EXAM 3 NK Cells and gamma delta T Cells Flashcards
NK cells are derived from a common ___ precursor
lymphoid
NK cells provide the interface between what?
adaptive and innate immunity
NK cells are developmentally similar to ___ cells
T cells
NK cells have diverse ___ expression and interaction
receptor
NK cells are regulated by interactions with ___
MHC I molecules
NK cells recognize targets by their lack of ___
MHC I
can NK cells form memory cells?
yes
what determines NK cell killing?
positive and negative signal balance
describe the 3 cell states that regulate NK cell targeting
- protection - healthy cells express both stimulating and inhibitory signals
- missing-self - unhealthy cells reduce MHC I expression
- induced-self - unhealthy cells increase stress ligand expression
do all NK cells detect MHC I receptors or stress ligands?
no
in NK cell targeting, ___ signals must overcome ___ signals
- stimulating
- inhibitory
NK cells must be educated to detect a lack of ___
receptor expression
what are the important roles cytokines play in NK cell targeting?
- stimulating signal
- receptor expression
- IFNs, IL-12
do NK cells express diverse combinations of receptors or do they only have a few?
diverse combinations
what are the activating and inhibitory receptors on NK cells?
- activating - NKG2D and CD16 (Fc receptor)
- inhibitory - NKG2A and KIR family
describe the CD16 NK cell receptor family
- activating receptor
- low affinity IgG Fc receptor
describe the NKG family of NK cell receptors
- NKG2A - inhibitory receptor that preferentially binds MHC I
- NKG2D - activating receptor that binds MIC proteins (stress ligands)
describe the KIR family of NK cell receptors
- killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor family
- binds MHC I
- inhibits NK cell activation (mostly, some exceptions)
- detects healthy self tissue
inhibitory NK cell receptors recognize conventional ___
MHC I
activating NK cell receptors recognize ___
stress ligands
MHC I related, non-classical molecules
cells usually express ___ or a ___ receptor, not both
NKG2A or KIR
detection of MHC I ___ NK killing, while lack of MHC I detection ___ NK killing
- prevents
- leads to
what are the NK cell activation responses?
- target cell interaction
- downregulated MHC I
- stress ligands
- CD16
- leukocyte interaction
- antigen presenting cells
- Th cells
- NKT cells
- cytokines
- IFNs, IL-12
- proliferation, receptor expression, cytokine and granule production
what are the NK cell effector functions?
cytokine release and cytotoxicity
how do NK cells detect and kill cells with altered MHC I expression?

what is the innate mechanism of NK cell activation?
- multiple (2) signals
- MHC surveillance
- stress ligands
- signals from two or more activating receptors are required to activate NK cells
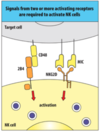
what is the adaptive mechanism of NK cell activation?
- single signal
- Ig targeting
- In the presence of IgG, the Fc receptor can activate NK cells without help from another receptor

describe NK cell cytotoxicity
- degranulation
- perforin and granzyme
- death-receptors
- FasL and TRAIL
- interferons and nitric oxide
___ T cells monitor tissue health
gamma delta
their major role is to remove diseased and malignant cells
gamma delta T cells are prominant where?
in tissues and mucosal surfaces
- sit in epithelial layers
- intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL)
which unique antigens do gamma delta T cells bind?
- phosphoantigens
- phopsholipids
- lipids
describe how gamma delta cells have both CD8-like and CD4-like activity
- direct killing
- cytokine and chemokine release
- NK, macrophage, and DC activation
___ cells can migrate to lymph nodes and function as antigen-presenting cells
gamma delta T cells
gamma delta T cells express ___ receptors
stress-ligand
- similar to NK cells
- detects the presence and absence of MHC I
gamma delta T cells promote ___
tissue repair and homeostasis


