EXAM 2 Sepsis Flashcards
what are the interrelationships that form the conceptual framework of sepsis?

what is described by the following:
sepsis-induced hypotension despite adequate fluid resuscitation along with the presence of perfusion abnormalities that may include, but are not limited to, lactic acidosis, oliguria, or an acute alteration in mental status
septic shock
what is described by the following:
presence of altered organ function in an acutely ill patient such that homeostasis cannot be maintained without intervention
multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS)
sepsis and severe sepsis lie on a background of disturbed ___
homeostasis
describe the progression of sepsis

who can get sepsis?
anyone can present with sepsis and severe sepsis
sepsis is most often present with ___
pre-existing diseases
historically, sepsis with gram ___ organisms was more common, however, between 1979-2000, gram ___ infections were more common in the US
negative, positive
describe the current worldwide distribution of sepsis organisms
- gram negative - 62%
- gram positive - 47%
- fungal - 19%
what is defined as hypotension?
- <90 mmHg systolic, or
- reduction of SBP of 40 mmHg from baseline, or
- evidence of hypo-perfusion (lactic acidosis, low urine output or change in mental state)
what is MAP?
- mean arterial pressure
- defined as the average pressure in a patient’s arteries during one cardiac cycle
- calculated using a formula of the SBP and the DBP
- MAP = SBP + 2 (DBP)/3
describe the differential diagnosis of shock/hypotension
- endocrine
- neurologic, anaphylactic
- drugs, distributive
- septic
- hypovolemia
- overdose, obstruction
- cardiogenic
- kills
___ is the clinical syndrome that results from a dysregulated inflammatory response to infection
sepsis
describe clinical signs of septic shock
- patient with continued hypotension after a fluid bolus - usually 10-30 ml/kg
- hypotension is relative to baseline
- <90 mmHg systolic or MAP of 70 mmHg
- or reduction of SBP of 40 mmHg from baseline
- hypotension is often associated with organ damage or dysfunction
what is primary multiple organ dysfunction caused by?
result of a well-defined insult (ie. renal failure from muscle breakdown products [rhabdomyolysis])
what is secondary multiple organ dysfunction caused by?
- not due to infection itself, but due to the host’s response
- possibly a dysregulation of the innate immune system
following identification of a patient with sepsis, the clinician must assess the patient for the presence of ___
acute organ dysfunction (severe sepsis)
the presence of acute organ dysfunction (severe sepsis) is often recognized clinically by the patient’s presenting signs and symptoms. however, in some instances, ___ will confirm the diagnosis of organ dysfunciton
laboratory data or results of invasive monitoring
what are the indications in the central nervous system of organ dysfunction?
altered consciousness, confusion, psychosis, delirium
what are the indications in the respiratory system of organ dysfunction?
tachypnea, hypoxemia, oxygen saturation <90%, decreased ratio of arterial oxygen vs inspired oxygen
what are the indications in the liver of organ dysfunction?
jaundice, increased liver enzymes, hypoalbuminemia, increased prothrombin time
what are the indications in the cardiovascular system of organ dysfunction?
tachycardia, hypotension, increased central venous pressure, increased pulmonary artery occlusive pressure
what are the indications in the kidney of organ dysfunction?
oliguria, anuria, increased creatinine
what are the hematological indications of organ dysfunction?
thrombocytopenia, abnormal coagulation tests, decreased levels of protein C, increased D-dimers
what are the 3 mechanisms of tissue injury?
- ischemia
- cytopathic injury
- increased apoptosis
describe ischemia as a mechanism of tissue injury
- decreased O2 given tissue needs
- often an uptake and not just a delivery problem
describe cytopathic injury as a mechanism of tissue injury
inflammatory mediators cause damage (direct and indirect)
what is PIRO?
a pneumonic for the timeline of sepsis
- predisposition - host factors, comorbidities, genetics
- insult - specific infecting organism with special weapons (PAMPs)
- response - activation of the immune system (DAMPs)
- organ dysfunction - the collateral damage
what are two examples of insults (PIRO) that are associated with sepsis?
- ebola
- gram negative with LPS or MRSA with cytolytic toxins
describe the balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory molecules and their relationship with sepsis
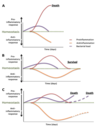
how do you monitor tissue perfusion?
- clinical assessment - skin, urine output, MSE, etc.
- pH and lactate
- historic survival is <10% if lactate is >10
- rate of lactate clearance
what are the mechanisms of monitoring pH and lactate?
- hypoxic- anaerobic production of lactate (global with shock or local with bowel infarction)
- non hypoxic- decreased clearance of lactate or accelerated aerobic glycolysis
describe what we do today for patients with sepsis
- fluids
- pressors
- monitoring tissue perfusion
- physiology and fluid responsiveness
- consensus, bundles, standardization


