Lower Limb Muscles Flashcards
(100 cards)
What are the 2 groups of muscles in the gluteal region?
What are their functions?
Superficial muscles:
- they abduct and extend the femur
Deep muscles:
- they laterally rotate the femur
What are the superficial muscles in the gluteal region?
- Gluteus maximus
- Gluteus medius
- Gluteus minimus
- Tensor fascia lata
They act to abduct and extend the lower limb at the hip joint
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of gluteus maximus?
origin:
- gluteal surface of ileum, sacrum and coccyx
attachment:
- iliotibial tract and gluteal tuberosity of femur
actions:
- main extensor of the thigh
- assists in lateral rotation
innervation:
- inferior gluteal nerve
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of gluteus medius?
Origin:
- gluteal surface of the ilium
Insertion:
- greater trochanter of femur
actions:
- abducts and medically rotates the lower limb
- secures the pelvis and prevents pelvic drop during walking
innervation:
- superior gluteal nerve
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of gluteus minimus?
origin:
- ilium
insertion:
- greater trochanter
actions:
- abducts and medically rotates the limb
- prevents pelvic drop of the opposite limb during walking
innervation:
- superior gluteal nerve
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of the tensor fascia lata?
Origin:
- anterior superior iliac spine
Insertion:
- iliotibial tract, which attaches to the lateral condyle of the tibia
action:
- assists gluteus medius and gluteus minimus in abduction and medial rotation of the lower limb
innervation:
- superior gluteal nerve
What are the deep muscles of the gluteal region?
- Piriformis
- Superior and inferior gemelli
- Quadratus femoris
- Obturator internus
They laterally rotate the lower limb
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of piriformis?
Origin:
- anterior surface of the sacrum
insertion:
- travels through greater sciatic foramen
- Inserts into greater trochanter of femur
actions:
- lateral rotation and abduction
innervation:
- nerve to piriformis
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of obturator internus?
Origin:
- pubis and ischium at obturator foramen
insertion:
- travels through lesser sciatic foramen
- attaches to greater trochanter of femur
actions:
- lateral rotation and abduction
innervation:
- nerve to obturator internus
What are the attachments, actions and innervations of the gemelli?
origin:
- superior gemellus - ischial spine
- inferior gemellus - ischial tuberosity
insertion:
- greater trochanter of femur
actions:
- lateral rotation and abduction
innervation:
- superior gemellus - nerve to obturator internus
- inferior gemellus - nerve to quadratus femoris
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of quadratus femoris?
Origin:
- ischial tuberosity
insertion:
- quadrate tuberosity on the intertrochanteric crest
actions:
- lateral rotation
innervation:
- nerve to quadratus femoris
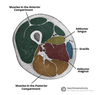
Label the muscles of the gluteal region


What is the innervation and general action of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the thigh?
Innervation:
- femoral nerve (L2-L4)
Action:
- extension of the leg at the knee joint
What are the muscles within the anterior compartment of the thigh?
- Pectineus
- Sartorius
- Quadriceps femoris
- Iliopsoas (the end passes into the anterior compartment)
What are the origins and insertions of iliopsoas?
Origin:
- Psoas major originates from the lumbar vertebrae
- iliacus originates from the iliac fossa
Insertion:
- lesser trochanter of femur
What are the actions and innervation of iliopsoas?
Actions:
- flexes the thigh at the hip joint
innervation:
- psoas major - anterior rami of L1-L3
- iliacus - femoral nerve
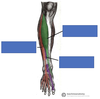
Label the muscles of the anterior thigh


What are the 4 muscles that make up quadriceps femoris?
- Rectus femoris
- Vastus lateralis
- Vastus medialis
- Vastus intermedius
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of vastus lateralis?
Origin:
- greater trochanter and lateral lip of linea aspera
Insertion:
- Quadriceps tendon, which attaches to the patella
Action:
- extends the knee joint and stabilises the patella
Innervation:
- femoral nerve
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of vastus medialis?
Origin:
- intertrochanteric line and medial lip of linea aspera
Actions:
- extends the knee joint and stabilises the patella
Innervation:
- femoral nerve
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of vastus intermedius?
Origin:
- anterior and lateral surfaces of femoral shaft
Actions:
- extends the knee joint and stabilises the patella
Innervation:
- femoral nerve
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of rectus femoris?
Origin:
- Ilium (just superior to acetabulum)
actions:
- flexes the thigh at the hip joint
- extends the leg at the knee joint
Innervation:
- femoral nerve
What are the attachments, actions and innervation of sartorius?
Origin:
- anterior superior iliac spine
Insertion:
- superior, medial surface of the tibia
Actions:
- flexes, abducts and laterally rotates the hip
- flexes the knee joint
Innervation:
- femoral nerve
Label the muscles