Brainstem & Cerebellum Flashcards
What are the 3 general functions of the brainstem?
- Conduit
- Integrative
- Cranial nerve
How does the brainstem act as a conduit?
It allows ascending and descending pathways to reach the thalamus and cerebellum from the spinal cord
It contains relay nuclei
These are a collection of grey matter (nerve cell bodies) within the CNS

How does the brainstem have an integrative function?
It is involved in the control of cardiovascular, respiratory and consciousness
Consciousness is controlled by the reticular formation
It is involved in complex motor patterns (e.g. balance)
What does locked in syndrome result from?
An infraction of vessels in the ventral pons
as the reticular formation is intact, the patient is conscious but is unable to move
What is the ‘cranial nerve” function of the brainstem?
These are the head’s equivalent to spinal nerves
They are involved in sight, hearing, equilibrium and gustation
There are cranial nerve nuclei and reflex centres within the brainstem
What are the 3 structures within the brainstem?
- Midbrain
- Pons
- Medulla oblongata
What are the rostral, caudal, ventral and dorsal relationships of the brainstem?
Rostrally:
- midbrain is continuous with the diencephalon
Caudally:
- medulla is continuous with the spinal cord at the level of the foramen magnum
Ventrally:
- clivus of occipital bone
Dorsally:
- cerebellum

What components of the ventricular system run through the brainstem?
- IVth ventricle (IVth)
- Cerebral aqueduct (Caq)
This is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord
These are cavities containing cerebral spinal fluid
Label the components of the ventricular system and brainstem


Which cranial nerves arise from the brainstem?
10 out of 12 cranial nerves arise from the brainstem
These are part of the PNS
They have sensory and motor parts

At any level of the brainstem, which 3 areas can be identified in cross section?
Tectum:
- the tectum is only present in the midbrain
Tegmentum:
- this contains cranial nerve nuclei and the reticular formation
Basal:
- descending motor fibres travel through here
Label the different areas in cross section of the brainstem


Where is the tectum found?
It is posterior to the ventricular system
The only region with substantial tectum (roof) is the midbrain (superior and inferior colliculi)

Where is the tegmentum found?
What does it contain?
Found anterior to the ventricular system
it contains cranial nerve nuclei and tracts, reticular formation and some ascending/descending pathways

Where is the basal found?
What does it contain?
It is found most anteriorly
it contains descending fibres from the cerebral cortex (pyramids, cerebral peduncles)

Which junction is labelled?

Pontomedullary junction (PMJ)
this is between the medulla of the brainstem and the pons

Where is the rhomboid fossa?
What is this?

It forms the floor of the IVth ventricle
It is exposed when the cerebellum is removed

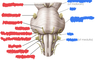
Label the ventral view of the medulla


What is the passage of the cranial nerves visible on the ventral view of the medulla like?
IX and X are lateral to the olives in the anterolateral sulcus
XI is below X
IX, X and XI all leave through the jugular foramen
XII emerges between the pyramids and olives and leaves through the foramen magnum
What is behind the pyramids?
Descending motor fibres - the pyramidal tract
What happens at the decussation of pyramids?
Fibres travelling from the cerebrum cross over and travel on the opposite side of the spinal cord
Label the dorsal view of the medulla


What is the obex?
The point at which the IVth ventricle becomes continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord