Platyhelminths - Fascioliosis Flashcards
Lifecycle of fasciola

Fasciola species
F. hepatica - worldwide (SI, ruminants)
F. gigantica - Asia/Africa (SI, ruminants)
F. magna - USA/parts of Europe (deer)
Fasciola snail IH
Lymnaeidae
Morphology of Fasciola hepatica
- Large (1-3cm), leaf like, broad
- Anterior end broader
- highly branched caeca
- spines on tegument

Whaich fasciola?

F. gigantica
What is this?
Lymnaea tomentosa

Common features of Lymnaea
- clockwise spiral
- no operculum
- Tentacles flat and triangular
- Length of shell 4-12cm (cometimes 10-25cm in lessoni)
Pathogensis of F. heapatica
Metacercariae ingested on plant near water
► Juvenile flukes penetrate intestinal wall to peritoneal cavity (24hrs) -> penetrate liver capsule -> migrate through liver (destruction/bleeding)
► Adult flukes establish in bile ducts and cause fibrosis -> hypertrophy of bile duct epithelium, calcification of parasites & bile stones
Acute/subactute phase of F. hepatica
- 4-6 weeks
Sheep > cattle
Massive intake of metacercariae (500-200)
Traumatic hepatitis, haemorrhage -> predispose to black disease by making room for clostridium novyi -> toxaemia -> black disease
- anaemia, abdominal pain, sudden death
Chronic phase of F. hepatica
>>> 6 weeks
PPP ~ 3 months
Cattle > Sheep
Cirrhosis of liver
Biliary calcification
- anaemia, bottle jaw/ ascites, diarrhoea, wasting
- hypoalbuminaemia
Acute findings of F. hepatica on PM
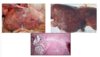
Liver is swollen, harmorrhagic, friable,
Subacute liver features

Atrophy, repair and regeneration -> cirrosis and adhesions
Diagnosis of actute fasciolasis
Necropsy
Swollen, haemorrhagic, friable, rounded, pale +/- fibrosed liver
- Take a cross section -> worm without coelon
Histology -> haemorrhade, evidence of black disease
- no eggs is faeces and no adults
Diagnsis of chronic fascioliasis
- Faecal float (heavy eggs)
sedementation - eggs are large, tan and have operculum
serology - look for IgG (4-6 weeks sheep, 6-8 weeks cattle)
Biochem/CBC
- anaemia, hypoproteinemia, elevated liver enzymes
Economic significance of F. hepatica
- Production loss - $60-80 million p.a.
- reduced production and quality of wool, low lambing rates, poor growth and feed conversion, sudden death
- Drenching cost $10 million
- Condemnation of liver
Epidemiology of F. hepatica
- Parasite, snail + rainfall (> 50 mm) + temp >10 degrees
- Freshwater, shallow, stagnant, pond, trickle stream, irrigatiojn channels
- in all states but WA and NT
Epidemiology -> pathogenesis in temperate climate zone
Eggs hatch and develop to miracidium mid Septepmber -> snail (-> cercariae) takes 2 months. By mid Novemeber start getting infections -> acute fasciolisis in sheep 4-6 weeks and cattle 6-8 weeks later.
-get deaths in Jan
Grazing habits-> disease
In winter rainfall areas snails breed and egg hatching in spring & early summer, get metacercariae early to mid Dec
Sheep graze near water in summer.
Treatment of fascioliasis
** Trichabendazon is the only drug that kills flukes as young as 2 weeks of age, specific to liver fluke, but resistance developing, only use when needed. Give just before they carc it in late Dec/Jan
Mid summer and autumn to get the adults
Closantel (also used in haemonchus) plus oxfendazole or albendazole get flukes 6 weeks of age.
Other drugs do adult flukes.
Oxycyclozanide with levamisol for dairy

How to control fasciola?
Environment - fence off snail prone areas
- drain marshy pastures
- build dams
Strategic flukicidal treatment
5-in-1 vaccine
Lifecycle of Fasciolopsis buski?



