SM 256: Eczema and Itchy Skin Flashcards
What is Eczema?
A morphological pattern seen visually or microscopically
What are the types of Eczema?
Atopic Dermatitis Contact Dermatitis Drug-Induced Dermatitis
What are the two types of Contact Dermatitis
Allergic Dermatitis Irritant Contact Dermatitis
How does Eczema present?
Symmetric Patches or Plaques with Erosions
Ill-defined and hard to delineate start/stop of lesion
Erythematous pink-red appearance Lichenification

What is Lichenification?
Thickening of Skin and accentuation of skin lines due to scratching

Is this Eczema, why or why not?
Not Eczema due to the well defined circular nature of the Rash - Eczema is ill-defined
Where does Atopic Dermatitis tend to develop in infants?
Atopic Dermatitis tends to develop in the facial and scal regions in infants

Where does Atopic Dermatitis develop in Toddlers?
Extensor surfaces like the elbows
Where does Atopic Dermatitis tend to develop in Older children and adults?
Flexor areas like the Antecubital and Popliteal Fossas
Where does Atopic Dermatits develop in Adults only?
In adults alone, Atopic Dermatitis develops in the head and neck
Does Lichenification imply a chronic or acute Atopic Dermatitis?
Lichenification implies a chronic Atopic Dermatitis because it’s driven by itching, which takes a while to make the Lichenification appearance
What is Spongiosis?
Fluid between Epidermal cells on Histology, common in Atopic Dermatitis
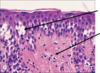
What does Histology of Atopic Dermatisis show?
Spongiosis (top) and Perivascular Infiltrate (bottom)

What is the role of Biopsy in diagnosing Eczema?
Only narrows the diagnosis down to the Eczema family, and rules out other disorders, but does not diagnose a specific type of Eczema
What do biomarkers and blood test reveal in Atopic Dermatitis?
Nothing - biomarkers and blood tests are not useful
What is the age prevalence of Eczema?
Eczema is common in childhood and may persist into adulthood, and also has some adult-onset cases as well
What protein is implicated in the development of Atopic Dermatitis and how?
Filaggrin 1, which is a major component of Natural Mositerizing Factor and maintaining the skin barrier function, is often dysfunctional in Atopic Dermatitis
What does Filaggrin 1 form?
Natural Moisterizing Factor - helps maintain the barrier function of the skin
Describe the protein precursors and products of Filaggrin?
Profilaggrin is cleaved into Filaggrin, which is eventually broken down into amino acids that form Natural Moisterizing Factor
What is the role of Profilaggrin?
Profilaggrin is a major component of Keratocyte Granules in the Granular layer of the Epidermis
Describe the mechanism of inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis?
Th2 cells produce IL-13 and Il-4, leading to decreased Fillagrin expression and compromising the barrier function of the skin
What cells and cytokines mediate inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis?
Th2 cells produce IL-4 and IL-13, which drive inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis
How does IgE drive Atopic Dermatitis pathophysiology?
It doesn’t - IgE elevation is a byproduct of IL-4 and IL-13 elevations due to Th2 cell activity
What causes the Dry Skin and Itchiness that accompanies Atopic Dermatitis?
IL-4 and IL-13


