menisci attached to [2]
- *anteriorly: ACL
posteriorly: tibial collateral ligament**
what is the lateral menisici attached to? [1]
pcl
NOT ATTACHED TO LATERAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT
which structures make up the unhappy triad? [3]
- Medial meniscus
- ACL
- Tibial collateral ligament
lower motor neurons innervate skeletal muslces (alpha-motor neurones)
where do you find the cell body of the motor unit of the NMJ? [1]
one alpha motor neuron innervates: [1]
- one muscle fibre
- a number of muscle fibres
where do you find the cell body of the motor unit of the NMJ? [1]
ventral (anterior) horn of the spinal cord
one alpha motor neuron innervates: [1]
- one muscle fibre
- *- a number of muscle fibres:** forms the motor end plate (presynaptic NMJ)

label A


what happens after Ach binds to Ach receptor?
- Ach binds to Ach-receptor
- opens Ach-receptor
- allows Na channel to open & Na goes through
- causes depolarisation of muscle membrane
- causes release of Calcium from sarcoplasmic reciticulum
… other steps… - muscle contraction
Where do you find:
L type calcium channels [2]
N type calcium channels [1]
L type calcium channels [2]
heart
vascular smooth muscle
N type calcium channels [1]
pre-synaptic terminals - very close to the vesicles
explain mechanism of docking at NMJ and release of Ach occurs at presynaptic vesicle
vesicles docks by:
- synaptobrevin interacts with syntaxin and SNAP25: holds the vesicle close to pre-synaptic membrane (but doesnt fuse) = docking.
- Ca2+ binds to synaptotagmin: interacts with SNAP25/ syntaxin complex and tightens interaction between the vesicle and presynaptic membrane complexs & causes it to merge & release of Ach = confirmational change occurs.

what does quantal release of Ach mean? [1]
every vesicle contains same amount of ACh: same amount of NM is released with each AP. get a 1:1 transmission of nerve & muscle.


















