Thorax- thoracic wall/pleural cavities Flashcards
Muscles of thoracic wall
External intercostal
Internal intercostal
Innermost intercostal
Subcostales
Transversus thoracis

Origin and insertio of subcostales
Internal surface of lower ribs to internal surface of second or third rib below

Origin and insertio of transversus thoracis
Inferior margin of 2-6th rib to inferior aspect of sternum, xiphoid and ribs 4-7

Innervation of muscles of thoracic wall
Intercostal nerves
Action of subcostales
May depress ribs
Action of transversus thoracis
Depress costal cartilages
Where do you find the vasculature in relation to ribs
Inferior border

Arterial supply of thoracic wall
Internal thoracic artery gives
- intercostal arteries
- superior gastric artery
- musculophrenic artery
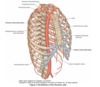
Venous drainage of thoracic wall
Intercostal veins either into azygous, hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins or internal thoracic vein

Chest drain insertion site
Lat dorsi, Pec major, apex of axilla and horizontal line across nipple

Where is suprapleural membrane
Covers superior aspect of cervical pleura

Where is the root of the lung
Mediastinal pleura between T5-T7 reflects off mediastinum
Covers lymph, vessels, nerves

Structures at the hilum of the lungs
Anterior to posterior:
Pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins
Bronchus

Ribs levels of lungs mid-clavicular, mid-axillary, and posteriorly
Anterior: 6th rib
Mid-axillary: 8th rib
Posteriorly: 10th rib
Ribs levels of pleura mid-clavicular, mid-axillary, and posteriorly
mid-clavicular: 8th rib
mid-axillary 10th rib
posteriorly 12th rib
(2 spaces below the lungs)

Trachea vertebral level
C6 to T4/5 (sternal angle)
Bronchal tree from proximal to distal
Main bronchus
Lobular bronchus
Segmental bronchus (*10 segments each)

Innervation of lungs
Vagus- constricts bronchioles
Sympathetic- dilates bronchioles
Lymph drainage of lungs
Other lymphs drain into bronchomediastinal lymph nodes
Which drain into deep veins at the base of neck/thoracic duct/right lymphatic trunk

Subclavian artery branches
VIT C&D
Vertebral
Internal thoracic
Thyrocervical
Costocervical
Dorsal scapular

Branches of thyrocervical artery
Inferior thyroid
Suprascapular
Transverse cervical

Branches of costcervical artery
Deep cervical
Highest intercostal

Which muscles does the breast lay anterior to
Pec major
Serratus anterior
External oblique
Arterial supply of breast
Internal mammary (thoracic) artery (subclavian a)
Lateral thoracic artery (axillary a)
Anterior intercostal arteries
Thoraco-acromial artery
Extension of parietal pleura into cervical region
Cupola: extends 2.5 cm above clavicle

Fascia between innermost intercostal muscle and pleura
endothoracic fascia
Which ribs level is costophrenic angle found
8-10
Where is stellate ganglion situated
Inferior cervical ganglion fuses with suoerior thoracic ganglion, forming stellate ganglion at level of C7
Anterior to neck of first rib
Anterior to scalene medius, posterior to subclavian artery
Compression results in horner syndrome sx

Position of recurrent laryngeal nerve in relation to oesophagus and trachea
Runs in the middle

What is azygous lobe
Commonest accessory lobe seen in 1% of pts
Azygous vein leaves a deep impression in the lung on that side during development

Azygous lobe appearance on xray
reverse comma sign

Where is aztgous lobe found
Right upper lobe
How many bronchopulmonary segments in each lung
10

Sympathetic ganglions
Paravertebral and prevertebral
Where are paravertebral ganglia located
anterior to abdo aorta
Coeliac, Superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric ganglia

Where are perivertebral ganglia found
Parallal to the spinal cord, from base of the skull down to pelvis, joining to form ganglia impar

Sympathetic innervation of head and neck
Branches of peri-arterial carotid nerve plexus
T1-T3
Sympathetic innervation of thorax
Cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves
T4-T6
Sympathetic innervation of abdomen
Greater, lesser and least splanchnic nerves
and
Coeliac, SM, IM plexuses
T7-T11

Sympathetic innervation of pelvis
Lumbar splanchnic nerve
T12-L3
Parasympathetic innervation of body
CN3, 7, 9, 10
and
Pelvic splanchnic nerve
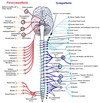
Pelvic splanchnic nerve aka
nerve erigentes
Route of thoracic duct
Ascends through aortic opening of diaphragm, to the right of descending aorta
Goes up posterior to oesophagus, when it crosses to the left side at T5
Ascends to the left of the oseophagus
Crossess the left subclavian artery to enter left brachiochalic vein

Areas of the body drained by thoracic duct
3/4 of body except the top right

Path of azygous vein in relation to right main bronchus
First posterior
Then arches superior to the right main bronchus

Sympathetic chain course through thorax and abdomen
Lateral to aorta and oesophagus
Enters abdo posterior to medial arcuate ligament over psoas major

Relation of vagus nerve to oesophagus
Left vagus: anterior to oesophagus
Right vagus: posterior to oesophagus

Sibsons fascia
Suprapleural fascia

Which artery at risk in level one axillary dissection
Thoraco-dorsal branch of subscapular artery

Which artery is at risk in level 3 axillary dissection
thoraco-acromial

Surface marking for lung fissures
Oblique → transverse process of T2 to 6th costal cartilage
Horizontal → under the 4th rib

Name different parts of the sternum and their vertebral level
Jugular notch: T2-3
Angle of louis: T4-5
Xiphoid process: T9

Sensory nerve supply of diaphragm
Central: phrenic (C3-5)
Peripheral: T5-T12
Central irritation such as splenic rupture refers to shoulder (C3-5)
Blood supply to diaphram
Superior and inferior phrenic from aorta
Musculophrenic from internal mammary
Describe female breast anatomy
Ducts + Glands + fat
Terminal duct-lobular units produce milk → 10-20 lactiferous ducts converging into the nipple with individual openings

Cooper ligament of breast
Supports the glandular tissue of the breast
From Dermis to deep fascia/posterior capsule behind breast
Support the shape of a young breast, but weaken with age

Lymph drainage of breast
Lateral parts mainly drained by axillary lymph nodes
Medial parts mostly by internal thoracic nodes
Multiple valveless channels connecting the 2 systems
Borders of the breast base
2nd to 6th intercostal space
Lateral sternum to mid axillary line
Blood supply of breast
Laterally: lateral thoracic
Medially: internal mammary
Inferiolateral: intercostal vessels
Deep: perforators to pec major (thoracoacromial trunk)
Nerve supply to breast skin
Supraclavicular (C3-4)
branches of intercostal nerves
intercostobrachial nerve
Which nerve supplies sensory to nipple
Fourth intercostal
Typical rib appearance
Facet on tubercle joins facet on transverse process
Facet on head joins facet on vertebral body

First rib anatomy
Scalene tubercle: attachment for scalene anterior

What layers do you go through for subclavian vein cannulation
Skin
Subcut fat
Deep fascia
Pec major
Clavicopectoral fascia
Subclavius
Subclavian vein wall

Structures at risk of damage during subclavian vein cannulation
Subclavian a
Phrenic n
Apex of lung
Thoracic duct (on the left side)


