Rheumatology, Orthopedics and Sports II Flashcards
What is the likely diagnosis in a young female that presents with a triad of polyarthalgias, tenosynovitis, and a vesiculopustular skin rash?
Disseminated gonococcal infection
What is the likely diagnosis in a young female that presents with foot pain? The patient experiences pain and a clicking sensation when the 3rd/4th metatarsal heads are squeezed together.
Morton neuroma
mechanically-induced degenerative neuropathy; treatment is conservative (e.g. metatarsal support, padded shoe inserts)
What is the likely diagnosis in a young female that presents with tenderness to palpation along the 2nd metatarsal bone? The patient is an avid runner and her BMI is 18 kg/m2.
Stress fracture
more common in patients with the “female athlete triad”; manifests as localized pain

What is the likely diagnosis in a young female with months of progressive achy pain in the anterior right knee? The pain is worsened with running and sitting for an extended period.
Patellofemoral pain syndrome
common cause of anterior knee pain in young women; usually due to chronic overuse or malalignment

What is the likely diagnosis in a young patient that presents with sharp, non-radiating pain on the medial side of the tibia just below the knee after falling one week ago? A valgus stress test has no effect on the pain.
Pes anserinus pain syndrome (anserine bursitis)
no pain with valgus stress test indicates no MCL involvement

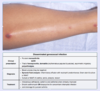
What is the likely diagnosis in a young patient with inflammatory bowel disease that presents with the leg ulcer below?

Pyoderma gangrenosum
What is the likely diagnosis in a young woman that presents with fever and migratory joint pain? Synovial fluid analysis reveals 65,000 WBC/mm3 with neutrophilic predominance.
Gonococcal septic arthritis
most common cause of septic arthritis in young, sexually active patients

What is the likely diagnosis in a young woman that presents with joint pain/swelling, especially in the wrists and MCP/PIP joints? She also experiences morning stiffness that lasts for more than an hour.
Rheumatoid arthritis
morning stiffness and involvement of the MCP/PIP joints is classic
What is the likely diagnosis in an afebrile patient that presents with acute right ankle pain that becomes “unbearable” over a few hours? He recalls having a similar episode 1 year ago that resolved with over-the-counter medication.
Gout
typically presents with acute monoarticular arthritis that progresses to maximum intensity within 12 - 24 hours; most commonly involves the big toe

What is the likely diagnosis in an asymptomatic elderly male with isolated elevated alkaline phosphatase? Physical exam, including rectal exam, is insignificant.
Paget disease of bone
most common cause of an asymptomatic elevation of alkaline phosphatase in an elderly patient

What is the likely diagnosis in an athlete that felt a “popping sensation” while playing soccer, followed by rapid pain/swelling? Aspiration of the knee yields grossly bloody joint fluid.
ACL injury
a “popping sensation” with rapid-onset pain/swelling and hemarthrosis are characteristic of ACL injuries (versus slowly progressive or absent effusion in meniscal tears)

What is the likely diagnosis in an elderly female that presents with back pain after lifting boxes? The pain is worse with standing, walking, and lying down. There is tenderness to palpation at the fourth lumbar vertebra.
Vertebral compression fracture

What is the likely diagnosis in an elderly male with low-grade fever, arthritis, diarrhea, and generalized lymphadenopathy? Small intestinal biopsy reveals PAS-positive, acid-fast negative macrophages.
Whipple’s disease
other commonly involved organs include the eye, CNS, and heart; macrophages containing Tropheryma whippelii bacteria stain PAS positive
What is the likely diagnosis in an elderly patient that presents with a 6-month history of unilateral knee pain? The pain is worse in the evening and with activity.
Osteoarthritis
major risk factors include obesity, advancing age, diabetes, and prior joint injury

What is the likely diagnosis in an elderly patient that presents with dry eyes and dry mouth? ANA is negative.
Age-related sicca syndrome
due to age-related exocrine gland atrophy; Sjogren syndrome typically presents in middle-aged patients with a positive ANA
What is the likely diagnosis in an elderly patient with right-sided neck pain and sensory deficits over the posterior forearm? Physical exam reveals limited neck rotation and lateral bending.
Cervical spondylosis
limited neck rotation and lateral bending is due to osteoarthritis with secondary muscle spasm; sensory deficit is due to osteophyte-induced radiculopathy
What is the likely diagnosis in an elderly woman with three months of neck, shoulder, and hip pain/stiffness, as well as malaise and weight loss? ESR is elevated and creatine kinase is normal.
Polymyalgia rheumatica

What is the likely diagnosis in an older patient with headache, bone pain, and hearing loss?
Paget disease of bone (osteitis deformans)
bone pain, hearing loss, headaches, and fracture are all consistent with Paget disease of bone

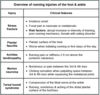
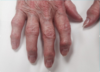
What is the likely diagnosis in an older woman that presents with pain/stiffness in the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints?

Osteoarthritis
the picture demonstrates prominent osteophytes at the DIP joint (Heberden nodes) and PIP joint (Bouchard nodes), which are classic of OA
What is the likely diagnosis in an older woman with pain behind the right heel several days after beginning treatment for a UTI?
Achilles tendinopathy
likely secondary to fluoroquinolone use; risk factors include old age (> 60) and female gender
What is the likely diagnosis in an older woman with unilateral headache, jaw pain, and vision loss? Fundoscopy shows a swollen pale disc with blurred margins. ESR is elevated.
Giant cell (temporal) arteritis
fundoscopy findings are consistent with anterior ischemic optic neuropathy

What is the most common extraskeletal complication of ankylosing spondylitis?
Anterior uveitis
presents with unilateral ocular pain and photophobia

What is the most common finding on cervical radiography in patients with cervical spondylosis?
Osteophytes
low specificity; other findings include disk space narrowing and hypertrophic vertebral bodies
What is the most definitive test for diagnosis of polymyositis?
Muscle biopsy
shows a CD8+ lymphocytic infiltrate in the endomysium (versus CD4+ infiltrate in the perimysium in dermatomyositis)