Pulma and Critical Care IV Flashcards
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with sudden-onset dyspnea and dysphagia and scattered urticaria?
Upper airway obstruction (e.g. laryngeal edema)
PE may reveal stridor and harsh respiratory sounds, however wheezing is typically absent
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with sudden-onset pleuritic chest pain, hemoptysis, dyspnea, and the CT findings below?

Pulmonary embolism
chest CT scan showing a wedge-shaped infarction (red arrows) is virtually pathognomonic for PE

What is the likely diagnosis in a plumber with months of progressive dyspnea, bibasilar crackles, and clubbing?
Asbestosis

What is the likely diagnosis in a post-operative patient with hypotension, JVD, and new-onset right bundle branch block?
Massive pulmonary embolism
massive PE is defined as PE complicated by hypotension and/or acute right heart strain (e.g. JVD, RBBB)

What is the likely diagnosis in a smoker with a chronic productive cough for multiple years without fever, weight loss, or dyspnea?
Chronic bronchitis
chronic bronchitis is defined as chronic productive cough for > 3 months in 2 successive years
What is the likely diagnosis in a young male with dyspnea on exertion accompanied by chronic lower back pain that is worse at night and improves with exercise?
Ankylosing spondylitis

What is the likely diagnosis in a young male with hemoptysis and hematuria without history of sinusitis?
Goodpasture’s disease
granulomatosis with polyangiitis can cause hemoptysis and hematuria with upper airway involvement (e.g. sinusitis, otitis media, etc.)
What is the likely diagnosis in a young man with an anterior mediastinal mass and elevated β-hCG/AFP?
Non-seminomatous germ cell tumor
e.g. yolk sac tumor, choricocarcinoma, embryonal carcinoma
What is the likely diagnosis in a young patient with chronic nasal congestion and dry cough without an identifiable trigger, eye symptoms, itching, or sneezing?
Non-allergic rhinitis
diagnosis is typically clinical

What is the likely diagnosis in a young patient with minimal smoking history who presents with progressive dyspnea, cough, and bilateral basilar hyperlucency on CXR?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency

What is the likely diagnosis in a young woman with exertional dyspnea and enlargement of the pulmonary arteries and right ventricle on CXR?
Primary pulmonary hypertension

What is the likely diagnosis in a young woman with shortness of breath and the CXR findings below?
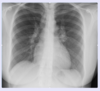
Sarcoidosis

What is the likely diagnosis in an immigrant with progressive dyspnea, orthopnea, palpitations, and an elevated left main bronchus on CXR?
Rheumatic heart disease
mitral stenosis results in left atrial enlargement, predisposing to arrhythmia (palpitations) and elevation of the left main bronchus

What is the likely diagnosis in an immunocompromised patient with fever, chest pain, hemoptysis and pulmonary nodules with ground-glass opacities on CT scan?
Invasive aspergillosis

What is the likely diagnosis in an infant with upper respiratory symptoms, wheezing/crackles, and respiratory distress?
Bronchiolitis

What is the likely diagnosis in an obese patient with daytime hypercapnia, hypoxemia, and respiratory acidosis?
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome

What is the likely diagnosis in an obese patient with daytime somnolence, morning headaches, and normal daytime CO2?
Obstructive sleep apnea
normal daytime CO2 helps distinguish from obesity hypoventilation syndrome (elevated daytime CO2)

What is the likely diagnosis in an older patient with no smoking history that presents with chronic, progressive dyspnea and dry cough? History and physical exam are unremarkable.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
may also be referred to as usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP); PFTs reveal a pattern similar to interstitial restrictive lung disease

What is the likely diagnosis in an unvaccinated child with high fever, drooling, and respiratory distress?
Epiglottitis (H. influenza type b)

What is the likely underlying etiology in a patient with bronchiectasis predominantly in the upper lobe and sputum cultures positive for Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Cystic fibrosis
upper lobe involvement is characteristic of bronchiectasis due to CF and helps differentiate it from bronchiectasis due to other causes

What is the likely underlying etiology of hypoxemia in patient with respiratory acidosis and normal A-a gradient?
Hypoventilation

What is the most common adverse effect associated with inhaled corticosteroids?
Oroparyngeal candidiasis (oral thrush)
What is the most common malignancy diagnosed in patients exposed to asbestos?
Bronchogenic carcinoma
bronchogenic carcinoma is more common than mesothelioma

What is the most common trigger of acute COPD exacerbation?
Upper respiratory infection (URI)
examination often reveals wheezes, tachypnea, prolonged expiration, and use of accessory muscles
What is the most common type of lung cancer overall?
Adenocarcinoma
typically presents as a solitary nodule with or without symptoms (e.g. weight loss, hemoptysis)

What is the most important risk factor for neonatal respiratory distress syndrome?
Prematurity
other risk factors include male sex, perinatal asphyxia, maternal diabetes, and C-section
What is the most significant risk factor for tuberculosis in the U.S.?
Emigration from an endemic area
What is the next step in management for a patient with acute COPD exacerbation who fails to improve after non-invasive positive pressure ventilation?
Tracheal intubation
may also be warranted if NPPV is contraindicated (e.g. severe acidosis, ARDS, hemodynamic instability)

What is the next step in management for a patient with acute COPD exacerbation with continued symptoms despite medical management?
Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation
if a trial of NPPV fails to improve symptoms, intubation can be considered (other contraindications to NPPV listed in chart below)

What is the next step in management for a patient with severe asthma exacerbation with an elevated PaCO2?
Endotracheal intubation
normal or elevated PaCO2 suggests impending respiratory failure (inability to meet increased respiratory demands)
What is the next step in management for a smoker with progressive dyspnea, weight loss, and evidence of pleural effusion on CXR?
Diagnostic thoracentesis
undiagnosed pleural effusion is best evaluated with thoracentesis to determine if the fluid is transudative or exudative;
exception: in patients with evidence of CHF (e.g. weight gain, pedal edema, bibasilar crackles), the first step is a trial of diuretics

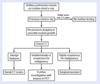
What is the next step in management for a solitary pulmonary nodule discovered on routine CXR in a patient with no previous imaging?
CT scan of chest
evaluate the lesion to determine future management based on risk

What is the next step in management for a solitary pulmonary nodule discovered on routine CXR?
Review previous CXR
What is the next step in management for a young patient taking omeprazole who presents with chronic nocturnal cough without post-nasal drip, fever, dyspnea, weight loss, or response to H1 blockers?
Pulmonary function tests

What is the next step in management for a young patient who presents with chronic nocturnal cough with a sensation of liquid dripping into the back of the throat?
Oral first-generation H1 blocker

What is the pathophysiologic mechanism underlying worsening hypoxemia when a patient with lobar pneumonia lies on the affected side?
Increased intrapulmonary shunting
lying on the affected side increases blood flow (Q) to this area due to gravity, where ventilation (V) is poor due to pneumonia, thus worsening the V/Q ratio

What is the recommended anticoagulation for pulmonary embolism in a patient with severe renal insufficiency (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2)?
Unfractionated heparin followed by warfarin
LMWH and factor Xa inhibitors are not recommended in renal insufficiency because they are metabolized by the kidney
What is the recommended empiric treatment for healthy patients with community-acquired pneumonia in an outpatient setting?
[…] or […]
macrolide or doxycycline
patients with comorbidities may receive same empiric treatment as inpatients (see below)

What is the recommended empiric treatment for patients with community-acquired pneumonia in an inpatient setting?
[…] or […] (IV)
fluoroquinolone or beta-lactam + macrolide (IV)

What is the recommended management after chest CT for solitary pulmonary nodules < 8 mm with low to intermediate malignancy risk?
Serial CT scan

What is the recommended management after chest CT for solitary pulmonary nodules > 8 mm with low to intermediate malignancy risk?
FDG-PET or biopsy
suspicious lesions of FDG-PET should be excised; non-suspicious lesions can be followed with serial CT

What is the recommended management after chest CT for solitary pulmonary nodules with high malignancy risk?
Surgical excision

What is the recommended management for amniotic fluid embolism syndrome?
Supportive (e.g. respiratory, hemodynamic support)
What is the recommended management for solitary pulmonary nodules with stable size and appearance for over 2-3 years on imaging?
Reassurance; no further testing required

What is the recommended management for symptomatic acute bronchitis?
NSAIDs, bronchodilators (symptomatic treatment)
antibiotics are not recommended



