SM 251/252: Peds MSK, Peds/Adult Sports Med Flashcards
(121 cards)
How do you describe a fracture?
Location: Bone involved, area in the bone, and SH classification Fracture type or pattern Displacement
What is the treatment for Medial Epicondlyle Apophysitis?
Rest and PT to strengthen core/spine while improving baseball throwing abiliity
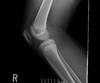
What is this?

Anterior Superior Iliac Spine Apophysis Avulsion Fracture
What’s the treatment for a muscle strain?
RICE and strengthening/stretching
What fracture pattern is this?

Comminuted fracture pattern
What are the main functions of bone?
Structure/skeletal support, mineral + electrolyte regulation, and hematopoiesis
What is Rotational displacement?
Rotational movement along the mid-axial line that can be difficult to detect Not the same as Angulation
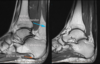
How does Sever disease present?
Insidious onset heel pain with mild weakness in dorsiflexion and tight calf muscles - in an 8 - 11 y/o
What meds can cause tendinopathy?
Fluoroquinolones and NSAIDS
What is the treatment for Nursemaid’s elbow?
Supination and Flexion to pop the radius back into place
What is the most common SH injury pattern?
Salter II
How does mechanical overload lead to Tendinopathy in adults?
Mechanical overload involves repeated microdamage with a failed healing response, causing a rise in inflammatory markers like IL-1b
How are Muscle strains graded?
Grade I = no tear Grade II = partial tear Grade III = full tear
What is Osgood-Schlatter syndrome?
Inflammation of the patellar ligament at the Tibial Tuberosity in teenagers playing sports, that gets worse with running/jumping
What is Sever disease?
A calcaneal apophysitis that effects children 8 - 11y/o causing mild weakness in dorsiflexion and tight calf muscles
What fracture is this and why?

Toddler’s fracture - oblique, nondisplaced fracture of a Tibia, likely due to twisting motion while falling
What is an ankle sprain?
Athletic activity that leads to injured ligaments
How is Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis treated?
Immediate surgical fixation to prevent further slippage and avoid avascular necrosis of the head of the Femur
What injury predisposes Osgood-Schlatter?
None
Does a Type I SH injury effect growth?
Generally no
What is imaging used for in Achilles Tendinopathy?
Look for tear or calcification with Ultrasound or MRI
Where on the tendon does Achilles Tendinopathy occur?
Mid-tendon > Calcaneal insertion
What are the complications of Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis?
Avascular necrosis of the hip, which increases in likelihood the longer the slip is untreated and the larger the slip
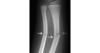
What fracture pattern is this?

Transverse fractures