Cardiovascular I Flashcards
2nd-degree, Mobitz type I heart block has a […] risk to develop into complete heart block.
2nd-degree, Mobitz type I heart block has a low risk to develop into complete heart block.
thus treatment typically is observation

2nd-degree, Mobitz type II heart block has a […] risk to develop into complete heart block.
2nd-degree, Mobitz type II heart block has a high risk to develop into complete heart block.
thus treatment typically consists of a pacemaker

Ascending aortic aneurysms are most often due to […] (due to aging) and connective tissue disorders.
Ascending aortic aneurysms are most often due to cystic medial necrosis (due to aging) and connective tissue disorders.
Ascending aortic aneurysms are most often due to cystic medial necrosis (due to aging) and […].
Ascending aortic aneurysms are most often due to cystic medial necrosis (due to aging) and connective tissue disorders.
Atrial flutter is most commonly caused by a re-entrant circuit around the […].
Atrial flutter is most commonly caused by a re-entrant circuit around the tricuspid annulus.
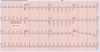
Atypical symptoms associated with MI are more common in […], […], and […].
Atypical symptoms associated with MI are more common in women, the elderly, and diabetics.
e.g. abdominal pain, nausea/vomiting

Beta blockers are a standard therapy in myocardial infarction but should be avoided in patients with […] or bradycardia.
Beta blockers are a standard therapy in myocardial infarction but should be avoided in patients with decompensated CHF or bradycardia.

Carotid endarterectomy is indicated in sympomatic men and women with […] - […]% stenosis.
Carotid endarterectomy is indicated in sympomatic men and women with 70 - 99% stenosis.
there is some evidence that asymptomatic patients with 80-99% stenosis may benefit from CEA as well

Cold-water immersion relieves symptoms of paraoxysmal supraventricular tachycardia by decreasing […].
Cold-water immersion relieves symptoms of paraoxysmal supraventricular tachycardia by decreasing AV node conductivity.
PSVT is most commonly due to an AV node re-entry circuit; vagal maneuvers increase parasympathetic tone, slowing AV node conductivity and terminating the AV nodal re-entry tachycardia
Cor pulmonale is impaired function of the right ventricle due to […].
Cor pulmonale is impaired function of the right ventricle due to pulmonary hypertension (pulmonary systolic pressure > 25 mmHg).
usually occurs due to chronic lung disease

Descending aortic aneurysms are usually due to underlying […].
Descending aortic aneurysms are usually due to underlying atherosclerosis.
Diagnosis of amyloidosis is confirmed using […].
Diagnosis of amyloidosis is confirmed using tissue biopsy. (e.g. abdominal fat pad)
Dobutamine improves symptoms of decompensated heart failure by increasing […].
Dobutamine improves symptoms of decompensated heart failure by increasing myocardial contractility.
leads to improved ejection fraction and reduced LV end-systolic volume
Features of severe aortic stenosis include a […]-peaking systolic murmur and a soft second heart sound.
Features of severe aortic stenosis include a late-peaking systolic murmur and a soft second heart sound.
also may have pulsus parvus et tardus; early-peaking systolic murmur is suggestive of mild to moderate AS
Features of severe aortic stenosis include a late-peaking systolic murmur and a […] second heart sound.
Features of severe aortic stenosis include a late-peaking systolic murmur and a soft second heart sound.
also may have pulsus parvus et tardus; early-peaking systolic murmur is suggestive of mild to moderate AS
First-line treatment options for beta blocker overdose include IV fluids and […].
First-line treatment options for beta blocker overdose include IV fluids and atropine.
IV fluid and atropine often do not completely reverse the cardiotoxic effects of beta blocker overdose; in such cases additional medications (e.g. glucagon) may be given as well
Flushing and pruritus secondary to niacin therapy is caused by […]-induced peripheral vasodilation.
Flushing and pruritus secondary to niacin therapy is caused by prostaglandin-induced peripheral vasodilation.
symptoms may be reduced with low-dose aspirin
How do serum levels of digoxin change in patients who begin taking amiodarone?
Increase
may lead to acute digoxin toxicity (typically GI symptoms); other anti-arrhythmics that increase digoxin levels include verapamil, quinidine, and propafenone

How do the following parameters change in an acute MI patient with hypotension, bibasilar crackles, and a systolic murmur (cardiac apex)?
Left atrial size: […]
LV end-diastolic pressure: […]
Left atrial size: No change
LV end-diastolic pressure: Increased
the patient has acute mitral regurgitation, which causes elevated LA and LV filling pressures but does not acutely result in changes in size
How do the following parameters change in LV systolic dysfunction (CHF)?
Cardiac output: […]
Systemic vascular resistance: […]
Left ventricular EDV: […]
Cardiac output: Decreased
Systemic vascular resistance: Increased
Left ventricular EDV: Increased

How does baroreceptor sensitivity change with aging?
Decreased sensitivity
predisposes to orthostatic hypotension; other predisposing factors include reduced sensitivity of the myocardium to sympathetic stimulation and decreased norepinephrine content of sympathetic nerve endings
In addition to history and physical, patients initially diagnosed with hypertension should have the following basic testing:
- […]
- Chemistry panel
- Lipid profile
- Baseline ECG
In addition to history and physical, patients initially diagnosed with hypertension should have the following basic testing:
- Urinalysis (for occult hematuria and urine protein/creatinine ratio)
- Chemistry panel
- Lipid profile
- Baseline ECG
In addition to history and physical, patients initially diagnosed with hypertension should have the following basic testing:
- Urinalysis (for occult hematuria and urine protein/creatinine ratio)
- […]
- Lipid profile
- Baseline ECG
In addition to history and physical, patients initially diagnosed with hypertension should have the following basic testing:
- Urinalysis (for occult hematuria and urine protein/creatinine ratio)
- Chemistry panel
- Lipid profile
- Baseline ECG
In addition to history and physical, patients initially diagnosed with hypertension should have the following basic testing:
- Urinalysis (for occult hematuria and urine protein/creatinine ratio)
- Chemistry panel
- […]
- Baseline ECG
In addition to history and physical, patients initially diagnosed with hypertension should have the following basic testing:
- Urinalysis (for occult hematuria and urine protein/creatinine ratio)
- Chemistry panel
- Lipid profile
- Baseline ECG
In addition to history and physical, patients initially diagnosed with hypertension should have the following basic testing:
- Urinalysis (for occult hematuria and urine protein/creatinine ratio)
- Chemistry panel
- Lipid profile
- […]
In addition to history and physical, patients initially diagnosed with hypertension should have the following basic testing:
- Urinalysis (for occult hematuria and urine protein/creatinine ratio)
- Chemistry panel
- Lipid profile
- Baseline ECG
In addition to statin therapy, what is the recommended management for a patient with known cardiovascular disease and a triglyceride level of 465 mg/dL (high)?
Lifestyle modifications (e.g. weight loss, exercise, decreased alcohol intake)
fibrates are not indicated for triglyceride levels < 1,000 mg/dL

Is a unilateral pleural effusion secondary to congestive heart failure more likely to be right-sided or left-sided?
Right-sided (27%)
the most common presentation, however, is bilateral pleural effusion (61%)
Management of acute decompensated heart failure includes supplemental O2, […], and possibly a vasodilator/vasopressor.
Management of acute decompensated heart failure includes supplemental O2, IV loop diuretics, and possibly a vasodilator/vasopressor.

Medications that have been shown to improve long-term survival in patients with LV systolic dysfunction include:
- […]
- ACE inhibitors
- ARBs
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
- Hydralazine + nitrates in African American patients
Medications that have been shown to improve long-term survival in patients with LV systolic dysfunction include:
- Beta blockers
- ACE inhibitors
- ARBs
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
- Hydralazine + nitrates in African American patients
helpful trick: drugs that improve survival usually will have some effect on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system!
- Renin - beta blockers
- Angiotensin - ACE inhibitors/ARBs
- Aldosterone - mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (e.g. spironolactone, eplrenon)
Medications that have been shown to improve long-term survival in patients with LV systolic dysfunction include:
- Beta blockers
- […]
- […]
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
- Hydralazine + nitrates in African American patients
- Beta blockers
- ACE inhibitors
- ARBs
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
- Hydralazine + nitrates in African American patients
helpful trick: drugs that improve survival usually will have some effect on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system!
- Renin - beta blockers
- Angiotensin - ACE inhibitors/ARBs
- Aldosterone - mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (e.g. spironolactone, eplrenon)
Medications that have been shown to improve long-term survival in patients with LV systolic dysfunction include:
- Beta blockers
- ACE inhibitors
- ARBs
- […]
- Hydralazine + nitrates in African American patients
Medications that have been shown to improve long-term survival in patients with LV systolic dysfunction include:
- Beta blockers
- ACE inhibitors
- ARBs
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
- Hydralazine + nitrates in African American patients
helpful trick: drugs that improve survival usually will have some effect on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system!
- Renin - beta blockers
- Angiotensin - ACE inhibitors/ARBs
- Aldosterone - mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (e.g. spironolactone, eplrenon)
Patients with an estimated 10-year ASCVD risk > […]% should be started on a moderate- to high-intensity statin.
Patients with an estimated 10-year ASCVD risk > 7.5% should be started on a moderate- to high-intensity statin.

Patients with an LDL > […] mg/dL are recommended to begin high-intensity statin therapy.
Patients with an LDL > 190 mg/dL are recommended to begin high-intensity statin therapy.

Patients with an LDL > 190 mg/dL are recommended to begin […]-intensity statin therapy.
Patients with an LDL > 190 mg/dL are recommended to begin high-intensity statin therapy.

Patients with beta blocker overdose that have refractory hypotension (e.g. to atropine, IV fluids) should be started on IV […].
Patients with beta blocker overdose that have refractory hypotension (e.g. to atropine, IV fluids) should be started on IV glucagon.
Patients with CHF often have preferential vasoconstriction of […] renal arterioles.
Patients with CHF often have preferential vasoconstriction of efferent renal arterioles.
due to activation of the RAAS and production of angiotensin II; causes increased intraglomerular pressure to maintain adequate GFR
Patients with recurrent vasovagal syncope may try […] maneuvers during the prodromal phase to abort or delay the syncopal episode.
Patients with recurrent vasovagal syncope may try physical counterpressure maneuvers during the prodromal phase to abort or delay the syncopal episode.
e.g. leg crossing with tensing of muscles, handgrip and tensing of arm muscles with clenched fists (improves venous return and cardiac output)

Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is recommended for patients with acute STEMI within […] hours of symptom onset and within […] minutes from first medical contact to device time at a PCI-capable facility.
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is recommended for patients with acute STEMI within 12 hours of symptom onset and within 90 minutes from first medical contact to device time at a PCI-capable facility.
or 120 minutes from first medical contact to device time at a non-PCI-capable facility (to allow time for transport)

Pretest probability of coronary artery disease is high in patients with typical angina > age […] (men) or […] (women).
Pretest probability of coronary artery disease is high in patients with typical angina > age 40 (men) or 60 (women).
these patients may be evaluated with coronary angiography to confirm the diagnosis

Pretest probability of coronary artery disease is intermediate in men with […] (all ages).
Pretest probability of coronary artery disease is intermediate in men with atypical angina (all ages).
these patients require further evaluation with a stress test

Pretest probability of coronary artery disease is intermediate in women with atypical angina > age […] or typical angina age 30 - 50.
Pretest probability of coronary artery disease is intermediate in women with atypical angina > age 50 or typical angina age 30 - 50.
these patients require further evaluation with a stress test

Pulmonic stenosis is associated with […] splitting of the S2 heart sound, especially during inspiration.
Pulmonic stenosis is associated with widened splitting of the S2 heart sound, especially during inspiration.
versus ASD, which is associated with a wide fixed split (doesn’t change during respiration)

The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:
C: […]
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:

C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:
C: Congestive heart failure
H: […]
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:
C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)

The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:
C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: […]
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:

C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:
C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: […]
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:

C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:
C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: […]
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:

C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:
C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: […]
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:

C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:
C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: […]
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:

C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:
C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: […]
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful for assessing thromboembolic risk in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation:

C: Congestive heart failure
H: Hypertension
A2: Age > 75* (2 points)
D: Diabetes mellitus
S2: Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism* (2 points)
V: Vascular disease (prior MI, PAD, or aortic plaque)
A: Age 65-74
Sc: Sex category (female)


