HD1 Histology Review (Male) Flashcards
what are the sertoli cells function? [2]
where are they located? [1]
what are nuclei like? [2]
what are the sertoli cells function? [1]
- *- form blood-testis barrier:** act as a bridge between interbular space and lume of tubule
- nourishment of spermatogenic cells
where are they located? [1]
- seminiferous tubules: span from the basement membrane to the lumen.
what are nuclei like? [2]
ovoid or triangular

label A & B of seminiferous tubule

A: sertoli cell
B: leydig cell
what is difference of nuclei between early spermatids and late spermatids? [1]
early: less condense
late: condensed nuclei - becomes elongated

where do you find leydig cells? [1]
what key feature do leydig cells normall have? [1]
where do you find leydig cells? [1]
outside of seminiferous tubules
what key feature do leydig cells normall have? [1]
Reinke crystals: rod shaped cytoplasmic inclusions (function unknown)

label A & B

A: Leydig cells
B: Reinke crystals
label a & B

A: testis
B: epididymis
which of the following is the vas deferens?
1
2
3
4
5
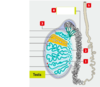
which of the following is the vas deferens?
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the epididymis?
1
2
3
4
5
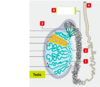
which of the following is the epididymis?
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the tubulus rectus?
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the tubulus rectus?
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the rete testis?
1
2
3
4
5

which of the following is the rete testis?
1
2
3
4
5

at the end of each seminfierous tubule there is a transition to straight tubules (aka WHAT)? [1]
what is the histological change that occurs here? [1]
what do the tubules empty into? [1]
at the end of each seminfierous tubule there is a transition to straight tubules (aka WHAT)? [1] tubuli recti
what is the histological change that occurs here?
changes to simple cuboidal epi
what do the tubules empty into? [1]
rete testis

what type of cells does the genital ducts become when it gets to the efferent ductules? [1]
what type of cells does the genital ducts become when it gets to the efferent ductules? [1]
pseudostratified columnar epi
looks saw toothed !

what type of cell is A? [1]
how can you tell? [1]
what is the function of A? [1]

what type of cell is A? [1]
leydig
how can you tell? [1]
clear cytoplasm
what is the function of A? [1]
The Leydig cells make and secrete testosterone, in response to lutenising hormone from the pituitary.
which part of the male reproductive system is this?
epididymis
tubulus rectus
vas deferens
efferent ductules

which part of the male reproductive system is this?
epididymis
tubulus rectus
vas deferens
efferent ductules: saw toothed !
which part of the male reproductive system is this?
epididymis
tubulus rectus
vas deferens
efferent ductules

which part of the male reproductive system is this?
epididymis
tubulus rectus
vas deferens
efferent ductules: saw toothed !
which cell types do you find in the epididymis? [3]
which cell types do you find in the epididymis? [3]
pseudo strat columnar epi
principal cells: have stereocilia!!
basal cells

what is distincitve features of vas deferens?
pseudostratified columnar epi
tall columnar cells with long microvilli
circular and long layers smooth muscle

seminal vesicles histology?
function?
high folding mucosa with primary folds folding into secondary and tertiary folds
supported by smooth muscle & LCT
function: contribute about 75% of volume of semen - including proteins like fructose

what are the 4 anatomically distinct zones of prostate glands? [4]
–Central zone: surrounds the ejaculatory ducts with mucosal glands. Resistant to carcinoma. Cells have larger nuclei and basophilic cytoplasm.
–Peripheral zone: Surrounds central zone with branched tubuloalveolar glands. Most carcinomas arise from this zone.
–Transitional zone: Surrounds the prostatic urethra with mucosal glands. In older individuals there is hyperplasia (BPH).
Periurethral zone: Contains mucosal and submucosal glands

what are the cell types / form (squamous etc) normally found in prostate gland? [1]
what are the cell types / form (squamous etc) normally found in prostate gland? [1]
normally simple columnar - but can change to all other others
older men have prostatic concretions: corporoa amylacea

what is histology of penis like?
- what is the name of the two masses of erectile tissue? [2]
- what is the name of the fibroelastic layer called? [1]
- what is the name of the two masses of erectile tissue? [2]
coprora cavernosa
corpora spongiosum - what is the name of the fibroelastic layer called? [1]
- *tunica albuginea**

label 1-8 of the seminiferous tubule


sperm deposition and transport:
- where is sperm depositied in the female? [1]
- what characterisitc of female genital tract assists sperm movement? [1]
- how long goes sperm transport to uterus take? [1]
- what happens to sperm during transport to uterus? [2]
sperm deposition and transport:
- where is sperm depositied in the female? [1]
- *cervical os**
- what characterisitc of female genital tract assists sperm movement? [1]
- *ciliated surface of cervical os**
- how long goes sperm transport to uterus take? [1]
- *2-7 hrs**
- what happens to sperm during transport to uterus? [2]
capacitation;
sperm become hyperactive and sensitive to surrounding signals
How is the number of cells fusing restricted?
Production of second messengers on sperm/egg binding triggers polyspermy blocking.
Slow block: release of calcium in a wave that occurs on fertilisation.
- Calcium triggers **cortical granule
- Release and activation of cell division**
label 1-5 of blastocyst leaving the zona pellucida


which of the following is the gonadal ridge?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7

which of the following is the gonadal ridge?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7

which of the following is the primordial germ cells?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7

which of the following is the primordial germ cells?
1
2
3
4
5
6 red dots
7

which of the following is the primordial germ cells?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7

which of the following is the primordial germ cells?
1
2
3
4
5
6 red dots
7

which of the following is the spermatids?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the spermatids?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the sertoli cells?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the sertoli cells?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the 1ary spermatocytes?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the 1ary spermatocytes?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the 2ary spermatocytes?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the 2ary spermatocytes?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the spermatozoa?
A
B
C
D
E
F

which of the following is the spermatozoa?
A
B
C
D
E
F

what are the the future roles of the trophoblast cells and pluriblast cells of morula? [2]
what are the the future roles of the trophoblast cells and pluriblast cells of morula? [2]
trophoblast cells: attach of embryo to uterus
pluriblast cells: future embryo


