NeuroAnatomy Revision Flashcards
Location of the longitudinal fissure?
Separates the right and left cerebral hemispheres

Which fissure separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum?
Transverse fissure

Which lobe is involved in complex learning?
Frontal
Which lobe is involved in language acquisition?
Parietal
Which lobe is involved in processing of visual information?
Occipital
Which lobe is involved in understanding of written word?
Occipital lobe
Which lobe is involved in processing of information associated with hearing and equilibrium?
Temporal lobe
Which sulcus separates the frontal from parietal lobe?
Central
Which sulcus separates the parietal and occipital lobes?
Parieto-occipital sulcus
What does the lateral sulcus separate?
Separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobes
Location of the insula?
Region of the cerebrum deep within the lateral sulcus

Function of the insula?
Processes information associated with hearing and equilibrium (is part of temporal lobe)
What is the corpus callosum?
Major bridge of white fibres that connect the two hemispheres of the cerebrum
Location of fornix? Function?
Bridge of white matter inferior to the corpus callosum; links regions of the limbic system (emotional brain) together
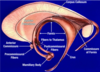
Location of the anterior commissure? Function?
Bridge of white fibres found near the anterior tip of the corpus callosum; connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum

Function of the caudate nucleus?
Basal nucleus; initiates voluntary movements and coordinates slow skeletal muscle contractions (e.g. posture and balance).
Location of the caudate nucleus? Shape?
- There are two – one on each side – sitting astride the thalamus and next to the lateral ventricles (below the cerebral cortex).
- C-shaped structure with head, body and tail.

overall function of basal nuclei?
The “basal ganglia” refers to a group of subcortical nuclei within the brain responsible primarily for motor control, as well as other roles such as motor learning, executive functions, emotional behaviours, and play an important role in reward and reinforcement, addictive behaviours and habit formation.
View of putamen and globus pallidus

What is putamen + globus pallidus known as?
Lentiform nucleus
What structure composes 80% of the diencephalon?
Thalamus
Function of the thalamus?
Major relay point and processing centre for sensory impulses

Which sense is the thalamus not involved in processing and relaying?
Olfaction
What is the ‘intermediate mass’ of the diencephalon?
Flattened grey band of tissue connecting the two halves of the thalamus

Function of the hypothalamus?
main regulatory centre involved in visceral control of the body and maintenance of overall homeostasis.
How does the hypothalamus link the nervous system to the endocrine system?
Via the pituitary gland
Function of mamillary bodies?
The primary function associated with the mammillary bodies is recollective memory. Memory information begins within the hippocampus. Information about memory transmits through the fornix to the mammillary bodies.
What does the infundibulum connect?
Neural stalk originating near mamillary bodies; connects pituitary gland to hypothalamus
Function of pituitary gland?
Glandular tissue under hypothalamus; important producer and releaser of endocrine hormones
Function of the pineal gland?
important producer and releaser of endocrine hormones

What does the posterior commissure connect?
Bridge of white fibres found inferior to the pineal gland; connects the two hemispheres of the cerebrum

Mid-sagittal section of brain showing diencephalon

Where are the cerebral peduncles located? What do they contain?
Paired bulges/stalks located on ventral aspect of midbrain that connect cerebrum and brainstem; contains large ascending and descending nerve tracts

Where are the superior and inferior colliculi located?
On the dorsal aspect of the rostral midbrain

Which nerve reflex do the superior colliculi contain?
Contains VISUAL nerve reflex centres; coordinated eye movements, focusing and papillary responses
What reflex is the inferior colliculus involved in?
Auditory
What fibres do the pyramids contain?
Motor fibres of corticospinal and corticonuclear tracts
What is the midline ridge of tissue that connects the two cerebellar hemispheres together?
Vermis
What are folia? Where are they located?
Fine, transversely orientated pleat-like gyri on the surface of the cerebellum; increase surface area
What are the cerebellar peduncles?
3 connection points between cerebellum and brainstem (superior, middle, inferior); contains fibre tracts running between the cerebellum and midbrain, pons, and medulla

What produces and secretes most of the CSF of the CNS?
Choroid plexus found in the ventricles
Where are the lateral ventricles located?
buried deep within each cerebral hemisphere

What structure does the third ventricle surround?
The thalamus
What does the Interventricular foramen/Foramen of Monro connect?
Each lateral ventricle to the 3rd ventricle
Which ventricle occupies the space between the dorsum of the pons/medulla and the overlying cerebellum?
4th ventricle
What is the passageway between third ventricle and fourth ventricle called?
Cerebral aqueduct
What is the central opening that runs through the medulla and is continuous with the spinal cord?
Central canal
What does the Foramen of Magendie connect?
Drains CSF from the fourth ventricle into the subarachnoid space or central spinal canal
What does the Foramen of Luschka connect?
Drains CSF from fourth ventricle into subarachnoid space or central spinal canal

How many Foramen of Luschka are there?
2
How many Foramen of Magendie are there?
1
4 functions of the meninges?
- Cover and protect brain
- Protect blood vessels and enclose venous sinuses
- Contain CSF
- Form partitions within skull
What does the pia mater mainly contain?
Blood vessels
Which layer of the meninges encloses venous sinuses?
Dura mater
Which layer of the meninges forms partitions within skull?
Dura mater
Label 1-8

1.
- Optic chiasm
- Infundibulum (not visible)
- Mamillary bodies
- Cerebral peduncles
- Pons
- Pyramid
- Olive
Label 1-12

- Cerebellum
- Arbor vitae
- Superior colliculi
- Inferior colliculi
- Pineal gland
- Posterior commissure
- Thalamus (intermediate mass)
- Corpus callosum
- Lateral ventricle
- Fornix
- Anterior commissure
- Optic chiasma


