AFL 5 Flashcards
(22 cards)
A patient arrives at A&E with a deep laceration above the left eyebrow that appears to have penetrated the skull. Which lobe of the brain is likely to be damaged?
Left frontal
A subdural haematoma is an acculumation of blood between the dura and:
arachnoid
An extradural haematoma is an acculumation of blood between the dura and:
skull
Arachnoid graulations are located between the _____ ______ and the _____ ______.
Periosteal dura; meningeal dura
Folds in the cortex are called ______; the spaces between these are called ______?
gyri and sulci
In the prosection illustrated below, vascular occlusion at the point indicated by the red pin would result in a lack of blood flow to which one of the following regions?

This is the posterior cerebral artery which supplies the medial occipital lobe of the cerebrum
In the prosection illustrated, vascular occlusion at the point indicated by the yellow pin would result in what change to blood flow to the cerebral hemisphere?

No change in the blood flow to the cerebral hemisphere
Massive cellular division and differentiation at the rostral end of the neural tubes leads to development of the:
Cerebral hemispheres
The forebrain is also known as the
prosencephalon
The forebrain is comprised of which regions of the brain?
cerebral hemispheres and diencephalon
The picture shows a dissection of the lateral aspect of the face. What nerve is indcated by the blue pin? What does it supply?

Buccal branch of the facial nerve - supplies motor innervation to buccinator

The picture shows a dissection of the mandibular region. Identify the corner of the mouth to orientate yourself.
Identify the structure indicated by the red pin.

Submandibular gland
The picture shows a dissection of the mandibular region. Identify the corner of the mouth to orientate yourself.
What is the vessel indicated by the blue pin?
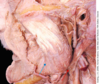
Facial artery - crosses the mandible just anterior to the masseter muscle.
At the level of the pons, the cerebrospinal fluid enters the subarachnoid space via the:
Lateral apertures (of Luschka)
Damage to which lobe of the brain would cause an interruption of flow through the inferior horn of the lateral ventircle?
temporal
What is the channel indicated by the blue pin?

links one lateral ventricle to the third ventricle –> foramen of Monro.
The embryologic central canal forms which chamber of the ventricular system at the level of the medulla and pons?
IVth ventricle
The inferior horn of the ventricular system is located in which lobe of the brain?
Temporal
This image shows a slice in which plane of section?

Sagittal
Which secondary brain vesicle includes the pons and cerebellum?
Metencephalon
Congenital narrowing (stenosis) of the cerebral aqueduct leads to expansion of:
both lateral ventricles and the third ventricle
The superior temporal gyrus on the lateral surface of the temporal lobe is supplied with blood by the
middle cerebral artery


