SM 268: Connective Tissue Disease in Skin Flashcards
What is Lupus Erythematous?
A chronic mulltiorgan disease with specific cutaneous presentations
What leads to the development of Lupus Erythematous?
Genetic susceptibility + UV light induced Keratinocyte damage + environmental stressors = autoantigens
What are the 3 ways Lupus can present cutaneously?
Chronic Cutaneous: Discoid Lupus Erythematous Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematous Acute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematous
What is the chronic mucocutaneous form of Lupus Erythematous?
Discoid Lupus Erythematous

Who does DLE effect and how does it present?
Discoid Lupus Erythematous is common among young african american women
Presents as scaly pink or brown plaques with an annular appearance on the head and upper body
Heals with dispigmentation
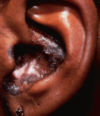
How does DLE Present and how does it heal?
Discoid Lupus Erythematous presents as scaly pink or brown plaques with an annular appearance on the head and upper body
Heals with light Dispigmentation and Alopecia

What is this and why?
Discoid Lupus Erythematous:
Young AA woman
Pink/brown Annular lesions on face/scalp
Alopecia and dispigmentation

How does Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematous present?
Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematous presents as Scaled, Annular pink papules and plaques in the face, upper trunk, and upper extensor extremities

What is this and why?

Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematous:
Annular Pink Lesion
Upper Extremity
Plaques
What antibody is associated with Subacute Cutaneous Lupus?
Anti-SSA (Ro)
What antibody would you expect in this patient’s blood?

Subacute Cutaneous Lupus:
Upper trunk
Pink Annular Papules/Plaques
Minor Scaling
= Anti-SSA
What tends to cause Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematous and how does this effect diagnosis?
Drugs, such as Thiazides and CCB’s
Get a detailed drug history!
How does Acute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematous present?
Classic Malar Rash that spares the Nasolabial folds
+
Painless Oral Ulcerations
Variable: erythema, edema, telangiectasia, erosions

What caues a classic malar rash?
Sun exposure
If you see this, what antibodies do you expect and what should you evaluate for?

Expect anti-dsDNA
Evaluate for Systemic Lupus: PFT’s, LFT’s, UA, etc.
How does Neonatal Lupus Erythematous arise, and how does it present?
Maternal Anti-SSA antibodies cross the placental barriers, causing a neonatal rash and potentially complete heart block

Does Neonatal Lupus Erythematous require sun exposure?
There is no sunlight in the womb, so no
What is Dermatomyositis and who gets it?
Effects women more than men, causes proximal extensor inflammatory myopathy
How does Dermatomyositis present and what shows up on labs?
Proximal extensor weakness that impede’s ADL’s
Heliotrope Rash
Shawl Sign
Dilated Fingernail Capillary Loops
Gottron’s Papules
Elevated CK
EMG/MRI abnormalities
What is this and what does it suggest?

Heliotrope Rash around the eyes that spares the nose
= Dermatomyositis
What are Gottron’s Papules and what do they suggest?
Gottron’s Papules = rash on extensor joints: MCP/IP/Elbow
Suggests Dermatomyositis

What is this and what does it suggest?

Rash on IP + MCP = Gottron’s Papules = Dermatomyositis
What’s shown here and what does it suggest?

Dilated Capillary Loops at the Proximal nail bed
Gottron’s Papules on the IP
= Dermatomyositis
What is this and what does it suggest?
Rash on sun-exposed areas that spares clothing covered areas = Shawl Sign
Suggests Dermatomyositis















