HD2 Revision4 Flashcards
(77 cards)
which part of the embryo is the area responsible for creation of m / f reproductive system? [1]
genital ridge

what is the name of for the loss of acrosome on sperm? [1]
where does this occur? [1]
capatication; in the female genital tract
the sperm acrosome is formed which organelle?
nucleus ribosome SER golgi apparatus lysosome
the sperm acrosome is formed which organelle?
nucleus ribosome SER **golgi apparatus** lysosome
which ion is associated of with acrosome reaction / fusion of egg & sperm?
K+ Na+ Cl- Ca2+ HCO3-
which ion is associated of with acrosome reaction / fusion of egg & sperm?
K+ Na+ Cl- **Ca2+** HCO3-
which part of prostate gland do most carnicomas arise from?
Central zone
Peripheral zone
Transitional zone
Periurethral zone
which part of prostate gland do most carnicomas arise from?
Central zone
Peripheral zone
Transitional zone
Periurethral zone
which part of prostate gland undergoes hyperplasia?
Central zone
Peripheral zone
Transitional zone
Periurethral zone
which part of prostate gland undergoes hyperplasia?
Central zone
Peripheral zone
Transitional zone
Periurethral zone
label A-C

A: corpus spongiosum
B: corpora cavernosa
C: Tunica albuginea
which of the following is A?
suspensory ligament
uterosacral ligament
ovarian ligament
broad ligament

which of the following is A?
suspensory ligament
uterosacral ligament
ovarian ligament
broad ligament
which of the following is B?
suspensory ligament
uterosacral ligament
ovarian ligament
broad ligament

which of the following is B?
suspensory ligament
uterosacral ligament
ovarian ligament
broad ligament
which of the following is C?
suspensory ligament
uterosacral ligament
ovarian ligament
broad ligament

which of the following is C?
suspensory ligament
uterosacral ligament
ovarian ligament
broad ligament
which of the following is D?
suspensory ligament
uterosacral ligament
ovarian ligament
broad ligament

which of the following is D?
suspensory ligament
uterosacral ligament
ovarian ligament
broad ligament
where are the two areas which have clinical significance as this may be the first location fluid accumulates within the abdomen/pelvis if there is pathology [2]?
vesicouterine pouch
rectouterine pouch

Why is an ectopic pregnancy dangerous?
The foetus will be squashed
Ectopic sites cannot expand and so rupture
Ectopic sites have other functions which are impaired by implantation
Why is an ectopic pregnancy dangerous?
The foetus will be squashed
Ectopic sites cannot expand and so rupture
Ectopic sites have other functions which are impaired by implantation
The main risk of ectopic pregnancies are that ectopic sites (usually the Fallopian tube) cannot expand to the same extent as the uterus, and the site ruptures, resulting in extensive haemorrhage.
Cho’s ectopic pregnancy is implanted in the Fallopian tube. If this site ruptures, what arteries will be the source of the haemorrhage? [2]
Uterine artery
Superior vesicular artery
Ovarian artery
Vaginal artery
Internal pudendal artery
Cho’s ectopic pregnancy is implanted in the Fallopian tube. If this site ruptures, what arteries will be the source of the haemorrhage?
Uterine artery
Superior vesicular artery
Ovarian artery
Vaginal artery
Internal pudendal artery
label 1-7 xx
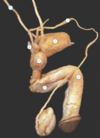
1: ureter
2. vas deferens
3: bladder
4: seminal vesicle
5: prostate
6: corpus cavernosum
7: corpuus spongiosum

which hormone controls the formation of external genitalia?
testosterone MIF DHT cHG LH
which hormone controls the formation of external genitalia?
testosterone MIF **DHT** cHG LH
name this structure [1]

bladder
name this structure [1]

external urethral sphincter
which of the following is the green?
membranous urethra
spongy urethra
prostatic urethra
preprostatic urethra:

which of the following is the green?
membranous urethra
spongy urethra
prostatic urethra
preprostatic urethra:
which of the following is the green?
membranous urethra
spongy urethra
prostatic urethra
preprostatic urethra:

which of the following is the green?
membranous urethra
spongy urethra
prostatic urethra
preprostatic urethra:
which hormone peaks at ovulation?
LH FSH Oestrogen Progesterone Testosterone
which hormone peaks at ovulation?
**LH** FSH Oestrogen Progesterone Testosterone
which hormone causes endometrial thickening?
LH FSH Oestrogen Progesterone Testosterone
which hormone causes corpus luteum formation?
**LH** FSH Oestrogen Progesterone Testosterone
which hormone causes oestrogen levels to rise?
LH FSH Oestrogen Progesterone Testosterone
which hormone causes oestrogen levels to rise?
LH **FSH** Oestrogen Progesterone Testosterone
which of following is A?
LH FSH Oestrogen Progesterone Testosterone

which of following is A?
LH FSH **Oestrogen** Progesterone Testosterone