The Foot Flashcards
What types of joints are present in the foot?
the small joints in the foot are synovial joints
this means they may be affected by both rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis
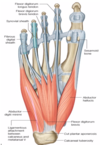
Label the bones of the foot


Label the tarsals, metatarsals and phalanges

What are the two inter-tarsal joints?
- subtalar joint
- transverse tarsal joint
Whar structures articulate at the subtalar joint?
What movements occur here?
the talus and calcaneus
it is involved with inversion and eversion of the foot
When do the phalanges and metatarsals become fractured?
when heavy objects are dropped onto or run over them
people may fracture or dislocate their toes by tripping over or kicking something hard
What are two conditions that commonly affect the first MTP joint?
bunions:
- known as hallux valgus
- it is a painful bony bump that develops on the metatarsophalangeal joint
gout:
- form of arthritis caused by excess uric acid in the bloodstream
- uric acid crystals form in the joints
What causes calcaneum fracture?
when a person falls from height and lands directly onto their feet (or foot)
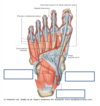
What are the 3 arches of the foot?
- medial longitudinal arch
- lateral longitudinal arch
- transverse arch
Label the arches of the foot


What are the important functions of the transverse and longitudinal arches of the foot?
they act as a spring and bear the weight of the body
they absorb the shock produced by locomotion
the flexibility conferred to the foot by these arches facilities functions such as walking and running
What structures maintain and support the arches of the foot?
they are supported by ligaments and tendons in the foot
(plantar ligaments)
What is pes planus?
“flat foot”
the longitudinal arches of the foot are lost
Where are the long extensor tendons of the toes visible?
Extensor digitorum longus and extensor hallucis longus tendons travel over the dorsum of the foot to their insertions
the tendons are visible under the skin of the foot
What are the 3 intrinsic muscles on the dorsum of the foot?
- extensor digitorum brevis
- extensor hallucis brevis
- 4 dorsal interossei
Which artery can be palpated on the dorsum of the foot?
dorsalis pedis artery
it arises at the anterior aspect of the ankle joint, as a continuation of the anterior tibial artery
label the tendons and muscles of the foot


what is the function of extensor digitorum brevis?
it extends the first four digits at the metatarsophalangeal joint
it assists in extending the second, third and fourth digits at the interphalangeal joint
it has no action on the fifth digit
What is the function of extensor hallucis brevis?
it assists in extension of the big toe
What is the function of the dorsal interossei?
abduction of the toes
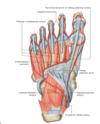
What lies deep to the tough skin on the sole of the foot?
a sheet of tough fibrous connective tissue - the plantar aponeurosis (or fascia)
this is thick and strong centrally but weaker in its medial and lateral parts
What is the role of the plantar aponeurosis?
it supports the arches of the foot and protects the deeper structures within the sole
What helps to cushion the heel of the foot?
there is a fat pad that lies between the skin and the calcaneum
How is the plantar fascia related to the flexor tendons of FDL and FHL?
fibrous bands project from the plantar fascia to merge with the fibrous sheaths that surround the long flexor tendons