Gi and Nutrition III Flashcards
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with melena and epigastric abdominal pain that is relieved with eating?
Peptic ulcer disease (duodenal ulcer)
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with obesity and diabetes who presents with hepatomegaly and mildly elevated LFTs in the absence of other causes for secondary hepatic fat accumulation?
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with recent travel history who develops foul-smelling stools, abdominal cramps, and bloating?
Giardiasis
common in rural areas and developing countries
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with severe RUQ/shoulder pain that occurs after fatty meals and resolves within 6 hours?
Biliary colic
quick resolution and lack of fever, abdominal tenderness on palpation, and leukocytosis help distinguish this process from acute cholecystitis
What is the likely diagnosis in a patient with sudden-onset odynophagia and retrosternal pain with a discrete ulcer in the mid-esophagus?
Pill esophagitis
mid-esophagus most common due to compression by the aortic arch or an enlarged left atrium

What is the likely diagnosis in a young patient with liver disease and neuropsychiatric symptoms?
Wilson disease

What is the likely diagnosis in a young woman with alternating constipation/diarrhea and chronic abdominal pain that is relieved after a bowel movement?
Irritable bowel syndrome

What is the likely diagnosis in an alcoholic who presents with epigastric pain and hematemesis following multiple episodes of vomiting (normal X-ray)?
Mallory-Weiss tear
i.e. a longitudinal tear in the mucosa often near the GE junction; most heal spontaneously

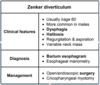
What is the likely diagnosis in an elderly man with dysphagia, regurgitation, halitosis, and aspiration?
Zenker’s diverticulum
treatment is generally surgical

What is the likely diagnosis in an elderly patient with chronic constipation, LLQ abdominal pain, fever, and leukocytosis?
Acute diverticulitis

What is the likely diagnosis in an elderly patient with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, elevated alkaline phosphatase, and painless jaundice?
Malignant biliary obstruction

What is the likely underlying cause of peptic ulcer disease in a patient who has emigrated from a low-income country?
H. pylori infection
symptoms include dyspepsia, nausea, and post-prandial fullness
What is the likely underlying etiology of ascites if the serum-ascites albumin gradient (SAAG) is > 1.1 g/dL?
Portal hypertension

What is the most common cause of esophageal rupture?
Endoscopy
other common causes include severe retching (Boerhaave syndrome) and penetrating trauma

What is the most common cause of gross lower GI bleeding in adults?
Diverticulosis
typically painless but may be associated with lightheadedness and hemodynamic instability with large-volume bleeds; usually resolves spontaneously
What is the most common site of colon cancer metastasis?
Liver
What is the most common source of liver metastases?
Colorectal cancer
in addition to tumors of the GI tract, lung and breast tumors also commonly metastasize to the liver
What is the most significant environmental risk factor for pancreatic cancer?
Smoking

What is the next step after an endoscopic biopsy is positive for gastric adenocarcinoma?
CT scan of abdomen/pelvis
imaging helps with disease staging, which determines prognosis and treatment options

What is the next step for establishing the diagnosis in a patient with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia and predominantly elevated alkaline phosphatase?
Abdominal imaging (US or CT)
presence of biliary dilatation is suggestive of extrahepatic cholestasis; absence of biliary dilatation suggests intrahepatic

What is the next step in management for a patient with acetaminophen toxicity that develops worsening acute liver failure despite N-acetylcysteine treatment?
Refer to liver transplant center
this is an ethically complicated issue, however, if there is no history of psychiatric illness or previous suicide attempt, liver transplantation is typically pursued
What is the next step in management for an elderly patient with newly discovered iron deficiency anemia?
colonoscopy and endoscopy
new IDA in an elderly patient is considered to be from GI blood loss until proven otherwise
What is the preferred diagnostic test for giardiasis?
Stool antigen assay
stool microscopy for oocysts and trophozoites may be used in resource-poor settings
What is the preferred initial study to evaluate patients with suspected oropharyngeal dysphagia?
Videofluroscopic modified barium swallow
evaluates swallowing mechanics, degree of dysfunction, and severity of aspiration