Cranial Nerves Flashcards
(83 cards)
Where do 10/12 cranial nerves emerge from? What system does this make them part of?
What are the 2 exceptions to this?
- Emerge from brainstem - part of peripheral nervous system
- CN I (olfactory) and CN II (optic) emerge from the cerebrum - part of the CNS

Where did CN II (optic nerve) actually develop from?
The diencephalon
Where did CN I (olfactory) actually develop from?
From the telencephalon
The oflactory bulb and the olfactory tract are components of the olfactory nerve. What are these components?
- As the olfactory nerve leaves the nasal epithelium to enter the cranial cavity, they synapse with the olfactory bulb and trac
- The bulb and tract then bring the information into the cerebral hemispheres
Where are the oflactory bulb and tract extensions from?
The telencephalon

Cross-section of midbrain
- Upside down mickey mouse shape
- Ears corresponding to cerebral peduncles
- Grey matter appears white
- White matter appears dark

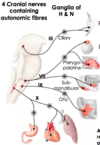
For each fibre type within a cranial nerve, there is a corresponding nucleus in the brainstem. I.e. these fibres arise from the nuclei
Example:
- How many fibre types does CN III (occulomotor) carry?
- What are these fibre types
- How and where are the corresponding nuclei?
- What are the corresponding nuclei called?
- CN III carries 2 fibre types
- Somatic motor fibres to extraocular muscles
- Visceral motor (autonomic) fibres (parasympathetic) to sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles
- 2 fibres there 2 corresponding nuclei in the midbrain (where CN III emerges)
- Oculomotor nucelus corresponds to somatic motor fibre
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus corresponds to visceral motor fibre

What are the 2 corresponding nuclei of CN III in the midbrain called?
- Oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
What is the Edinger-Westphal nucleus? Location? What does it innervate?
- A small parasympathetic motor nucleus in the midbrain
- Parasympathetic fibres emerge from this nucleus
- One of the two nuclei for the oculomotor nerve
- Innervates the iris sphincter muscle and the ciliary muscle
What is the oculomotor nucleus? Location? What does it innervate?
- A small somatic motor nucleus in the midbrain
- Somatic motor fibres emerge from here
- One of the two nuclei for the oculomotor nerve
- The fibers of the oculomotor nerve arise from a nucleus in the midbrain
How do fibres from both the Edinger-Westphal and Oculomotor nucelus form the Oculomotor nerve?
Fibres arise from both of these nuclei in the midbrain (at the level of the interpeduncular fossa between the 2 cerebral peduncles) and combine to form the Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Cranial nerve nuclei are scattered throughout the brainstem.
Spread out in the midbrain (III, IV), the pons (V, VI, VII, VIII), and the medulla (IX, X, XI, XII).
- Where are the sensory nuclei located?
- Where are the motor nuclei located?
- Sensory nuclei are located lateral
- Motor nuclei are located medial
Notice how cranial nerve nuclei are located anterior to the ventricular system, but not tightly against the anterior border. Ie. located in tegmentum.

General organisation of CN nuclei in brainstem.
This is a cross-section through open medulla oblongata (can see 4th ventricle at the back).
- Sensory nuclei more lateral
- Visceral sensory
- Special sensory
- Somatic sensory
- Motor nuclei more medial
- Somatic motor
- Parasympathetic motor
- Head and neck motor

Each cranial nerve can be described as being sensory, motor or both. They can more specifically transmit seven types of information; three are unique to cranial nerves (SSS, SVS and SVM).
- What are the sensory modalities?
- What are the motor modalities?
- Sensory:
- Special –> special senses (vision, taste, olfactory, hearing, balance)
- Somatic –> somatic sensation
- Visceral –> monitors states of internal organs and glands
- Motor:
- Somatic –> for skeletal muscles
- Parasympathetic –> e.g for secretions from glands
- Head and neck –> some muscles of head and neck
Cranial Nerve Summary:
- Part of the PNS (except I & II), which are extensions of the forebrain
- Nerves of head and neck carry either sensory (afferent) and/or motor (efferent) fibres:
- eg. Sensory from skin of face
- eg. Taste sense from tongue
- eg. Motor to eye muscles
- eg. Motor to neck muscles
- eg. Visceral motor to salivary glands
- eg. Visceral sensory from organs
- Each cranial nerve may carry several different fibre types
- Can be purely motor, purely sensory or mixed
- For each fibre type within a cranial nerve, there is a corresponding nucleus in the brainstem
How many cranial nerves are purely motor (efferent)? Purely sensory (afferent)? Mixed?
5 cranial nerves are purely motor (efferent); 3 are purely sensory (afferent); the rest are mixed
What is a nucelus?
A nucleus is a functional group of neurons within the CNS
Cranial Nerve Summary 2:
- Cranial nerve nuclei are located within the tegmentum of the brainstem
- Found in all brainstem parts (midbrain, pons and medulla)
- Generally, two types of cranial nerve nuclei:
- Sensory: Receive information from fibres entering brainstem in cranial nerves which synapse here, and nuclei then send fibres to appropriate higher centre
- Motor: Receive motor information from higher centre which synapse in nuclei which then give rise to motor fibres that leave the brainstem in cranial nerves
How are cranial nerves I and II different?
Derived from forebrain not brainstem - part of CNS
What is CN I?
Olfactory nerve
Olfactory nerve (CN I):
- Where is the true location of CN I
- Function?
- Foramina?
- Modality?
- Test?
- Location: from nasal mucosa, merge with olfactory bulbs and olfactory tracts (extensions of the telencephalon)
- Function : smell
- *Foramina*:cribriform plate** of ethmoid bone
- Modality: special sensory
-
Test:
- Offer a familiar smelling item (e.g. orange)
- Any changes in sense of smell?

What is anosmia?
Loss of smell
Optic nerve (CN II):
- Location of CN II?
- Function?
- Foramina?
- Modality?
- Test?
-
Location: One leaves each eyeball, emerging from the retina to the optic chiasma. Optic tract then carry visual info to the thalamus
- Optic chiasma is where info from the two optic nerves merge
- Function: Vision
- Foramina: Optic canals
- Modality: Special sensory
- Test: Visual tests e.g. fundoscopy

What is the only sensory modality to not pass through the thalamus?
Sense of smell