Peripheral Nerve Lesions - Brachial Plexus Injuries Flashcards
(34 cards)
What are the contributions to the axillary nerve?
C5 and C6 only
What are the contributions to the musculocutaneous nerve?
C5-C7
What is a dermatome?
an area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve
Label the anterior dermatomes


Label the posterior dermatomes


What is a myotome?
a muscle (or group of muscles) that is innervated by a single spinal nerve
What types of trauma/injury to the nerves is possible?
- stretching of nerves
- tearing of nerves
- laceration of nerves
- avulsion of nerves from the spinal cord
What is meant by avulsion of nerves?
when the nerves are torn out of the spinal cord during injury
What are the 4 categories of brachial plexus pathology?
- injuries at birth
- blunt trauma
- penetrating trauma (wounds to the neck or axilla)
- disease e.g. tumour at apex of lung that can impact on the plexus
What is more likely; a brachial plexus or a peripheral nerve injury?
peripheral nerve injury
the brachial plexus is higher up and is much more protected from injury than the peripheral nerves
What are the 2 types of Brachial Plexus injury and the differences between them?
Erb’s Palsy:
this is an upper brachial plexus injury affecting C5 and C6
(sometimes C7)
Klumpke’s palsy:
this is a lower brachial plexus injury affecting C8 and T1
(sometimes C7)
What types of injuries will affect the roots and trunks of the brachial plexus?
Roots:
affected by cervical cord injuries and traction injuries
Trunks:
affected by injuries to the 1st rib
What are the 2 most common causes of brachial plexus injury?
- during delivery (obstetric)
- through adult trauma
What happens if there is an injury to the whole brachial plexus?
the entire innervation of the upper limb is lost
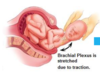
What is the most common cause of whole plexus injuries?
motorbike accidents
when people are thrown from bikes, as they hit the ground their head turns in the opposite direction to their shoulder
this stretches the brachial plexus and pulls the nerve roots out of the spinal cord
Why may the skin look different after a whole plexus injury?
the skin requires an autonomic nerve supply (T1) for vasoconstriction and vasodilation
How may the pupil look different after a whole plexus injury?
constriction of the pupil is due to injury to T1 and loss of autonomic function
When may Erb’s palsy (upper BP injury) happen in children?
when there is excessive stretching of the neck during delivery
this leads to damage to C5 and C6 nerve roots
What is the most common cause of excessive stretching of the neck during delivery, leading to Erb’s palsy?
shoulder dystocia
this is when the baby’s shoulders are too large for the birth canal so there is tugging on the neck during delivery
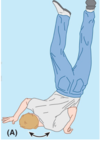
What is the result of Erb’s palsy in children?
The arm is medially rotated and hangs limply by the side
There is loss of ability to flex the elbow
Why is there medial rotation of the arm in Erb’s palsy?
medial rotation is unopposed as the lateral rotators are not functioning
teres minor and infraspinatus (lateral rotators) are innervated by C5 and C6
Why is there loss of elbow flexion in Erb’s palsy?
Biceps brachii and brachialis are not functioning due to injury ot C5, 6 and 7
Supination of the forearm by biceps cannot occur
Why does the arm hang limply by the side in Erb’s palsy?
Damage to the axillary nerve (C5, C6) means that there is loss of the abductors (deltoid)
What happens to the muscles in Erb’s palsy later on in life?
Muscular atrophy as they cannot be used
They appear smaller and less well developed than normal