Neuroanatomy/peripheral nerves Flashcards
Spinal cord - Reflexes:
- Patellar
- Achilles
Patellar: L 3/4
Achilles: S1, 2
Lumbar plexus nerve roots
L1-4
Branches of the lumbar plexus (6)
- Iliohypogastric nerve
- Ilioinguinal nerve
- Genitofemoral nerve
- Lateral cutaneous nerve
- Femoral nerve
- Obturator nerve
A useful memory aid for the branches of the lumbar plexus is: I, I Get Leftovers On Fridays. This stands for the Iliohypogastric, Ilioinguinal, Genitofemoral, Lateral cuteanous nerve of the thigh, Obturator and Femoral.
The nerve roots that contribute to the sacral plexus
L 4, 5
S 1, 2, 3, 4
Branches of the sacral plexus
- Superior gluteal
- Inferior gluteal
- Sciatic
- Posterior femoral cutaneous
- Pudendal
A useful memory aid for the major branches of the sacral plexus is ‘Some Irish Sailor Pesters Polly’. This stands for Superior Gluteal, Inferior Gluteal, Sciatic, Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh, Pudendal.
Femoral nerve:
- Nerve roots
- Motor function
- Sensory function
1. Nerve roots L2-4
2. Motor function
Hip flex and knee ext
3. Sensory function
Supplies cutaneous branches to the anteromedial thigh (anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve) and the medial side of the leg and foot (saphenous nerve)
Obturator nerve:
- Nerve roots
- Motor function
- Sensory function
Nerve roots: L2-L4
Motor functions: Innervates the muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh (obturator externus, adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus and gracilis).
Adducts and laterally rotates the thigh
Sensory functions: Cutaneous branches of the obturator nerve innervate the skin of the medial thigh.

Sciatic nerve:
- Nerve roots
- Motor function
- Sensory function
1. Nerve roots: L4-S4
2. Motor functions:
Innervates the muscles of the posterior thigh (biceps femoris, semimembranosus and semitendinosus) and the hamstring portion of the adductor magnus (remaining portion of which is supplied by the obturator nerve).
Indirectly innervates (via its terminal branches) all the muscles of the leg and foot.
3. Sensory functions:
No direct sensory functions. Indirectly innervates (via its terminal branches) the skin of the lateral leg, heel, and both the dorsal and plantar surfaces of the foot.

Terminal branches of the sciatic nerve
Tibial nerve
Common fibula nerve
Tibial nerve
- Nerve roots
- Motor function
- Sensory function
- L4-S3
- Innervates the posterior compartment of the leg and the majority of the intrinsic foot muscles
- Plantar flexes ankle
- Flexes big toe
- Unlocks the knee by laterally rotating the femur on the tibia
- Inverts the foot - Innervates the skin of the posterolateral side of the leg, lateral side of the foot, and the sole of the foot.
Common fibular nerve
1) Nerve roots
2) Motor function
3) Sensory function
- L4-S2
- Innervates the short head of the biceps femoris directly. Also supplies (via branches) the muscles in the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg.
- Foot eversion
- Dorsiflexion
- Toe extension
- Innervates the skin over the upper lateral and lower posterolateral leg. Also supplies (via branches) cutaneous innervation to the skin of the anterolateral leg, and the dorsum of the foot.
Differentiating between L5 nerve root injury and common fibular nerve injury
Common fibula would affect the ankle reflex
L5 nerve root would affect the tibialis posterior (which causes foot inversion and is innervated by the tibia nerve not the common fibula nerve)
action of tibalis posterior and what is it innervated by
foot inversion, innervated by the tibial nerve (L5 nerve root action)
Lumber sacral myotomes

What nerve root is the Babinski response
S1 dermatome
Nerve root and actions of these muscles

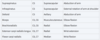
Nerve root and actions of these muscles




