The Knee Joint Flashcards
What are the 3 broad categories of reason for knee injury?
acute injuries:
- present to A&E
- sports, falls in the elderly
- fractures and tears/sprain of soft tissues
chronic knee pain/swelling:
- often seen by GP
- osteoarthritis, bursitis
atraumatic acute swelling/pain:
- present to A&E
acute gout, flare of osteoarthritis, septic joint
What are the 2 different components of the knee that could be injured?
bony injuries:
fractures of the patella, tibia or distal femur
dislocations
soft tissue injuries:
meniscal tears or ligament tears/rupture
Where do fractures of the patella, tibia or distal femur tend to occur?
- traumatic
- osteoporotic bone - low energy forces can cause fracture
- peri-prosthetic (around a prosthesis)
dislocation of the whole knee joint is uncommon and catastrophic
What are the 2 types of meniscal tears?
- due to acute injury/trauma
- due to chronic wear & tear and degeneration
What type of joint is the knee joint?
Which bones make up the knee joint?
It is a synovial hinge joint
It consists of:
- distal femur
- proximal tibia
- patella
The fibula is NOT associated with the knee joint
What are the 3 articulations involved with the knee joint?
2 femorotibial
this is the articulation between the femoral condyles and tibial condyles
1 femoropatellar
this is the articulation between the posterior patella and anterior surface of the femur
What is the fit like at the knee joint?
Why?
The tibial plateau is a poor fit for the rounded femoral condyles
This is because the tibial plateau is flat
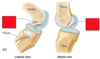
Label the components of the knee joint


What structure helps to make the fit of the knee joint better?
menisci
these are wedge-shaped plates of fibrocartilage that sit on top of the tibial plateaus
they deepen the tibial articular surface to receive the rounded femoral condyles
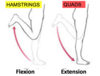
When is the knee joint most stable and least stable?
Why?
Most stable during extension:
this is when there is the best possible fit between the femur and tibia
Least stable during flexion:
this is when there is the least congruence between the tibia and the femur

Label the diagram as if you were looking down onto the inside of a left knee


Where do the menisci attach to?
Where are they thicker?
The external edges attach to the fibrous capsule of the joint
They are crescent shaped discs of fibrocartilage that are ticker at the external margins
What are the 4 functions of the menisci?
- increase joint congruency
- distribute weight evenly throughout the joint
- shock absorption
- assist in locking mechanism
Label the 6 types of meniscal tear


What tends to cause meniscal tears?
What is the damage associated with?
caused by injury or degenerative changes
damage associated with development of osteoarthritis in later life
What can meniscal tears cause?
What is the treatment?
displaced cartilage can become trapped during knee movements
this causes pain or locking
treatment is by repair or resection
What components involved in stability are represented by the red, green and blue lines?

red:
intra-articular ligaments (inside the joint)
green:
extra-articular ligaments (outside the joint)
blue:
surrounding muscles
What are the ‘intra-articular’ ligaments of the knee?
cruciate ligaments
there is an anterior and a posterior cruciate ligament
What are the ‘extra-articular’ ligaments?
collateral ligaments
there is a fibular and a tibial collateral ligament
Label the 2 ligaments
What is their main function?

they sit in a crossed fashion inside the joint and prevent lateral displacement of the femur and tibia

What is the origin and attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament?
it attaches to the posterior intercondylar region of the tibia
it travels supero-anteriorly to insert onto the medial femoral condyle
What is the attachment and insertion of the anterior cruciate ligament?
it attaches to the anterior intercondylar region of the tibia
it travels supero-posteriorly to attach to the lateral femoral condyle
Which cruciate ligament is stronger?
the posterior cruciate ligament is STRONGER than the anterior cruciate ligament
Label the cruciate ligaments as if looking down inside a left knee