Pulm and Critical Care II Flashcards
Normal or high PaCO2 in a patient with an acute asthma exacerbation is suggestive of impending […].
Normal or high PaCO2 in a patient with an acute asthma exacerbation is suggestive of impending respiratory failure.
demonstrates an inability to maintain adequate ventilation as patients are hyperventilating and should have low PaCO2
Obstructive lung disease is characterized by an FEV1/FVC ratio […]% of predicted.
Obstructive lung disease is characterized by an FEV1/FVC ratio < 70% of predicted.
additionally, the individual values for both FEV1 and FVC are decreased

Oxygenation, and thus PaO2, in mechanically ventilated patients may be improved by increasing the […] or PEEP.
Oxygenation, and thus PaO2, in mechanically ventilated patients may be improved by increasing the FiO2 or PEEP.
Oxygenation, and thus PaO2, in mechanically ventilated patients may be improved by increasing the FiO2 or […].
Oxygenation, and thus PaO2, in mechanically ventilated patients may be improved by increasing the FiO2 or PEEP.
Patients with COPD and signs of right heart failure or hematocrit > 55% should be started on home oxygen if PaO2 < […] mmHg or SaO2 < […].
Patients with COPD and signs of right heart failure or hematocrit > 55% should be started on home oxygen if PaO2 < 59 mmHg or SaO2 < 89%.
has been shown to prolong survival and improve quality of life
Patients with COPD have an increased work of breathing due to a […] diaphragm.
Patients with COPD have an increased work of breathing due to a flattened diaphragm.
the flattened diaphragm has more difficulty contracting to expand the thoracic cavity

Patients with COPD who have resting PaO2 < […] mmHg or SaO2 < […] are candidates for long-term home O2 treatment.
Patients with COPD who have resting PaO2 < 55 mmHg or SaO2 < 88% are candidates for long-term home O2 treatment.
has been shown to prolong survival and improve quality of life
Patients with hypovolemia often have […] levels of urine sodium.
Patients with hypovolemia often have decreased levels of urine sodium.
due to activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; hypovolemia may manifest as orthostatic hypotension/syncope
Pleural effusion and atelectasis result in […] breath sounds, […] tactile fremitus, and […] to percussion.
Pleural effusion and atelectasis result in decreased breath sounds, decreased tactile fremitus, and dullness to percussion.
fluid is present outside the lung in the thoracic cavity, which insulates breath sounds and vibration (fremitus) originating within the lung

Pneumothorax and emphysema result in […] breath sounds, […] tactile fremitus, and […] to percussion.
Pneumothorax and emphysema result in decreased breath sounds, decreased tactile fremitus, and hyperresonance to percussion.
air is present outside the lung in the thoracic cavity, which insulates breath sounds and vibration (fremitus) originating within the lung

Renal biopsy showing linear IgG antibodies along the glomerular basement membrane is diagnostic for […].
Renal biopsy showing linear IgG antibodies along the glomerular basement membrane is diagnostic for Goodpasture’s disease.
Restrictive lung disease is characterized by an FEV1/FVC ratio […]% of predicted.
Restrictive lung disease is characterized by an FEV1/FVC ratio > 70% of predicted.
however, the individual values for both FEV1 and FVC are decreased
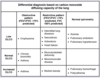
Sarcoidosis is associated with elevated serum levels of the enzyme […].
Sarcoidosis is associated with elevated serum levels of the enzyme angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE).
Sarcoidosis is associated with hypercalcemia due to increased […] activity in epithelioid histiocytes.
Sarcoidosis is associated with hypercalcemia due to increased 1α-hydroxylase activity in epithelioid histiocytes.
activates vitamin D; can occur in any disease with many non-caseating granulomas (e.g. berylliosis)
Tachycardia, tachypnea, and increased shivering are associated with […] hypothermia (severity).
Tachycardia, tachypnea, and increased shivering are associated with mild hypothermia (severity).
seen with temperatures between 90-95 F

The CURB-65 criteria help guide treatment and treatment location for patients with community-acquired pneumonia:
C: […]
U: Urea > 20 mg/dL
R: Respirations > 30/min
B: Blood pressure (systolic < 90 or diastolic < 60 mmHg)
65: Age > 65
The CURB-65 criteria help guide treatment and treatment location for patients with community-acquired pneumonia:
C: Confusion
U: Urea > 20 mg/dL
R: Respirations > 30/min
B: Blood pressure (systolic < 90 or diastolic < 60 mmHg)
65: Age > 65
+1 for each criteria met; higher score is associated with increased mortality

The CURB-65 criteria help guide treatment and treatment location for patients with community-acquired pneumonia:
C: Confusion
U: […]
R: Respirations > 30/min
B: Blood pressure (systolic < 90 or diastolic < 60 mmHg)
65: Age > 65
The CURB-65 criteria help guide treatment and treatment location for patients with community-acquired pneumonia:
C: Confusion
U: Urea > 20 mg/dL
R: Respirations > 30/min
B: Blood pressure (systolic < 90 or diastolic < 60 mmHg)
65: Age > 65
+1 for each criteria met; higher score is associated with increased mortality

The CURB-65 criteria help guide treatment and treatment location for patients with community-acquired pneumonia:
C: Confusion
U: Urea > 20 mg/dL
R: […]
B: Blood pressure (systolic < 90 or diastolic < 60 mmHg)
65: Age > 65
The CURB-65 criteria help guide treatment and treatment location for patients with community-acquired pneumonia:
C: Confusion
U: Urea > 20 mg/dL
R: Respirations > 30/min
B: Blood pressure (systolic < 90 or diastolic < 60 mmHg)
65: Age > 65
+1 for each criteria met; higher score is associated with increased mortality

The CURB-65 criteria help guide treatment and treatment location for patients with community-acquired pneumonia:
C: Confusion
U: Urea > 20 mg/dL
R: Respirations > 30/min
B: […]
65: Age > 65
The CURB-65 criteria help guide treatment and treatment location for patients with community-acquired pneumonia:
C: Confusion
U: Urea > 20 mg/dL
R: Respirations > 30/min
B: Blood pressure (systolic < 90 or diastolic < 60 mmHg)
65: Age > 65
+1 for each criteria met; higher score is associated with increased mortality

The diagnosis of asthma can be made in patients with normal or increased DLCO and a >[…]% increase in FEV1 following bronchodilator administration.
The diagnosis of asthma can be made in patients with normal or increased DLCO and a >12% increase in FEV1 following bronchodilator administration.
patients with COPD typically have a decreased DLCO and < 12% increase in FEV1 after bronchodilators
The diagnosis of upper-airway cough syndrome (postnasal drip) is confirmed by elimination of nasal discharge and cough with the use of […].
The diagnosis of upper-airway cough syndrome (postnasal drip) is confirmed by elimination of nasal discharge and cough with the use of first-generation H1 receptor antagonists (e.g. chlorpheniramine).
an alternative treatment regimen is a combined antihistamine-decongestant (e.g. brompheniramine and pseudoephedrine)
The flow-volume loop shifts to the left in patients with […] lung disease (obstructive or restrictive).
The flow-volume loop shifts to the left in patients with obstructive lung disease (obstructive or restrictive).

The flow-volume loop shifts to the right in patients with […] lung disease (obstructive or restrictive).
The flow-volume loop shifts to the right in patients with restrictive lung disease (obstructive or restrictive).

The initial pathophysiology of a massive PE involves dilation and hypokinesis of the […] ventricle with subsequent dysfunction.
The initial pathophysiology of a massive PE involves dilation and hypokinesis of the right ventricle with subsequent dysfunction.

The modified Wells criteria is used to assess pretest probability of acute […].
The modified Wells criteria is used to assess pretest probability of acute pulmonary embolism.

The most common causes of secondary digital clubbing are […], cystic fibrosis, and right-to-left cardiac shunts.
The most common causes of secondary digital clubbing are lung malignancy, cystic fibrosis, and right-to-left cardiac shunts.

The pathogenesis of bronchiectasis involves an […] insult with impaired bacterial clearance.
The pathogenesis of bronchiectasis involves an infectious insult with impaired bacterial clearance.

The presence of digital clubbing in patients with COPD should prompt a search for […].
The presence of digital clubbing in patients with COPD should prompt a search for occult malignancy.
COPD itself, with or without hypoxemia, does NOT cause clubbing

The primary long-term intervention for COPD is a daily long-acting […] inhaler.
The primary long-term intervention for COPD is a daily long-acting anticholinergic inhaler.
e.g. ipratropium, tiotropium; may be combined with a SABA for greater symptom relief
The primary long-term intervention for persistent asthma is daily inhaled […].
he primary long-term intervention for persistent asthma is daily inhaled corticosteroids.
versus a long-acting anticholinergic inhaler (COPD)
The three most common causes of chronic cough are […], asthma, and GERD.
The three most common causes of chronic cough are upper-airway cough syndrome (postnasal drip), asthma, and GERD.
The three most common causes of chronic cough are upper-airway cough syndrome (postnasal drip), […], and GERD.
The three most common causes of chronic cough are upper-airway cough syndrome (postnasal drip), asthma, and GERD.
The three most common causes of chronic cough are upper-airway cough syndrome (postnasal drip), asthma, and […].
The three most common causes of chronic cough are upper-airway cough syndrome (postnasal drip), asthma, and GERD.
The underlying histopathologic lesion of sarcoidosis is […] on tissue biopsy.
The underlying histopathologic lesion of sarcoidosis is non-caseating granulomas on tissue biopsy.
Transudative pleural effusions are characterized by […] pleural/serum protein ratio.
Transudative pleural effusions are characterized by < 0.5 (low) pleural/serum protein ratio.

Transudative pleural effusions are characterized by […] pleural/serum LDH ratio.
Transudative pleural effusions are characterized by < 0.6 (low) pleural/serum LDH ratio.
or pleural LDH < 2/3 upper normal limit of serum LDH

Treatment of invasive aspergillosis often involves IV […] and an echinocandin (e.g. caspofungin).
Treatment of invasive aspergillosis often involves IV voriconazole and an echinocandin (e.g. caspofungin).

Ventilation, and thus PaCO2, in mechanically ventilated patients may be altered by changing either […] or tidal volume.
Ventilation, and thus PaCO2, in mechanically ventilated patients may be altered by changing either respiratory rate or tidal volume.
Ventilation, and thus PaCO2, in mechanically ventilated patients may be altered by changing either respiratory rate or […].
Ventilation, and thus PaCO2, in mechanically ventilated patients may be altered by changing either respiratory rate or tidal volume.
What anti-hypertensive medication is associated with dry cough?
ACE inhibitors
due to increased circulating kinins, substance P, prostaglandins, and thromboxane
What asthma medication may cause CNS stimulation, cardiac arrhythmia, and GI disturbances as possible side effects?
Theophylline
narrow therapeutic window that may be altered by drugs that inhibit CYP-450
What asthma severity is characterized by SABA use < 2 days a week with < 2 nighttime awakenings a month?
Intermittent

What asthma severity is characterized by SABA use > 2 days a week (not daily) with 3-4 nighttime awakenings a month?
Mild persistent

What asthma severity is characterized by SABA use daily with >1 nighttime awakening a week (not nightly)?
Moderate persistent

What autoantibody is classically elevated in granulomatosis with polyangiiitis?
ANCA (typically c-ANCA)
aids with diagnosis; definitive diagnosis made with tissue biopsy showing granulomatous inflammation



