Psych, Substance Abuse, Poisoning Flashcards
Antidotes for cyanide poisoning include […] (preferred) or […]; alternatively nitrites may be used to induce methemoglobinemia.
Antidotes for cyanide poisoning include hydroxycobalamin (preferred) or sodium thiosulphate; alternatively nitrites may be used to induce methemoglobinemia.

Antidotes for cyanide poisoning include hydroxycobalamin (preferred) or sodium thiosulphate; alternatively […] may be used to induce methemoglobinemia.
Antidotes for cyanide poisoning include hydroxycobalamin (preferred) or sodium thiosulphate; alternatively nitrites may be used to induce methemoglobinemia.

Exertional heat stroke occurs in healthy individuals undergoing conditioning in extreme heat/humidity due to […].
Exertional heat stroke occurs in healthy individuals undergoing conditioning in extreme heat/humidity due to thermoregulation failure.
vs heat exhaustion, which is due to inadequate fluid and salt replacement
Sodium bicarbonate alleviates the cardiotoxicity associated with TCA overdose by decreasing the drugs affinity for […].
Sodium bicarbonate alleviates the cardiotoxicity associated with TCA overdose by decreasing the drugs affinity for fast-acting Na+ channels.
NaHCO3 increases serum pH and extracellular sodium, which alleviates the cardio-depressant action of TCAs on sodium channels

Treatment of salicylate intoxication includes alkalinization of the urine with […].
Treatment of salicylate intoxication includes alkalinization of the urine with sodium bicarbonate.
improves renal excretion
What acid-base disturbance is associated with cyanide poisoning?
Metabolic acidosis
cyanide blocks cytochrome oxidase a3 in the mitochondrial ETC, thus promoting anaerobic metabolism and causing lactic acidosis
What anti-emetic agents may cause extraparkinsonian symptoms (e.g. acute dystonia) as a possible side effect?
metoclopramide and prochlorperazine
other EPS include akathisia and parkinsonism; due to dopamine receptor blockade
What antidote is frequently used to treat methanol and/or ethylene glycol poisoning?
Fomepizole
inhibits alcohol dehydrogenase; ethanol may be used as well

What is the likely diagnosis in a farmer that presents to the hospital with agitation, vomiting, and watery eyes? Physical exam reveals 1 mm pupils bilaterally and increased bowel sounds.
Organophosphate (acetylcholinesterase inhibitor) poisoning
What is the likely diagnosis in a group of individuals that present with headache, nausea/vomiting, and confusion after eating at an indoor barbecue? Physical examination of one patient reveals tachycardia, tachypnea, and pinkish-skin hue.
Carbon monoxide poisoning
diagnosis is confirmed by measuring carboxyhemoglobin levels (> 3% in non-smokers; > 10% in smokers)
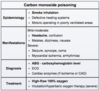
What is the likely diagnosis in a homeless patient that presents with confusion, epigastric pain, and blurred vision? Laboratory studies reveal anion gap metabolic acidosis.
Methanol poisoning
methanol intoxication effects the eyes (vs ethylene glycol, which effects the kidneys)

What is the likely diagnosis in a homeless patient that presents with confusion, flank pain, and hematuria? Laboratory studies show anion gap metabolic acidosis and urine microscopy reveals calcium oxalate crystals.
Ethylene glycol poisoning
ethylene glycol doesn’t typically affect the eyes (vs methanol)

What is the likely diagnosis in a middle-aged man with a history of poorly controlled HIV that presents with changes in personality and bizarre behavior? The patient also appears to have impaired attention and calculation. Brain MRI reveals a diffuse increase in intensity in the white matter.
HIV-associated neurocognitive dysfunction

What is the likely diagnosis in a military recruit that collapses during training exercises on a hot, humid day? The patient is disoriented and has a fever of 105.8 F.
Exertional heat stroke
vs heat exhaustion, which typically presents with lower-grade fever (< 104 F) and no altered mental status

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient brought to the ED with severe agitation and combativeness? Urine toxicology is negative. The patient is admitted and remained psychotic for one week before symptoms subsided.
Bath salts intoxication
PCP and cocaine intoxication may present similarly but with shorter durations of effect; additionally, PCP and cocaine are typically included in hospital urine toxicology screens
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that develops confusion, agitation, diaphoresis, and tremors three days after being admitted to the hospital following a motor vehicle accident? Physical exam reveals tachycardia, tachypnea, and hypertension.
Delirium tremens
defined by autonomic excitation, agitation, tremor, and altered sensorium 48 - 96 hours after the last drink

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that experiences sleep difficulties with “normal” bed times? The patient has no difficulty going to bed and waking up late (e.g. sleeping from 4 am to 12 pm).
Delayed sleep phase syndrome
circadian rhythm disorder characterized by inability to fall asleep at “normal” bedtimes (“night owls”);
vs.
advanced sleep phase syndrome, where patients cannot stay up late and have early morning insomnia (“early birds”)
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that presents with confusion and blurry vision after overdosing on an unknown medication? Physical examination reveals dry mucous membranes, decreased bowel sounds, and 8 mm pupils bilaterally.
Anticholinergic toxicity
“mad as a hatter, blind as a bat, dry as a bone, full as a flask, red as a beet”; may be reversed with physostigmine (cholinesterase inhibitor)

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that presents with heavy drooling, dysphagia, and a white tongue after being found next to an empty bottle of an unknown substance?
Caustic ingestion
in severe cases, perforation of the esophagus or stomach can occur, resulting in mediastinitis or peritonitis

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that presents with progressive worsening peripheral neuropathy? Physical exam reveals areas of hyper- and hypopigmentation, as well as hyperkeratosis. The patient restores antique furniture as a hobby.
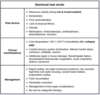
Arsenic poisoning (chronic)
arsenic may be found in pressure-treated wood and insecticides; diagnosis is confirmed with elevated urine arsenic levels. Mees lines are a characteristic finding
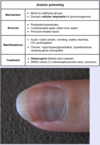
What is the likely diagnosis in an automobile mechanic that presents with constipation, increased forgetfulness, and peripheral neuropathy? Laboratory studies reveal microcytic anemia.
Lead poisoning
triad of GI, neurologic, and hematologic symptoms is classic for lead poisoning; peripheraly blood smear may reveal basophilic stippling, though this finding is not specific for lead poisoning
What is the likely drug intoxication in a patient that presents with slurred speech, lethargy, and difficulty walking? Pupils are 5 mm and respiratory rate is 8/min.
benzodiazepine or alcohol overdose
lack of pupillary constriction and severe respiratory depression distinguishes benzodiazepine overdose from opioid overdose
What is the most common cause of death in patients with TCA overdose?
Cardiac toxicity (e.g. ventricular arrhythmias)

What is the next step in management for a patient that presents after ingesting twenty acetaminophen tablets two hours ago? Physical exam and laboratory studies, including LFTs, are normal.
administer activated charcoal and measure serum acetaminophen levels
if a single dose of > 7.5g of acetaminophen is ingested and it’s been < 4hrs since ingestion, activated charcoal should be administered

What is the next step in management for a patient that presents with drooling and retrosternal/epigastric pain after ingesting sodium hydroxide (lye)? The patient has been decontaminated and is hemodynamically stable with a normal CXR.
Endoscopy
endoscopy is recommended within the first 12-24 hours to assess the severity of damage and guide further therapy

What is the next step in management for an unresponsive patient that presents with respiratory depression and decreased bowel sounds? The patient smells of alcohol. Physical examination reveals 3 mm pupils bilaterally and a respiratory rate of 5/minute.
Naloxone
this patient likely has opioid intoxication (decreased respiratory rate is the most reliable and predictive sign of OI); miosis may be absent!

What is the recommended initial management of frostbite?
Rapid rewarming with warm water
however, rewarming should not be attempted if there is a possibility of refreezing before definitive care can be provided

What is the recommended treatment for anticholinergic poisoning?
physostigmine (cholinesterase inhibitor)
What is the recommended treatment for carbon monoxide poisoning?
100% O2 or hyperbaric O2
What is the recommended treatment for organophosphate or acetylcholinesterase inhibitor poisoning?
atropine +/- pralidoxime
equally important is the removal of any clothes, which may be contaminated with pesticides, and washing of skin to prevent further cutaneous absorption
What is the treatment for arsenic toxicity?
Chelating agents, such as dimercaprol or DMSA

What is the treatment of choice for acute opioid withdrawal?
low-dose methadone + adjunctive medications for symptoms
e.g. loperamide for diarrhea, ibuprofen for myalgias, etc…

What is the treatment of choice for patients with alcohol withdrawal?
Benzodiazepines (e.g. lorazepam)

What medication is administered to patients with suspected TCA toxicity to improve the effects of cardiac toxicity (e.g. hypotension, prolonged QRS interval, arrhythmia)?
Sodium bicarbonate
indicated if QRS > 100 ms or presence of arrhythmia

What medication is administered to treat seizures in patients with suspected TCA toxicity?
Benzodiazepines



