Renal, Urinary Systems and Electrolytes II Flashcards
What acid-base disorders are associated with aspirin (salicylate) toxicity?
[…] (early) and […] (late)
What acid-base disorders are associated with aspirin (salicylate) toxicity?
respiratory alkalosis (early) and metabolic acidosis (late)
respiratory alkalosis due to increased respiratory drive; metabolic acidosis due to increased production/decreased elimination of organic acids
What acid-base disturbance is associated with primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison disease)?
Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis
decreased aldosterone results in retention of H+
What antibiotic is associated with hyperkalemia and elevated serum creatinine?
Trimethoprim
due to blockade of epithelial Na+ channels (ENaC) in the collecting tubule; elevated creatinine is an artificial increase due to inhibition of renal creatinine secretion (GFR remains the same)
What are the most common renal pathologies (2) seen with analgesic nephropathy?
papillary necrosis and chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis
may have sterile pyuria, WBC casts, microscopic hematuria, and/or mild proteinuria on urinalysis

What BUN:creatinine ratio is suggestive of prerenal acute kidney injury?
> 20:1 BUN:creatinine

What class of anti-depressants is commonly associated with SIADH?
SSRIs
especially in elderly patients

What class of antibiotics used to treat severe gram-negative infections is potentially nephrotoxic?
Aminoglycosides
What class of drugs are useful for patients with urge incontinence?
Anti-muscarinics (e.g. oxybutynin)
first-line treatments include bladder training and pelvic floor muscle exercises; medical therapy is reserved for those who don’t respond

What classes of medications (2) are used for pain management in patients with kidney stones?
narcotics and NSAIDs (preferred with normal renal function)
e.g. morphine (narcotic) and ketolorac (NSAID)
What complication may result from correcting hypernatremia too quickly?
Cerebral edema
“high to low, your brain will blow”
What complication may result from correcting hyponatremia too quickly?
Osmotic demyelination syndrome (central pontine myelinolysis)
“low to high, your pons will die”
What does a positive leukocyte esterase on urine dipstick indicate?
Significant pyuria
What does positive nitrites on urine dipstick indicate?
Gram negative bacteria
What drug class is useful for the management of recurrent nephrolithiasis secondary to idiopathic hypercalciuria?
Thiazide diuretics
other preventive measures include increased fluid intake and a low Na+/protein diet

What drug should be discontinued in an acutely ill patient with sepsis and acute renal failure taking low-dose aspirin, atorvastatin, metformin, and sitagliptin?
Metformin
nephrotoxins, such as NSAIDs and metformin, should NOT be given to patients with acute renal failure or sepsis; low-dose aspirin has not been shown to precipitate or worsen renal failure
What effect does intracellular magnesium have on renal K+ secretion?
Decreased K+ secretion
via inhibition of renal outer medullary potassium (ROMK) channels
What formula is used to calculate the anion gap in patients with metabolic acidosis?
AG = (Na+) - (HCO3- + Cl-)
should be calculated in all patients with metabolic acidosis to narrow the differential
What formula is used to calculate the osmolal gap?
measured serum osmolality - calculated serum osmolality

What formula is used to calculate the serum osmolality?
the normal osmolal gap (measured - calculated) is < 10

What hematologic laboratory values are consistent with abnormal hemostasis due to chronic renal failure?
PT: […]
PTT: […]
Platelet count: […]
Bleeding time: […]
What hematologic laboratory values are consistent with abnormal hemostasis due to chronic renal failure?
PT: Normal
PTT: Normal
Platelet count: Normal
Bleeding time: Prolonged
underlying cause is platelet dysfunction
What imaging modalities (2) are preferred for detecting kidney stones?
CT scan of the abdomen without contrast (preferred) or ultrasound
high sensitivity and specificity; also can detect radiolucent stones, which are missed on abdominal X-ray
What imaging modality is preferred for diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma?
CT scan of the abdomen

What is recommended treatment for an acute rejection of a renal transplant?
IV steroids
What is the best test to screen for the initial stages of diabetic nephropathy?
Urine test for microalbumin:creatinine ratio
either spot or timed urine collection; dipsticks only detect excess urinary protein when > 300mg/24hr (macroalbuminuria) and thus are not useful for screening
What is the current recommended screening regimen for bladder cancer?
Not recommended, even in patients with significant smoking and family histories
What is the earliest renal abnormality seen in diabetic nephropathy?
Glomerular hyperfiltration
hyperfiltration is also the major pathophysiologic mechanism of glomerular injury; GBM thickening is the first change that can be quantitated

What is the immediate treatment for severe hypercalcemia (> 14mg/dL or symptomatic)?
saline hydration + calcitonin
hypercalcemia may induce nephrogenic diabetes insipidus leading to polyuria and fluid loss; other symptoms include weakness, GI distress, and neuropsychiatric symptoms

What is the initial step in management for a post-operative patient with acute renal failure and oliguria (< 250 mL urine in 12 hours)?
Bedside bladder scan to assess for urinary retention

What is the initial therapy for patients with hypertension and renal artery stenosis?
ACE inhibitors or ARBs
an acceptable rise in serum creatinine is < 30%; renal artery stenting or surgical revascularization is reserved for patients who fail to achieve adequate BP control with medical therapy
What is the initial treatment for acute hyponatremic encephalopathy (e.g. headache, nausea/vomiting, AMS)?
Hypertonic (3%) saline
may occur as a complication of hypotonic fluid administration (iatrogenic hyponatremia)

What is the initial treatment for prerenal acute kidney injury?
IV normal saline
need to restore renal perfusion and prevent development of acute tubular necrosis

What is the likely cause of acute kidney injury in patients receiving IV acyclovir?
Renal tubular obstruction (crystal-induced AKI)
most patients develop AKI within 24 - 48 hours after drug exposure

What is the likely cause of acute renal failure in a patient with high anion and osmolal gap metabolic acidosis and calcium oxalate crystals on urinalysis?
Ethylene glycol poisoning
calcium oxalate crystals are described as envelope-shaped

What is the likely cause of anion gap metabolic acidosis in a patient with a recent generalized tonic-clonic seizure?
Post-ictal lactic acidosis
transient and typically resolves without treatment within 90 minutes following resolution of seizure activity
What is the likely cause of metabolic alkalosis in a young woman with low urine Cl-?
Self-induced vomiting
other etiologies include nasogastric suctioning and prior diuretic use

What is the likely diagnosis in a cirrhotic patient with decreasing GFR, normal urinalysis, lack of improvement with IV fluids, and no other renal dysfunction?
Hepatorenal syndrome
common inciting factors include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and GI bleeding

What is the likely diagnosis in a euvolemic patient with high serum osmolality and low urine osmolality?
Diabetes insipidus (central or nephrogenic)
common cause of euvolemic hypernatremia
What is the likely diagnosis in a euvolemic patient with low serum osmolality (< 275 mOsm/kg) and normal/high urine osmolality (> 100 mOsm/kg)?
SIADH
also typically have elevated urine sodium concentration (> 40 mEq/L)

What is the likely diagnosis in a female with bladder pain that is relieved with voiding, as well as dyspareunia, urinary frequency/urgency, and normal urinalysis?
Interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome)
treatment is palliative and includes trigger avoidance, amitriptyline, and analgesics

What is the likely diagnosis in a hepatitis C patient with palpable purpura, hematuria, proteinuria, and low serum complement?
Mixed cryoglobulinemia
other symptoms include arthralgias, hepatosplenomegaly, peripheral neuropathy, and non-specific systemic symptoms
What is the likely diagnosis in a middle-aged patient with chronic renal failure, a palpable right flank mass, and an enlarged liver?
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
the right kidney, which is lower and easier to palpate than the left; other symptoms of ADPKD include intermittent flank pain, hematuria, UTIs, and nephrolithiasis
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient on RIPE therapy for tuberculosis who presents with painless “red” urine?
Drug reaction
rifampin may result in red to orange discoloration of bodily fluids (e.g. urine, saliva, sweat, tears)
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient started on nitroprusside who presents with flushing, confusion, and metabolic acidosis?
Cyanide toxicity
risk factors for cyanide toxicity due to nitroprusside include prolonged infusion (> 24 hours) and high rates (5-10 μg/kg/min), as well as chronic kidney disease

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient who develops a spike in creatinine a day after having a CT with IV contrast?
Contrast-induced nephropathy
transient increase that normalizes within 5-7 days; higher risk in patients with elevated baseline creatinine and diabetes
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient who overdosed on cocaine and presents with elevated K+ and creatine phosphokinase (CPK)?
Rhabdomyolysis
another key clinical feature is a positive urine dipstick for blood, but no RBCs seen on microscopy (due to myoglobin in the urine)
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient who presents with periorbital swelling and hematuria three weeks after a skin infection?
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
urinalysis may show hematuria with RBC casts and mild proteinuria; additionally, C3 complement levels are low

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with a recent infection who presents with fever and rash with WBC casts and eosinophiluria on urinalysis?
Drug-induced interstitial nephritis
the patient’s infection is likely being treated with an antibiotic that precipitated the nephritis; treatment is to discontinue the offending agent

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with a recent seizure who has a large amount of blood on urinalysis with few RBCs on microscopy?
Myoglobinuria (secondary to rhabdomyolysis)
urinalysis cannot detect the difference between hemoglobin and myoglobin but microscopic exam for RBCs can add clarity
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with a renal transplant for 3 days who presents with oliguria, elevated creatinine/BUN, lymphocytic infiltration on biopsy, and normal serum cyclosporine levels?
Acute transplant rejection
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with a unilateral varicocele that fails to empty when the patient is recumbent, as well as hematuria, fever, and thrombocytosis?
Renal cell carcinoma
unilateral varicoceles that fail to empty when a patient is recumbent should raise suspicion for an underlying mass that obstructs venous flow

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with an elevated serum Ca2+ and low urine Ca2+/Cr clearance ratio (< 0.01)?
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia
due to abnormal calcium-sensing receptors (CaSR); differentiated from primary hyperparathyroidism by low urine Ca2+ excretion (< 0.01)

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with an elevated serum PTH/Ca2+ and normal urine Ca2+/Cr clearance ratio (> 0.02)?
[…]
Primary hyperparathyroidism
differentiated from familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia by increased urine Ca2+ excretion (> 0.02)
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with anasarca, pulmonary edema, hematuria, and proteinuria (1+)?
Acute nephritic syndrome
the presence of hematuria and pulmonary edema helps distinguish nephritic syndrome from other causes of edema (e.g. hypoalbuminemia, cirrhosis, heart failure)
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with colicky flank pain that radiates to the groin?
Nephrolithiasis
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with cor pulmonale treated with loop diuretics that develops elevated creatinine and BUN?
Prerenal acute kidney injury
suggested by BUN:creatinine ratio > 20

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with elevated BUN and creatinine (< 20:1 ratio) after an episode of hypovolemic shock?
Acute tubular necrosis
characterized by muddy brown casts; distinguishing features from pre-renal AKI include BUN:creatinine ratio < 20:1, urine Na+ > 20 mEq/L, and FeNA > 2%
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with hematuria a few days after an upper respiratory infection with normal complement levels?
IgA nephropathy (synpharyngitic glomerulonephritis)
quicker onset (within 5 days) and normal complement levels help differentiate IgA nephropathy from PSGN

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with intermittent flank pain, low-volume voids, and occasional episodes of high-volume voids?
Obstructive uropathy
e.g. due to renal calculi; high-volume voids occur due to large volume of retained urine overcoming the obstruction (post-obstructive diuresis)
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with lethargy and asterixis, and the laboratory findings below?
BUN: 78 mg/dL
Albumin: 3.8 g/dL
AST: 38 U/L
ALT: 44 U/L
Creatine kinase: 32,000 U/L
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with lethargy and asterixis, and the laboratory findings below?
BUN: 78 mg/dL
Albumin: 3.8 g/dL
AST: 38 U/L
ALT: 44 U/L
Creatine kinase: 32,000 U/L
Uremic encephalopathy
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with lower extremity edema, 4+ proteinuria, and a kidney biopsy demonstrating dense deposits within the GBM?
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) type II
also known as “dense deposit disease”
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with poorly controlled diabetes that presents with overflow incontinence with a high post-void residual volume (> 50 mL)?
Diabetic autonomic neuropathy
symptoms include dribbling and poor urinary stream

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with QRS widening and peaked T waves on ECG?
Hyperkalemia
other EKG changes include loss of the P wave and prolonged PR and/or shortened QT interval
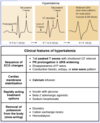
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with tuberculosis who presents with hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and eosinophilia?
Primary adrenal insufficiency

What is the likely diagnosis in a young female with hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, normotension, and low urine Cl-?
Surreptitious vomiting
low urine Cl- helps distinguish vomiting from other causes of hypokalemia, alkalosis, and normotension (e.g. diuretic abuse, Bartter syndrome, and Gitelman’s syndrome)


