SM 265: Skin of Color Flashcards
What is Skin of Color?
Individuals of racial and ethnic backgrounds with similar cutaneous characteristics and conditions as well as reaction patterns to those conditions
How does Skin of Color compare to White Skin, in terms of number of Melanoycytes, and size/Melanin content/distribution of Melanosomes?
Same number of Melanocytes
More Melanin per Melanosome
Larger Melanosomes
Melanosomes distributed more uniformly in the epidermis
What does the Fitzpatrick Skin type consider?
Natural skin color
Ability to Tan
Reaction to Sun Exposure
When is the Fitzpatrick skin type less accurate?
Fitzpatrick skin type is less accurate in Asians and African Americans
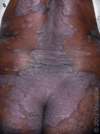
What are PIgmentary Demarcation Lines and who are they common in? Are they pathological?
PDL = abrupt transition in color of skin over a sharply demarcated line
Common in Infants + Adults of Color
Benign

What is this showing?
A Pigmentary Demarcation Line - it’s benign
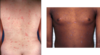
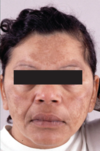
What is Periorbital Hyperpigmentation, and who is it common in? Is it benign?
Periorbital Hyperpigmentation is dark circles around the lower eyelid, and is common in Patients of Color
Benign
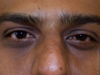
What is this showing?

Periorbital Hyperpigmentation
What is this showing? Who is it common in? Is it Benign?

Palmar/Plantar Hyperpigmentation
Common in African Americans
May be benign or pathologic
What are these? Are they benign?

Punctate Keratoses of Palmar Creases
Benign
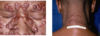
Where is Mucous Membrane Hyperpigmentation normal in Skin of Color?
Mucous Membrane Hyperpigmentation is common in the Oral mucosa in skin of color

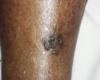
What is this? Who is it common in? Is it dangerous?

Melanonychia Striata
Common in older patients of color
Single Nail = Dangerous for Melanoma
Multiple Nails = Normal
What is this? Where does it tend to occur? Is it dangerous?

Guttate Hypomelanosis: small white spots on the skin
Common in Upepr extremities and Anterior shin
Benign
What is this? Where does it occur and in who? Is it dangerous?

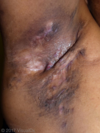
Congenital Dermal Melanocytosis
Common in Asian/AA infants; blue-green patches around Sacrococyxial area
Benign and resolves on it’s own
What is this? Who is it common in? Is it dangerous?

Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra
Common in adults of color, increasing with age
Not dangerous
What is Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra?
1 -2 benign brown papules with a “stuck-on” appearance that are commonly found in adults of color, and increase in frequency with age
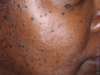
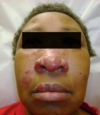
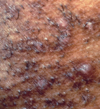
What is this and why?

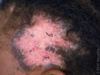
Acne Vulgaris: Comedone stage since there’s no cysts/papules/pustules
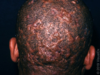
What is this and why?

Acne Vulgaris: Inflammatory stage, due to presence of Papules/Pustules/Cysts
How does Acne Fulminans vary in skin of color?
Less severe in African Americans than Hispanics and Whites
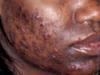
How does Acne Vulgaris resolve differently in skin of color? How does this effect treatment?
Acne vulgaris is more likely to leave behind post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation as well as create scars like Keloids
Need to be more aggressive in treatment
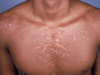
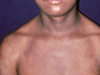
What is Atopic Dermatitis and how does it present on White skin?
Atopic Dermatitis is a symmetric, ill-defined erythematous patch that feels very itchy and leads to Lichenification; commonly found in:
Face/Extensor/Flexor/Head
Infants/Toddlers/Children/Adults

How does Atopic Dermatitis differ in skin of color?
Still itchy, but less erythema is visible due to darker skin and more papular or follicular presentation in patients of color
Also more likely to end in post-inflammatory pigmentation changes

What is this and why?

Atopic Dermatitis: symmetric lesion with lichenification prominent
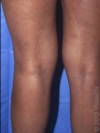
How does Psoriasis appear in white skin?
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory condition that presents as thickened rash with lots of Scale and a red outline on the Elbows and Knees