Neuroanatomy Practical 1 Flashcards
Which cranial fossa does the temporal lobe lie in?
Middle cranial fossa
Which artery gives rise to the posterior cerebral artery?
Vertebral/basilar system
What sits in the posterior cranial fossa?
Brainstem and cerebellum –> not the occipital lobes as these sit above the cerebellum
What separates the frontal and parietal lobes?
Central sulcus
When talking about the cerebrum, what is the dorsal aspect the same as?
The superior aspect
When talking about the cerebrum, what is the ventral aspect the same as?
Ventral = inferior surface of cerebrum
What is the corpus callosum?
- Connects the two hemispheres
- Consists of white matter fibres
- Part of telencephalon (cerebral hemispheres)
- Is supplied by the anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
What suture is this? What does it separate?

Coronal suture - divides frontal bone from parietal bones
What suture is this?

Sagittal suture separating the 2 parietal lobes
Floor of cranial cavity: what fossa is this? What sits here?

Anterior cranial fossa - frontal lobes sits here (one in the right hemisphere of your brain and one in the left hemisphere of your brain)
What sits in the middle cranial fossa?

Temporal lobes
What sits in the posterior cranial fossa?
Cerebellum and brainstem

What is this projection? What attaches here?

- Projection of the ethmoid bone –> crista gali
- Anterior attachment point of falx cerebri
What is the posterior attachment point of the falx cerebri?
Internal occipital protuberance of the occipital bone

What fissure sepaartes the cerebral hemispheres?

Longitudinal fissure/sulcus
What is being pointed to?

Corpus callosum
What is the frontal pole?
One of the three poles of the brain (along with the occipital pole and temporal pole), and corresponds to the anterior most rounded point of the frontal lobe.

What is the temporal pole?
an anatomical landmark that corresponds to the anterior end of the temporal lobe, lying in the middle cranial fossa.

What is the occipital pole?
an anatomical landmark that corresponds to the posterior portion of the occipital lobe

What sulcus/fissure is this?

Lateral sulcus - divides temporal lobe inferiorly from parietal and frontal lobes superiorly
What suclus is this (ventral view)?

Longitudinal
What are these extensions of the telencephalon?

- Dilated area –> olfactory bulb
- Olfactory tract brings fibres to cerebral cortex
What is this?

- Optic chiasm
- Crossing point of 2 optic nerves
Where are the optic nerves and optic chiasm extensions from?
Diencephalon
What structure would normally be hanging from here?

Pituitary stalk/infundibulum - connecting to pituitary gland
What are these two structures? Where have they come from?

- Mamillary bodies
- Part of diencephalon
What is found just lateral to the mamillary bodies?
The midbrain - the cerebral peduncles

What sulcus is this?

Central sulcus
What is the blue pin? Yellow pin?

- Blue pin:
- Fold of grey matter
- The precentral gyrus –> primary motor cortex
- Yellow pin:
- Fold of grey matter
- The postcentral gyrus –> primary somatosensory cortex
What is being pointed to?

Optic nerve (rest has been cut off)
What is this stalk?
Pituitary stalk/infundibulum
From which subdivision did the medulla oblongata come from?
Myelencephalon
From which subdivision did the cerebral hemispheres develop from?
Telencephalon
From which subdivision did the midbrain develop from?
Mesencephalon
From which subdivision did the cerebellum develop from?
The metencephalon
From which subdivision did the pons develop from?
Metencephalon
From which subdivision did the thalamus develop from?
Thalamus
What 1ary structure did the telencephalon and diencephalon develop from?
Prosencephalon
What 1ary structure did the metencephalon and mylencephalon develop from?
Rhombencephalon
What 1ary structure did the mesencephalon develop from?
Mesencephalon
What does the cerebral cortex consist of?
six layers of stacked nerve cell bodies
what term is used to describe cell bodies of neurons in the PNS?
Ganglion
What term is used to describe cell bodies of neurons in the CNS?
nucleus
What is a fasciculus?
Collection of highly organised myelinated axons (fibres)
What is a tract?
a bundle of nerve fibers (axons) connecting nuclei of the central nervous system
What are axons of neurons in the PNS called? In the CNS?
- PNS: Nerve
- CNS: White matter, tract, fasciculus
Grey matter stained blue and white matter remains white.
- Grey matter confined to surface of cerebral cortex
- Some grey matter deep within hemispheres
- E.g. basal ganglia, thalamus
- Corpus callosum
- Bundle of white matter connecting the two hemispheres

View of some ventricles

View of corpus callosum. Which ventricle can be seen here?
- The space seen here is the lateral ventricle

What structure is being pointed to?

1/2 of the thalamus (been cut in the middle)
Diagram of thalamus and hypothalamus

Which layer of meninges forms the tentorium cerebelli?
Dura mater
Where is the superior sagittal sinus contained?
The intracranial dura mater contains the superior sagittal sinus in the attached edge of the falx cerebri
Under which meninges layer is CSF found?
Under the arachnoid layer
Cadaveric view of dura mater

Cadaveric view of arachnoid mater

Location of superior sagittal sinus

Where can the straight sinus be found?
Along the meeting point of the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli

In which meningeal layer are the meningeal arteries found in?
found in the outer portion of the dura

What forms the falx cerebri?
The falx cerebri is a sickle-shaped structure formed from the invagination of the dura mater into the longitudinal fissure between the cerebral hemispheres
Which invagination of dural layers is being seen here?

Tentorium cerebelli (one on each side)
What does the tentorium cerebelli separate?
Separates the cerebral hemispheres above from the cerebellum below
Attachments of falx cerebri?
Anteriorly: attaches anteriorly at the crista galli of the ethmoid bone
Posteriorly: upper surface of the tentorium cerebelli
What sinus is this? How is it formed?

- Transverse sinus (paired) - formed by separation of outer and inner layers of dura mater
- Venous blood flows into this space
Superior sagittal sinus draining into the confluence of sinuses at the back


What does the confluence of sinuses then drain into?

Drains to the left and right transverse sinuses that run within the lateral edge of the tentorium cerebelli.

Which meningeal layer is being pointed to?
Arachnoid mater (thin translucent membrane)

When the pia mater is exposed, what can be seen?
Gyri and sulci
What is being pointed to?

Falx cerebri (of tough fibrous dura mater)
What is being pointed to?

Tentorium cerebelli
What is being pointed to?

Falx cerebelli (separates hemispheres of cerebellum)

What are bridging veins?
Bridging veins are veins in the subarachnoid space that puncture the dura mater and empty into the dural venous sinuses.
What is the result of a rupture of a bridging vein?
a subdural hematoma.
What is being pointed to?

Falx cerebri
Which sinus is found in the free edge of the falx cerebri?

Inferior sagittal sinus
What does the inferior sagittal sinus receive blood from/drain into?
It receives blood from the deep and medial aspects of the cerebral hemispheres and drains into the straight sinus.

What fold of dura mater is this?

Falx cerebelli - a small sickle shaped fold of dura mater, projecting between the two cerebellar hemispheres.
View of superior sagittal sinus, lateral sinus turning into the sigmoid sinus. What does the sigmoid sinus ultimately drain blood into?

Ultimately drains blood into the internal jugular vein

Where does the internal carotid artery arise from?
From the common carotid artery in the neck
Which artery transverses the foramina transversaria of cervical vertebrae?
Vertebral artery
Which artery forms the basilar artery?
Vertebral artery
Which artery gives rise to the anterior and middle cerebral arteries?
Internal carotid artery
What does the Circle of Willis surround?
The optic chiasma, infundibulum and the interpeduncular region
Label 1-5 on this angiogram
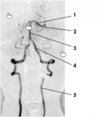
- 5 - vertebral artery ascending through the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae
- 4 - foramen magnum where vertebral arteries enter cranium
- 3 - the two vertebral arteries join to form basilar artery
- 2 - superior cerebellar artery (branch of basilar)
- 1 - terminal branch of basilar is the posterior cerebral artery
What vessel is this?

Vertebral artery
What vessel is this?

Basilar artery formed by the two vertebral arteries coming together on the ventral surface of the pons
What is this branch straight off of the vertebral artery? What does it supply?

- Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) (paired)
- Branch of vertebral artery
- Goes towards cerebellum to supply posterior and inferior aspect of cerebellum
What are these small branches here? What vessel do they form? What does this vessel supply?

- Contributions from right and left vertebral artery join to form the anterior spinal artery
- Descends and supplies all the anterior aspect of the spinal cord
Which vessel supplies the anterior aspect of the spinal cord?
Anterior spinal artery
What is this branch?

- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) (paired)
- Branch of basilar artery (which is formed by vertebral artery)
- Goes towards cerebellum to supply the anterior and inferior aspect of the cerebellum
What branch is this? What does it supply?

- Superior branch of basilar artery (paired)
- Superior cerebellar artery
- Branch of basilar artery which is formed by vertebral arteries
- Supplies the superior aspect of the cerebellum
What is the final branch of the basilar artery?

- Posterior cerebral artery (paired)
- Terminal branch of the basilar artery
- Supplies the inferior/medial surface of the temporal lobe and the occipital lobe
Which nerve is sandwiched between the superior cerebellar artery and the posterior cerebral artery?
The oculomotor nerve (CN III)

What is the middle meningeal artery a branch of? What foramen does it travel through to enter the cranium? What does it supply?
- Normally branches off the maxillary artery, which is an extension of the external carotid artery
- Travels through the foramen spinosum to supply blood to the dura mater
What are the branches of the vertebral artery and the basilar artery?
Vertebral artery:
- meningeal branches,
- anterior spinal artery,
- posterior spinal artery
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery
The 2 vertebral arteries join to form the basilar artery:
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)
- pontine arteries
- superior cerebellar artery (SCA)
- terminates by splitting into left and right posterior cerebral arteries
Diagram of circle of Willis

What vessel is being pointed to? Where does it emerge?

- Internal carotid artery
- Emerges at base of brain lateral to optic chiasma
What vessel is this? What is it a branch of? What does it supply?

- Middle cerebral artery
- The largest branch of the internal carotid
- Supplies a portion of the frontal lobe and the lateral surface of the temporal and parietal lobes
After the middle cerebral artery, what is the next branch of the internal carotid?
Anterior cerebral artery

What is the circle of Willis?
- An interconnection between the internal carotid system and the vertebral basilar system
- An arterial circle at the base of the brain surrounding the optic chiasma and infundibulum
What are the components of the Circle of Willis?
- Posterior cerebral artery (terminal branch of basilar artery) connected to internal carotid via the posterior communicating artery
- Anterior cerebral artery (branch of internal carotid) connected to internal carotid via the anterior communicating artery
- Middle cerebral arteries also contribute
- Basilar artery contributes and forms closed loop

What vessel is this? What does it connect?
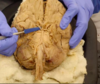
Posterior communicating artery connecting the posterior cerebral artery with the internal carotid artery
What do the pontine arteries supply? Where do they branch off of?
come off at right angles from either side of the basilar artery and supply the pons and adjacent parts of the brain.
What vessel is this?

Internal carotid
What vessel is this?

- Middle cerebral artery
- Branch from internal carotid
- Moves laterally
Dura tightly fused to skull and meningeal vessels

Space of epidural haemorrhage

Brain showing a stroke - region of grey matter here has died due to lack of blood supply

Berry aneurysm. Where do these usually happen?

- Usually at branching points
- This one occurred at the branching point between the internal carotid and middle cerebral artery
Burst berry aneurysm

Intracerebral haemorrhage

What causes a brain aneurysm?
Brain aneurysms are caused by a weakness in the walls of blood vessels in the brain
A patient presents with a stroke with paralysis of right arm and leg as well as loss of speech. Which is the most likely region to have been affected by the stroke that could account for limb paralysis?
Precentral gyrus –> primary motor cortex (controls movement)


