Pulm and Critical Care I Flashcards
A modified Wells score > […] suggests that pulmonary embolism is likely.
A modified Wells score > 4 suggests that pulmonary embolism is likely.

All patients with acute COPD exacerbation should receive inhaled bronchodilators and systemic […].
All patients with acute COPD exacerbation should receive inhaled bronchodilators and systemic corticosteroids.
corticosteroids have been shown to improve lung function and promote a shorter hospital stay; supplemental O2, antibiotics and ventilatory support should be administered when indicated

An endotracheal tube that is advanced too far will preferentially enter into the […] mainstem bronchus (left or right).
An endotracheal tube that is advanced too far will preferentially enter into the right mainstem bronchus (left or right).
causes asymmetric chest expansion and markedly decreased breath sounds on the contralateral side
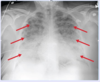
An infant with a fever, runny nose, and cough has the X-ray findings below. What does the arrow on the CXR point to?

Thymus

Antibiotics should be given to patients with COPD exacerbation if they have > 2 of the following: increased […], increased cough, or increased sputum production (cardinal symptoms).
Antibiotics should be given to patients with COPD exacerbation if they have > 2 of the following: increased dyspnea, increased cough, or increased sputum production (cardinal symptoms).
or if they require mechanical ventilation

Antibiotics should be given to patients with COPD exacerbation if they have > 2 of the following: increased dyspnea, increased […], or increased sputum production (cardinal symptoms).
Antibiotics should be given to patients with COPD exacerbation if they have > 2 of the following: increased dyspnea, increased cough, or increased sputum production (cardinal symptoms).
or if they require mechanical ventilation

Are lung adenocarcinomas typically centrally or peripherally located?
Peripherally

Bradycardia, hypoventilation, and decreased shivering are associated with […] hypothermia (severity).
Bradycardia, hypoventilation, and decreased shivering are associated with moderate hypothermia (severity).
seen with temperatures between 82-90 F; the bradycardia seen with hypothermia is often refractory to treatment with atropine/cardiac pacing, but improves with correction of hypothermia

Chronic bronchitis is defined as a chronic productive cough for > […] months in 2 successive years.
Chronic bronchitis is defined as a chronic productive cough for > 3 months in 2 successive years.
cigarette smoking is the leading cause
Chronic bronchitis-predominant COPD is characterized by a […] DLCO.
Chronic bronchitis-predominant COPD is characterized by a normal DLCO.
also has prominent vascular markings on CXR vs. emphysema, which has decreased vascular markings and low DLCO

Coma and cardiovascular collapse are associated with […] hypothermia (severity).
Coma and cardiovascular collapse are associated with severe hypothermia (severity).
seen with temperatures

Consolidation of the lung results in […] breath sounds, […] tactile fremitus, and […] to percussion (e.g. lobar pneumonia).
Consolidation of the lung results in increased breath sounds, increased tactile fremitus, and dullness to percussion (e.g. lobar pneumonia).
fluid is present within the lung in the thoracic cavity and sound travels faster in solid or liquids than air

Does hypoxemia secondary to intrapulmonary shunt correct with supplemental O2?
No
important distinguishing feature of shunting versus other causes of hypoxemia

Emphysema-predominant COPD is characterized by a […] DLCO.
Emphysema-predominant COPD is characterized by a low DLCO.
also has decreased vascular markings on CXR vs. chronic bronchitis, which has increased vascular markings and normal DLCO

Extrinsic causes of restrictive lung disease are characterized by a […] DLCO.
Extrinsic causes of restrictive lung disease are characterized by a normal DLCO.
e.g. myasthenia gravis, ALS

Exudative pleural effusions are characterized by a […] pleural/serum protein ratio.
Exudative pleural effusions are characterized by a > 0.5 (high) pleural/serum protein ratio.

Exudative pleural effusions are characterized by […] pleural/serum LDH ratio.
Exudative pleural effusions are characterized by > 0.6 (high) pleural/serum LDH ratio.
or pleural LDH > 2/3 upper normal limit of serum LDH

Features of a high-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size > […] cm, age > 60, and smoking cessation within the last 5 years (or current smoker).
Features of a high-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size > 2 cm, age > 60, and smoking cessation within the last 5 years (or current smoker).

Features of a high-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size > 2 cm, age > […], and smoking cessation within the last 5 years (or current smoker).
Features of a high-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size > 2 cm, age > 60, and smoking cessation within the last 5 years (or current smoker).

Features of a low-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size […], age < 40, and smoking cessation for > 15 years (or never smoked).
Features of a low-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size 0.8 cm, age < 40, and smoking cessation for > 15 years (or never smoked).

Features of a low-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size 0.8 cm, age […] and smoking cessation for > 15 years (or never smoked).
Features of a low-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size 0.8 cm, age < 40, and smoking cessation for > 15 years (or never smoked).

Features of an intermediate-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size […] - […] cm, age 40 - 60, and smoking cessation within the last 5 - 15 years (or current smoker).
Features of an intermediate-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size 0.8 - 2 cm, age 40 - 60, and smoking cessation within the last 5 - 15 years (or current smoker).

Features of an intermediate-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size 0.8 - 2 cm, age […] - […], and smoking cessation within the last 5 - 15 years (or current smoker).
Features of an intermediate-risk solitary pulmonary nodule include size 0.8 - 2 cm, age 40 - 60, and smoking cessation within the last 5 - 15 years (or current smoker).

Goodpasture’s disease is characterized by antibodies against glomerular and alveolar […].
Goodpasture’s disease is characterized by antibodies against glomerular and alveolar basement membranes.
specifically against the alpha-3 chain of type IV collagen