The Visual Pathway Flashcards
(55 cards)
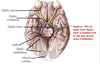
Label the anatomical features of the eye


what is the neural layer of the retina?
what cells are found here?
A layer of the retina that contains neurones that transmit photons of light into electrochemical energy
contains photoreceptors, bipolar cells and ganglion cells
ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve
What is the optic disk?
The point at which the optic nerve leaves the retina
there are no photoreceptors in the optic disk so any image in this area cannot be detected
it is the blind spot
What is the macula and fovea?
The macula is along the visual axis and has a high density of photoreceptors
the fovea only contains cones and has the highest visual acuity

How can the retina be divided?
The retina is an extension from the diencephalon
it can be divided into a neuronal and non-neuronal layer
the non-neuronal layer consists of pigmented epithelium that is light absorbing
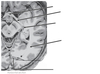
What are the 2 components of the outer layer of the eye?
What is the function of these areas?
Cornea:
- thick, transparent and avascular layer
- major area of refraction
sclera:
- “white of the eye” that covers most of the ocular surface and continuous with the cornea
- insertion point for muscles that move the eyeball
What are the 3 components of the middle (vascular) layer of the eye?
Choroid:
- highly vascular and nourishes the cornea and retina
iris:
- pigmented and vascular
- the muscles of the iris control the amount of light entering the eye by controlling the diameter of the pupil
ciliary body:
- controls the shape of the lens by pulling on the suspensory ligaments
What is the role of the lens?
It is a biconvex avascular structure through which light passes after passing through the pupil
What pigment is contained within the pigmented epithelium of the retina?
What is the role of this layer?
It contains melanin, which absorbs light
it provides nutrients to the photoreceptors
What are the 2 main neurones involved in the neuronal part of the retina?
1o bipolar cells:
- these link photoreceptors (rods and cones) to ganglion cells
2o ganglion cells:
- their axons exit the retina and fuse to form the optic nerve

What are the 2 different interneurones within the retina?
What are their roles?
They connect the rods and cones to the 1o and 2o neurones and modulate information
horizontal interneuron:
- modulates transmission
amacrine interneuron:
- modulates activity of ganglion cells

What does it mean that the optic nerve (CN II) is actually part of the CNS?
The optic nerve is an outgrowth from the diencephalon
when it exits via the optic canal, it takes all 3 layers of meninges with it
the optic nerve has meninges surrounding it to the eyeball
Label the components of the optic nerve

The sub arachnoid space contains CSF
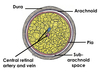
How does a rise in CSF pressure affect the optic nerve?
A rise in CSF pressure leads to papilloedema
this is due to a thin layer of CSF surrounding the optic nerve
What is papilloedema?
What causes it?
A swelling of the optic disk
as the optic nerve is surrounded by meninges, increases in CSF pressure can swell the optic nerve
increase in pressure compresses the central retinal vein (and artery) preventing venous drainage from the eye

What are the symptoms of papilloedema?
- Headaches
- drowsiness
- blurred vision
- vomiting
Label the anatomy of the visual pathway


What structures are involved in the visual pathway from start to end?
- Both optic nerves converge to form the optic chiasma
- fibres from the optic chiasma enter the optic tract
- fibres radiate away from the optic tract and into the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus
- this gives rise to optic radiations that lead to the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe

What features are shown in the different colours?

A lesion at any point causes specific visual defects
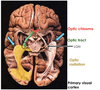
What is shown here?
What areas surround this structure?

Calcarine sulcus
primary visual cortex:
- this is where visual information first gets perceived
visual association cortices:
- this is where information gets interpreted and given meaning
- e.g putting a name to a face and forming associations

What are the 3 neurones involved in the visual pathway from the photoreceptors in the retina to the primary visual cortex?
Within CNS:
- 1o neurones in the retina are bipolar cells
- these synapse with the 2o neurones, which are ganglion cells
- axons of the ganglion cells run over the retina to the optic disk to form the optic nerve
Within thalamus:
- the optic nerve enters the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
- it synapses with the 3o thalamocortical neurones (optic radiations)
Cerebral cortex:
- optic radiations travel to the primary visual cortex

What is meant by the visual pathway being retinotopically organised?
- Left half of visual field goes to the right hemisphere
- Right half of visual field goes to the left hemisphere
- upper visual field goes to the lower bank of calcarine sulcus
- lower visual field goes to the upper bank of calcarine sulcus
- the centre of the visual axis (macula) goes to the occipital pole