HD1 Anatomy 2 Flashcards
what divides the centrepoint of the perineum diamond? [1]
what are the two perineal triangles? [2]
perineal body
urogenital triangle
anal triangle

what are the layers of fascia found in the urogenital triangle?
(pelvic floor muscles)
perineal membrane
deep perineal pouch
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal fascia
superficial perineal fascia
(fascia of pelvic floor)

which of the following prevents the prolapse of heavy organs such as bladder and uterus?
perineal membrane
deep perineal pouch
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal fascia
superficial perineal fascia
which of the following prevents the prolapse of heavy organs such as bladder and uterus?
perineal membrane
deep perineal pouch
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal fascia
superficial perineal fascia

which of the following contains the external genitalia?
perineal membrane
deep perineal pouch
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal fascia
superficial perineal fascia
which of the following contains the external genitalia?
perineal membrane
deep perineal pouch
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal fascia
superficial perineal fascia
which of the following is most superficial?
deep perineal fascia
perineal membrane
superficial perineal fascia
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal pouch
which of the following is most superficial?
deep perineal fascia
perineal membrane
superficial perineal fascia
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal pouch


which of the following is the space in the urogenital triangle found between the fascia of the pelvic floor muscles and perineal membrane?
deep perineal fascia
perineal membrane
superficial perineal fascia
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal pouch
which of the following is the space in the urogenital triangle found between the fascia of the pelvic floor muscles and perineal membrane?
deep perineal fascia
perineal membrane
superficial perineal fascia
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal pouch
what is in the deep perineal pouch for
a) males
b) females
what is in the deep perineal pouch for
a) males
* *membranous urethra, the external urethral sphincter, the deep transverse perineal muscles, and the bulbourethral glands** (Cowper’s glands), which secrete a lubricating pre-ejaculatory fluid.
b) females
consisting of the true sphincter, the compressor urethrae and the urethrovaginal sphincter. The deep transverse perineal muscles are also present
which of the following is found superficial to the perineal membrane?
deep perineal fascia
perineal membrane
superficial perineal fascia
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal pouch
which of the following is found superficial to the perineal membrane?
deep perineal fascia
perineal membrane
superficial perineal fascia
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal pouch
which of the following contains the erectile tissues of the external genitalia?
deep perineal fascia
perineal membrane
superficial perineal fascia
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal pouch
which of the following contains the erectile tissues of the external genitalia?
deep perineal fascia
perineal membrane
superficial perineal fascia
superficial perineal pouch
deep perineal pouch
what are the erectile tissues in males? [4]
what are the erectile tissues in males? [2]
- *corpus spongiosum (**mouth of insect)
- *corpus cavernersa** (eyes of insect)
- *bulbospongiosus (**superifical to corpus spongiosum)
- *ischiocavernosus (**superifical to corpus spongiosum)

which of the following is the urethra found in?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus
which of the following is the urethra found in?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus
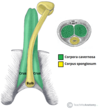
which of the following is this highlighted muscle?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus

which of the following is this highlighted muscle?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus
which of the following is this highlighted muscle?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus

which of the following is this highlighted muscle?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus
what is highlighted here? [1]

crux of penis
which of the following is this highlighted muscle?

which is this muscle?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus
which is this muscle?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus
which of the following is the green muscle?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus

which of the following is the green muscle?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus
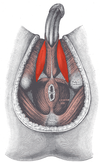
label these muscles




what are vestibular bulbs [1]
what are vestibular glands [1]
Either side of the vaginal vestibule is the bulb of the vestibule.
The crura of the clitoris are equivalent to the crura arising from the corpora cavernosa. In females, the greater vestibular glands (Bartholin’s glands) can be found posterior to the vestibular bulbs. These are equivalent to the bulbourethral glands found in the male, and also secrete and lubricating fluid.
what is highlighted? [1]
vesitubular glands
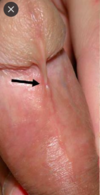
what attaches the glans penis to the foreskin/ [1]
freneleum
Which part of the urethra is located in the corpus spongiosum of the penis? [1]
Acceptable responses: spongy, spongy part, penile
which part of the female external genitalia enclose the vestibule of the vagina?
which part of the female external genitalia enclose the vestibule of the vagina?
labia minoria
the clitoris is analagous to which part of the penis?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus
the clitoris is analagous to which part of the penis?
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernersa
bulbospongiosus
ischiocavernosus
which way is the urogenital triangled angled? [1]
anteriorly !!


which 1-5 is the corpus cavernersa
1
2
3
4
5

which 1-5 is the corpus cavernersa
1
2
3
4
5

which 1-5 is the bulbospongiosus
1
2
3
4
5

which 1-5 is the bulbospongiosus
1
2
3
4
5

which 1-5 is the corpus spongiosum
1
2
3
4
5

which 1-5 is the corpus spongiosum
1
2
3
4
5

which 1-5 is the Superficial transverse perineal muscle
1
2
3
4
5

which 1-5 is the Superficial transverse perineal muscle
1
2
3
4
5

which 1-5 is the Ischiocavernosus
1
2
3
4
5

which 1-5 is the Ischiocavernosus
1
2
3
4
5

what are the 3 nerve branches of the perineum? [3] what do they supply [3]
Inferior rectal - supplies the external anal sphincter and inferior anal canal
Perineal - supplies the anterior perineum
Dorsal nerve of penis/clitoris - supplies the external genitalia
The pudendal nerve can be located clinically by palpating for the WHAT? [1]
The pudendal nerve can be located clinically by palpating for the ischial spine, as the nerve loops around it posteriorly.
A young man attends his GP because he has been experiencing erectile dysfunction. Fibres from which branch of the autonomic nervous system are responsible for genital erection? [1]
Acceptable responses: parasympathetic, parasympathetic nervous system
Which is the main muscle involved in helping to maintain erection? [1]
Acceptable responses: bulbosongiosus, bulbospongiosus
Atherosclerosis of which artery is most likely to cause erectile dysfunction?
Superior gluteal artery
Inferior gluteal artery
Inferior rectal artery
Internal iliac artery
Perineal artery
Atherosclerosis of which artery is most likely to cause erectile dysfunction?
Superior gluteal artery
Inferior gluteal artery
Inferior rectal artery
Internal iliac artery
Perineal artery
The penile artery arises from the internal pudendal artery, which. arises from the internal iliac artery.
what is highlighted? [1]
what is the function of ^? [1]
which structure is found within here? [1]

Ischioanal fossa
**expansion and deformation of the anal canal to facilitate the passage of faeces
contain pudendal canals**
which structures are found in the is the pudendal canal? [3]
is the pudendal canal (Alcock’s canal), which contains the pudendal nerve and internal pudendal artery and vein.

the structures of the upper anal canal follow the pattern of:
hindgut
midgut
foregut
the structures of the upper anal canal follow the pattern of:
hindgut
midgut
foregut
which of the following is the external anal sphincter
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the external anal sphincter
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the Anococcygeal ligament
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the Anococcygeal ligament
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the perineal body
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the perineal body
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the Gluteus maximus
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the Gluteus maximus
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following serves as an attachment point for perineal muscles
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following serves as an attachment point for perineal muscles
1: perineal body
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the ischioanal fossa (cleared)
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the ischioanal fossa (cleared)
1
2
3
4
5

Spermatozoa are produced in the:
vas (ductus) deferens.
rete testis
epididymis
tunica albuginea
seminiferous tubules
Spermatozoa are produced in the:
vas (ductus) deferens.
rete testis
epididymis
tunica albuginea
seminiferous tubules
mature spermatozoa are stored in the
vas (ductus) deferens.
rete testis
epididymis
tunica albuginea
seminiferous tubules
mature spermatozoa are stored in the
vas (ductus) deferens.
rete testis
epididymis
tunica albuginea
seminiferous tubules

which of the following is the tunica albuginea
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the tunica albuginea
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the epididymis
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the epididymis
A
B
C
D
E
F
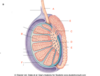
which of the following is the seminiferous tubule
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the seminiferous tubule
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the rete testis
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the rete testis
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the where spermatozoa is produced
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the where spermatozoa is produced
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the rete testis
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the rete testis
A
B
C
D
E
F

The testes begin development on …………. [1]
They are dragged down through the …… into the scrotum by the …….., along with their blood, nerve, and lymph supply. [2]
The testes begin development on posterior abdominal wall[1]
They are dragged down through the anterior abdominal wall into the scrotum by the gurbernaculum along with their blood, nerve, and lymph supply. [2]
what does the peritoneal layer of the spermatic cord persist of [1]
what does the peritoneal layer of the spermatic cord persist of [1]
tunica vaginalis
Where would you expect pain from the testes (as oppose to the scrotum) be experienced?
Thorax
Adbomen
Pelvis
Perineum
Where would you expect pain from the testes (as oppose to the scrotum) be experienced?
Thorax
Adbomen
Pelvis
Perineum
To allow passage of the testes through the abdominal wall, a tunnel must be created - this tunnel is known as the ……. which passes obliquely through the muscular layer [1]
It is formed by an outpouching of …… (the processus vaginalis) passing through the layers of the abdominal wall, acquiring a covering from ……, ……… and …… aponeurosis along the way [4]
To allow passage of the testes through the abdominal wall, a tunnel must be created - this tunnel is known as the inguinal canal which passes obliquely through the muscular layer [1]
It is formed by an outpouching of peritoneum (the processus vaginalis) passing through the layers of the abdominal wall, acquiring a covering from transversalis fascia, internal oblique and external oblique aponeurosis along the way.

label A & B [2]

A: gubernaculum
B: processus vaginalis
which structures are found within the spermatic cord?
These include the vas deferens (and its artery and vein)
the testicular artery and veins (making up the pampiniform venous plexus),
the artery and vein to cremaster muscle,
the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, sympathetic and visceral afferent nerves supplying the testis and vas, and some lymphatics.

which of the following is the Tunica vaginalis
1
2
3
4
5
6

which of the following is the Tunica vaginalis
1
2
3
4
5
6
The tunica vaginalis is the remnant of the processus vaginalis, which was the outpouching of parietal peritoneum. It is a serous covering of the testis in the scrotum

which of the following is the Vas deferens
1
2
3
4
5
6

which of the following is the Vas deferens
1
2
3
4
5
6

which of the following is the testicular artery
1
2
3
4
5
6
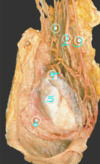
which of the following is the
1
2
3
4
5
6

which of the following is the head of the epididymis
1
2
3
4
5
6

which of the following is the head of the epididymis
1
2
3
4
5
6

which of the following is the tunica albuginea
1
2
3
4
5
6

which of the following is the tunica albuginea
1
2
3
4
5
6

which of the following is the Testicular veins (pampiniform plexus)
1
2
3
4
5
6
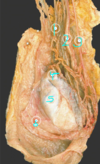
which of the following is the Testicular veins (pampiniform plexus)
1
2
3
4
5
6

Where does the testicular artery come from? [1]
Acceptable responses: aorta, abdominal aorta, aorta l2, l2, l2 abdominal aorta
what are direct and indirect inguinal hernias formed from?
Indirect inguinal hernias:
An indirect inguinal hernia enters the deep ring, travels the length of the canal, and exits at the superficial ring, often extending into the scrotum. It is most common in infant males, due to a patent processus vaginalis
Direct inguinal hernias
Direct inguinal hernias do not pass through the deep ring. They bulge through another weak point of the anterior abdominal wall.
They then protrude through the superficial ring. Direct hernias are more common in people who are obese, and who have frequent increased intra-abdominal pressure, due to chronic cough or weightlifting, for example.
Which ligaments comprise the borders of the greater and lesser sciatic foramen? [2]
Acceptable responses: sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments
What effect does relaxin and progesterone have on pelvic ligaments during pregnancy?
Acceptable responses: Relax muscles and loosen ligaments and joints, Relax ligaments, Ligaments become lax
Which of branches of the internal iliac artery leave the pelvis? [3]
Which of branches of the internal iliac artery leave the pelvis? [3]
Obturator artery
Inferior gluteal artery
Superior gluteal artery
relaxed detrusor muscle
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
relaxed detrusor muscle
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor

contracts the detrusor muscle
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
contracts the detrusor muscle
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
contracts the internal urethral sphincter
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
contracts the internal urethral sphincter
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
relaxes the internal urethral sphincter
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
relaxes the internal urethral sphincter
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
contracts the external urethral sphincter
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
contracts the external urethral sphincter
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
contracts the detrusor muscle
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
contracts the detrusor muscle
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
Deficits in which of these fibres may cause urinary retention?
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
Deficits in which of these fibres may cause urinary retention?
visceral afferents
sympathetic
parasympathetic
somatomotor
emerges from superficial inguinal ring
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
emerges from superficial inguinal ring
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
passes through deep inguinal ring
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
passes through deep inguinal ring
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
bulges through hesselbacks triangle
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
bulges through hesselbacks triangle
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
may extend into scrotum
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
may extend into scrotum
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
medial to inferior epigastric vessels
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
medial to inferior epigastric vessels
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
most common in baby boys
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
most common in baby boys
direct inguinal ligament
indirect inguinal ligament
both
Persistence of which structure is normally responsible for indirect inguinal hernia development? [1]
Acceptable responses: Patent processus vaginalis, processus vaginalis, Open processus vaginalis
What is the surface landmark for the deep inguinal ring?
Midpoint of the inguinal ligament
Mid inguinal point
What is the surface landmark for the deep inguinal ring?
Midpoint of the inguinal ligament
Mid inguinal point
which structures provide muscle control for the flow of urine? [2]
The internal urethral sphincter and the external urethral sphincter both provide muscle control for the flow of urine. The internal sphincter is involuntary. It surrounds the opening of the bladder to the urethra and relaxes to allow urine to pass.


