SM 254: Benign Skin Neoplasms Flashcards
Do benign skin growths need treatment?
Generally no, unless they’re causing pain or other problems
What does Seborrheic Keratosis look like?
Grey-brown in color, elevated Papular plaque with a dry cracked appearance, common after age 30 on all body surfaces except palms and soles

What are Seborrheic Keratosis?
Superficial, raised epidermal growths with a stuck-on quality +/- cracks on the surface

How can you check to see if something is Seborrheic Keratosis?
Pick at the lesion gently, and it may crumble or flake off if it is a superficial lesion like Seborrheic Keratosis
Are Seborrheic Keratoses singular or widespread?
Either or, though they increase in frequency over time
What is a Solar Lentigo and how is it treated?
Aka Liver spots, flat light brown Macules on the dorsal hands/face which are exposed to Sun; not cancerous or precancerous and no treatment required

What causes Solar Lentigo?
Sun exposure throughout life, which results in them forming on sun exposed areas like the dorsal surfaces of hands and the face or upper back

How do Solar Lentigo relate to skin cancer?
Not precancerous or cancerous, but due to high UV light exposure, indicating a risk for skin cancer - tell them to use sun protection
What causes the discoloration in Solar Lentigo?
Increase in Melanin but not in Melanocytes, causing the light brown color

How can Solar Lentigo be distinguished from Melanoma?
Melanoma is darker and larger, and will change over time - generally, a Melanoma spot is an “ugly duckling” and will stand out from other spots
What are Acrochordons?
Skin tags. Raised fleshy Papules that protrude out of the skin, generally occurs on neck or eyelids and discolor the skin towards a brown coloration and may be connected to the skin with a small stalk (pedunculated)

What is a Dermatofibroma?
Single small round Papules that are pinkinsh or reddish brown. Slightly raised, firm, with a shiny or smooth surface and found on the lower extrimeties

What causes a Dermatofibroma?
Scar tissue after injury to the skin like an insect bite
Where are Dermatofibromas found?
Lower extremities

Where are Acrochordons found?
Generally the neck

What is a Keloid?
A raised, firm Nodule that protrudes out of the skin at the site of previous tissue trauma Often has a shiny/smooth surface, and appears hyperpigmented, may be itchy

Where are Keloids found?
Occur at sites of known previous trauma, like the chest or behind the ears (ear peircing)

Why do Keloids form?
Excess scar formation after injury to skin
How are Keloids treated?
Steroid injections to help flatten out the scar or lessen pain/inflammation
What is a Cherry Angioma?
A shiny bright red raised Papule that can happen anywhere on the body, but often in multiple spots on the trunk - known genetic component

When do Cherry Angiomas increase in frequency?
Pregnancy = more Cherry Angiomas

What causes Cherry Angiomas?
Dilated capillaries that protrude through the skin

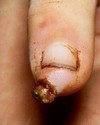
What is a Pyogenic Granuloma?
An eruptive, small solitary vascular red raised Papule that bleeds easy with trauma and rapidly grows bigger
What is an Epidermal Inclusion Cyst?
A mobile subcutaneous nodule often with an overlying punctum, such as a hair follicle, that is filled with debris that collects in a sack and creates foul smelling exudates






























