Infectious Disease I Flashcards
A PPD is considered positive in HIV patients if the induration size is > […] mm.
A PPD is considered positive in HIV patients if the induration size is > 5 mm.
may be false-negative in patients with CD4+ counts < 200/mm3

Antibiotic prophylaxis in HIV patients with CD4+ count < 50/mm3 should include […] (MAC) and […] (PCP, toxoplasma).
Antibiotic prophylaxis in HIV patients with CD4+ count < 50/mm3 should include azithromycin (MAC) and TMP-SMX (PCP, toxoplasma).

How do humans typically contract an Echinococcus granulosus infection?
Consumption of food or water contaminated with dog feces
sheep are the intermediate host

How is cutaneous larva migrans typically acquired (mode of transmission)?
Walking barefoot on contaminated sand or soil

How is the diagnosis of mucormycosis established?
sinus endoscopy with biopsy & culture

In addition to empiric antibiotics, what other medication should be administered to patients with suspected bacterial meningitis?
Corticosteroids
helps prevent the neurological deficits associated with pneumococcal meningitis (e.g. deafness, focal deficits); should be discontinued if pneumococcal meningitis is ruled out
In areas with high rates of chloroquine-resistant malaria, chemoprophylaxis typically includes […], […], or […].
In areas with high rates of chloroquine-resistant malaria, chemoprophylaxis typically includes atovaquone-proguanil, doxycycline, or mefloquine
e.g. Africa, Asia (including India), and Oceania

In healthy adults, acute hepatitis B infection is self-limited in > […]% of cases.
In healthy adults, acute hepatitis B infection is self-limited in > 90-95% of cases.
In the United States, a PPD is considered negative in healthy patients with low likelihood of TB if the induration size is […].
In the United States, a PPD is considered negative in healthy patients with low likelihood of TB if the induration size is 15 mm.
the cutoff for intermediate-risk patients (e.g. healthcare workers, recent immigrants) is < 10 mm

In the United States, a PPD is considered positive in those with high risk of TB if the induration size is > […] mm (e.g. immunosuppressed patients, recent contacts of known TB case).
In the United States, a PPD is considered positive in those with high risk of TB if the induration size is > 5 mm (e.g. immunosuppressed patients, recent contacts of known TB case).
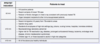
In the United States, a PPD is considered positive in those with intermediate risk of TB if the induration size is > […] mm (e.g. healthcare workers, IVDA, recent immigrants).
In the United States, a PPD is considered positive in those with intermediate risk of TB if the induration size is > 10 mm (e.g. healthcare workers, IVDA, recent immigrants).

Indications for corticosteroid use in Pneumocystis pneumonia treatment (in addition to TMP-SMX) include PaO2 […] mmHg.
Indications for corticosteroid use in Pneumocystis pneumonia treatment (in addition to TMP-SMX) include PaO2 < 70mmHg or A-a gradient > 35 mmHg.
also indicated if SaO2 < 92%
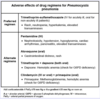
Infection with Vibrio vulnificus causes severe infection in patients who have […] disease (organ).
Infection with Vibrio vulnificus causes severe infection in patients who have liver disease (organ).
e.g. cirrhosis, hepatitis, hemochromatosis

One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is septic arterial or pulmonary […].
One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is septic arterial or pulmonary emboli.
mnemonic: FROM JANE; may cause various nodes/lesions associated with bacterial endocarditis
One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is […], which occurs as a result of increased release of hepcidin.
One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is anemia of chronic disease, which occurs as a result of increased release of hepcidin.
mnemonic: FROM JANE; ACD is a microcytic anemia with high ferritin and low serum iron
One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is […], which are small, nontender, erythematous lesions on the palm or sole.
One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is Janeway lesions, which are small, nontender, erythematous lesions on the palm or sole.
mnemonic: FROM JANE

One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is […], which occurs as blood flows over vegetations on the heart valve.
One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is murmur, which occurs as blood flows over vegetations on the heart valve.
mnemonic: FROM JANE
One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is […], which are tender, raised lesions on the finger or toe pads.
One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is Osler nodes, which are tender, raised lesions on the finger or toe pads.

One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is […], which are round, white spots on the retina surrounded by hemorrhage.
One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is Roth spots, which are round, white spots on the retina surrounded by hemorrhage.
mnemonic: FROM JANE

One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is […] in the nail bed.
One symptom associated with bacterial endocarditis is splinter hemorrhages in the nail bed.
mnemonic: FROM JANE; occurs due to embolization of septic vegetations
Osteomyelitis in diabetic patients is typically preceded by a long-standing foot ulcer that spreads […] to bone, causing a […]-microbial infection.
Osteomyelitis in diabetic patients is typically preceded by a long-standing foot ulcer that spreads contiguously to bone, causing a poly-microbial infection.
Patients who received blood transfusions before […] should be screened for hepatitis C.
Patients who received blood transfusions before 1992 should be screened for hepatitis C.
do you need to memorize the year? probably not… suspend this card if you want 3
Patients with HIV who present with an AIDS defining illness secondary to lack of anti-retroviral therapy should be initiated on HAART […] after treatment of the infection.
Patients with HIV who present with an AIDS defining illness secondary to lack of anti-retroviral therapy should be initiated on HAART two weeks after treatment of the infection.
to prevent immune reconstitution syndrome
Patients with suspected aspiration pneumonia should be treated with antibiotics that include […] coverage.
Patients with suspected aspiration pneumonia should be treated with antibiotics that include anaerobic coverage.
e.g. clindamycin, metronidazole + amoxicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate
Severe Vibrio vulnificus infection is more common in those with liver disease, especially […].
Severe Vibrio vulnificus infection is more common in those with liver disease, especially hereditary hemochromatosis.
iron acts as a growth catalyst for the organism

What anti-malarial drug is used to prevent dormant hepatic hypnozoites in patients infected with Plasmodium vivax?
Primaquine

What antibody is typically positive during the window phase of hepatitis B infection?
IgM anti-HBc

What are the indications for sequential PCV13 vaccine, followed by PPSV23 vaccine 6-12 months later, in adults?
age > 65 or very high risk patients < 65 (e.g. asplenia, cochlear implants, immunocompromised, CKD)
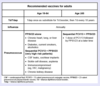
What are the indications for the PPSV23 vaccine, alone, in adults?
age < 65 with other chronic medical conditions (e.g. heart/lung/liver disease, diabetes, smoking)
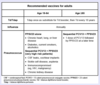
What are the recommendations regarding live attenuated virus vaccination (e.g. MMR, zoster, varicella) in HIV patients?
Vaccinate if CD4+ counts > 200/mm3 and titers are low
What are the recommended empiric antibiotics for immunocompromised patients with suspected bacterial meningitis?
vancomycin + ampicillin + cefepime
provides coverage for major organisms of bacterial meningitis and pseudomonas (cefepime), Listeria (ampicillin), and cephalosporin-resistant pneumococci (vancomycin); ampicillin is also added for patients > 50 years of age

What are the two most common causes of secondary bacterial pneumonia?
Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus
typically presents with worsening fever and pulmonary symptoms after initial symptomatic improvement
What autoimmune antibody may be elevated in patients with infective endocarditis?
Rheumatoid factor
rheumatoid factor is a non-specific finding; don’t let it throw you off the diagnosis if symptoms otherwise point to infective endocarditis!

What bacteria is the most common cause of community-acquired bacterial meningitis?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
treatment typically involves vancomycin and a third-generation cephalosporin +/- ampicillin

What combined antiviral therapy is effective against most strains of hepatitis C (e.g. genotypes 1-6)?
Sofosbuvir-velpatasvir
HCV genotyping should be done prior to initiation of antiviral therapy
What enzyme is often elevated in patients with Pneumocystis pneumonia?
LDH
other indications of PCP pneumonia include hypoxia (PaO2 < 75 mmHg) and diffuse, bilateral infiltrates on CXR

What is the diagnostic test of choice for patients with suspected leprosy?
Skin biopsy from the edge of a lesion

What is the diagnostic test of choice for patients with suspected Pneumocystis pneumonia without an adequate induced sputum sample?
Bronchoalveolar lavage

What is the empiric treatment for ehrlichiosis?
Doxycycline

What is the initial treatment of choice for most patients with early localized Lyme disease?
Oral doxycycline
amoxicillin or cefuroxime may be used in children < 8 years old and pregnant women, where doxycycline is contraindicated
What is the like causative organism in an HIV patient with a CD4+ count of 85/mm3 that presents with three weeks of copious, watery diarrhea and low-grade fever?
Cryptosporidium

What is the likely causative microorganism in a patient with infective endocarditis after having a tooth extraction one month ago?
Viridans group streptococci

What is the likely causative microorganism in a renal transplant patient that develops fever, progressive dyspnea on exertion, abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and elevated LFTs?
Cytomegalovirus
solid organ transplant patients that develop systemic illness involving multiple organ systems (e.g. pneumonitis, gastroenteritis, hepatitis) likely have CMV; versus PCP, which presents primarily with pulmonary symptoms
What is the likely causative microorganism in an alcoholic sailor that develops high-grade fever hours after cutting his foot while sailing in the ocean? The cut is surrounded by erythema and dark-colored bullae with streaking erythema extending proximally up the limb.
Vibrio vulnificus
V. vulnificus is found in marine environments and causes severe disease (e.g. rapidly progressive septicemia, necrotizing fasciitis) in patients with liver disease

What is the likely causative organism in a male that presents with dysuria, urinary frequency, and mucopurulent discharge? Gram stain and urine culture are negative.
Chlamydia trachomatis
gram stain shows gram-negative cocci in 95% of cases of gonoccocal arthritis

What is the likely causative organism in a patient that develops osteomyelitis after stepping on a rusty nail? The nail pierced the patient’s shoes and pierced the heel.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Staph aureus and Pseudomonas are responsible for most deep infections following puncture wounds; the sole of a shoe (warm, moist) is a hospitable environment for Pseudomonas
What is the likely causative organism in a patient that presents with fever and mild pharyngeal erythema without lymphadenopathy? A heterophile antibody test is negative.

Cytomegalovirus
CMV can cause a mononucleosis-like illness (resembling EBV) but with mild/absent pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, and splenomegaly and a negative heterophile antibody test
What is the likely causative organism in a patient who develops infective endocarditis after having a recent cystoscopy for persistent dysuria?
Enterococci (e.g. Enterococcus faecalis)

What is the likely causative organism in a patient with poorly controlled HIV that presents with large, reddish pedunculated skin lesions that bleed easily? CT scan of the abdomen reveals hypodense liver lesions that enhance with IV contrast.
Bartonella quintana
the patient likely has bacillary angiomatosis (pedunculated/exophytic lesions and liver involvement are more typical of BA than Kaposi sarcoma); treatment typically includes doxycycline or erythromycin

What is the likely causative organism in an HIV patient with a CD4+ count of 30/mm3 that presents with one month of fever, intermittent bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss?
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
diagnosis is confirmed with colonoscopy + biopsy; HIV patients with active CMV disease require ocular exam to rule out concurrent retinitis

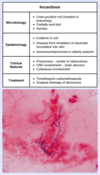
What is the likely causative organism in an immunocompromised patient with multiple lung cavitary lesions and brain abscesses identified on imaging? Sputum cultures grow partially acid-fast, gram-positive, branching rods.
Nocardia
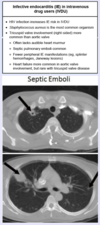
What is the likely causative organism in an IV drug user that presents with three days of fever, pleuritic chest pain, and shortness of breath? Chest imaging reveals multiple nodular lesions with small cavities.
Staphylococcus aureus
likely due to septic emboli from tricuspid endocarditis
What is the likely chief complaint in a patient diagnosed with Cryptosporidium parvum infection?
Prolonged, profuse, watery diarrhea (typically 10 - 14 days)
Traveler’s diarrhea that is prolonged, profuse, and watery is often due to a parasitic pathogen; patients may also complain of nausea, abdominal pain, low-grade fever, or malaise
What is the likely diagnosis and causative organism in a patient that presents with a 1-day history of fever and a warm, tender, erythematous rash with raised, well-demarcated borders?
Erysipelas; Streptococcus pyogenes (group A strep)

What is the likely diagnosis in a college student with a recent viral URI that presents with high-grade fever, productive cough with hemoptysis, and leukopenia? CXR reveals bilateral alveolar infiltrates and multiple cavitations.
Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) infection
CA-MRSA has a predilection for young patients with recent influenza
What is the likely diagnosis in a hemodynamically unstable patient that presents with fever, vomiting, and a diffuse, confluent maculopapular rash on the trunk and extremities? The patient recently had anterior packing in the emergency department for a nose bleed.
Toxic shock syndrome
secondary to Staphylococcus aureus, likely due to unremoved nasal packing

What is the likely diagnosis in a HIV patient from Missouri with a CD4+ count of 50/mm3 that presents with cough/dyspnea, mouth ulcers, and diffuse lymphadenopathy? Laboratory exam reveals pancytopenia and elevated LFTs.
Disseminated histoplasmosis
seen in patients with CD4+ counts < 100/mm3; characterized by prominent pulmonary, mucocutaneous, and reticuloendothelial manifestations

What is the likely diagnosis in a landscaper with a finger ulceration, draining an odorless discharge, that spread to include similar nodules along the forearm? There is no lymphadenopathy on physical exam.
Sporotrichosis
dimorphic fungus typically found in decaying plant matter/soil; no lymphadenopathy helps rule out other diagnoses (e.g. cat scratch fever)

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that developed sudden-onset abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting after returning from a hike and eating leftover Chinese food?
Bacillus cereus food poisoning
characterized by rapid symptom onset (1 - 6 hours) due to preformed enterotoxin; vomiting is the primary manifestation

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that emigrated from Southeast Asia and presents with a well-circumscribed, hypopigmented patch on the arm with no sensation to pinprick? The ulnar nerve on ipsilateral arm is thickened and tender.
Leprosy
leprosy typically affects the skin and peripheral nerves

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that presents in the winter with abrupt onset high-grade fever, headache, and severe myalgias? No lymphadenopathy or abnormal lung sounds are appreciated on physical exam.
Influenza

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that presents with an intensely pruritic lesion on the foot (picture below)?

Cutaneous larva migrans
typically begins as a pruritic, papular lesion at the entry site, followed by intensely pruritic, migrating, serpiginous reddish-brown tracks; ivermectin is typically given to speed resolution and clearance

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that presents with fever, sore throat, drooling, and muffled voice with pooled secretions visible in the oropharynx? There is no visible swelling of the floor of the mouth.
Epiglottitis
most commonly due to H. influenzae type B, especially in unvaccinated individuals

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that presents with fever, sore throat, drooling, and muffled voice? The bilateral submandibular area is tender and indurated with palpable crepitus.
Ludwig angina
rapidly progressive cellulitis of the submandibular space, usually due to dental infections; treatment involves IV antibiotics and removal of the inciting tooth
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that presents with flu-like symptoms without a rash after being bitten by a tick two weeks ago? Laboratory exam reveals leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and signs of hemolytic anemia.
Babesiosis
Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever are less likely given the absence of rash; Erlichiosis is less likely given the leukocytosis and signs of intravascular hemolysis



