Localisation Flashcards
What do the cerebral hemispheres consist of?
Include a dense core of white matter with an overlying thin layer of grey matter (cortex)
Describe the cerebral cortex
- Varies in thickness from 2-4mm
- Heavily folded to increase surface area (over half the total surface area is hidden by the walls of the sulci)
- Laminar arrangement (I-IV)
- 6 layers with specific cells
- Specific sulci are used to divide the cerebral hemispheres into lobes and specific gyri
What does the central sulcus divide? What is found on either side of the central sulcus?
- Divides the frontal lobe from the parietal lobes
- Precentral gyrus in front
- Postcentral gyrus behind

Sulci and gyri view

Which sulci and gyri are found on the lateral aspect of the frontal lobe?
2 sulci:
- Superior
- Inferior
Therefore 3 gyri:
- Superior
- Middle
- Inferior

What does the lateral sulcus separate?
Separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe

Which sulci and gyri are found on the lateral aspect of the temporal lobe?
2 sulci:
- Superior
- Inferior
Therefore 3 gyri:
- Superior
- Middle
- Inferior

What does the parieto-occipital sulcus separate?
The parietal lobe from the occipital lobe

Where is the calcarine sulcus found?
located on the medial surface of the occipital lobe

Which sulcus runs parallel with the corpus callosum?
The cingulate sulcus

What does the cingulate sulcus separate?
Separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the cingulate gyrus

In which view of the brain is the cingulate sulcus seen?
Only in the medial view
Where is the collateral sulcus found?
On the medial surface of the temporal lobe

What does the collateral sulcus define?
Defines the position of the parahippocampal gyrus

What is the uncus?
- an anterior extremity of the parahippocampal gyrus
- the most medial part of the temporal lobe

What is the parahippocampal gyrus? What lobe is it part of?
A cortical region in the medial temporal lobe that surrounds the hippocampus

Sulci and gyri: medial vs lateral view


What is the limbic system?
- A set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus
- Formed mainly of the subcallosal gyrus, the cingulate gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, and the hippocampus.
- Deal with emotion and memory

What part of the brain is circled in red?

Diencephalon
What is an uncal herniation? What is compressed?
- Occurs due to rising intracranial pressure
- Uncal parts of temporal lobe herniate below the tentorium cerebelli
- Compresses midbrain

What is a tonsillar herniation? What does it compress?
- Cerebellar tonsils herniate through the foramen magnum
- This compresses the medulla
Lobes medial and lateral

What is a ‘Broddman area’?
- A region of the cerebral cortex
- 46 areas in total
- Based on cellular organisation of cerebral cortex
- Specific areas of cortex are believed to carry out specific functions
- (you don’t have to remember numbers)

There are primary projection areas in the brain.
- What occurs at the primary sensory areas?
- What occurs at the primary motor areas?
- Sensory: specific sensory pathways terminate here –> perceived sensation
- Motor: specific motor pathways originate here
The primary sensory areas have different modalities. What cortical area is associated with each modality:
- General sensation (somaesthetic)
- Visual
- Auditory
- Olfactory
- Gustatory
- Post-central gyrus
- Either side of calcarine sulcus (striate cortex) and occipital pole
- Heschl’s gyrus (superior temporal gyrus)
- Uncus
- Inferior post-central gyrus

Which cortical area is the primary motor cortex?
Pre-central gyrus
Medial and lateral view of primary motor and sensory areas

What are secondary association areas?
Lie near the primary projection areas and are associated with further processing
What is the function of 2ary sensory areas?
- Receive input from 1ary sensory areas
- Involved in interpretation/understanding
- 1ary areas perceive info
- 2ary areas interpret info (give it meaning)
What is the function of the 2ary motor areas?
- Sends output to 1ary motor area
- Organises patterns of movement
- Organises instruction and then sends to 1ary area
- 1ary area then sends command to move that body part
The secondary sensory areas have different modalities. Which cortical area is associated with:
- General sensation (somaesthetic)?
- Visual?
- Auditory?
- Superior parietal lobe
- Pre-striate area
- Lateral fissure/superior temporal gyri

The 2ary motor areas have different modalities. What cortical area is associated with:
- Premotor area?
- Supplementary motor area?
- Frontal eye field?
- Anterior to precentral sulcus on lateral surface
- Anterior to precentral sulcus on medial surface
- Anterior to premotor

What is function of primary motor cortex in pre-central gryus?
- Sends descending motor fibres through brainstem, through spinal cord via specific tracts to perform muscle contractions
- Controls voluntary contraction of specific muscles
- Somatotopically organised

Where are the associated motor areas located?
Anterior to primary motor cortex

What are the association motor areas?
- Supplementary motor (sm)
- Pre-motor (pm)
- Frontal eye field (8)
- Broca’s area (44, 45)

Where are the supplementary motor and pre-motor association areas located? What is their function?
- Located anteriorly to primary motor cortex (pre-central gyrus)
- Sm located more medially
- Pm located more laterally
- Function: learned complex motor activities and storage of those activities
- Organise instructions to perform a complex motor activity and send it to the pre-central gyrus to execute this movement
- E.g. learning to tie shoelaces
- Storage of those activities (so can perform activity again)
- Organise instructions to perform a complex motor activity and send it to the pre-central gyrus to execute this movement
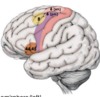
Where is the frontal eye field located? What is its function?
- Frontal lobe (8)
- Controls voluntary scanning movements of the eyes

Where is Broca’s area located? What is its function?
- Located in inferior frontal gyrus
- Localised to dominant hemisphere (left in most people)
- Function: regulates pattern of breathing and vocalisation needed for normal speech

What is result of injury to pre-central gyrus?
Paresis (impaired movement) or even paralysis (if severe)
What is result of injury to association motor area?
- Still able to move body parts
- Lost ability to perform highly skilled movement e.g. tieing shoelace
What does the primary somatosensory cortex located in the post-central gyrus do?
-
Receives sensory pathways for touch, temperature, vibration, pain, proprioception
- Sensory receptors all round body project to spinal cord, through specific tracts and ascends to the post-central gyrus
- HOWEVER, this info stops in the thalamus and is then relayed to the primary somatosensory cortex
- Thalamus = relay station
- Somatotopically organised

What is the VPL and VPM?
- There are 2 subdivisions VPL (ventral posterolateral nucleus):
- Lateral VPL
- Medial VPL
- VPN: ventral posteromedial nucleus
These are nuclei of the thalamus which are part of the somatosensory system.

Function of VPL?
- Lateral VPL: receives input from leg and projects to midline
- Medial VPL: recives input from arm and projects to lateral region
Function of VPM?
Receives input from the face and projects to lateral region
Where does the lateral VPL receive info from? Where does it project to?
- Receives from leg
- Projects to midline
Where does the medial VPL receive info from? Where does it project to?
- Receives from: arm
- Projects to: lateral region
Where does the VPM receive info from? Where does it project to?
- Receives from: face
- Projects to: lateral region
Somatotopic organisation:
Pre-central gyri: pink
Post-central gyri: blue

Organisation explained: pre-central gyrus
- Somatotopy is the point-for-point correspondence of an area of the body to a specific point on the central nervous system.
- I.e. specific regions within pre-central gyrus that controls specific areas of the body
- Info to move the hands starts more laterally than info to move the toes
- General rule:
- Legs (most medially)
- Then trunk
- Then arms
- Then face (most laterally)

Organisation explained: post-central gyrus
- Sensory info coming from body reaches the thalamus
- The thalamus knows where the info has come from and then projects this info to specific parts of post-central gyrus
- General rule:
- Face located (more laterally)
- Then arms
- Then trunk
- Then leg (more medially)

What is a motor homunculus?
- It’s important to notice that the size of the area of the pre-central gyrus does not correspond to the size of the body parts
- A motor homunculus represents a map of brain areas dedicated to motor processing for different anatomical divisions of the body.
- Hand so big as we perform many specific actions with our hands –> many motor commands go here

What is a sensory homunculus?
- The sensory homunculus is a map along the cerebral cortex of where each part of the body is processed.
- Many sensory receptors in hand and face (especially lips and tongue)

Where is the somatosensory association cortex (areas 5 and 7) located? What is its function?
- Directly posterior to the sensory cortex in the superior parietal lobes.
- Function: interpretation, understanding and recognition
- Gives meaning to those sensations
- If your arm is being stroked, your 1ary somatosensory cortex knows you are being stroked BUT your somatosensory association cortex knows what kind of stroke (e.g. kind, feather, unpleasant, burning etc)
- Gives meaning to those sensations

What is result of injury to 1ary somatosensory cortex (post-central gyrus)?
- Diminished sensation –> Hypoesthesia
- Absent sensation –> Anaesthesia
What is result of injury to association somatosensory area?
Tactile agnosia
What is tactile agnosia?
the loss of the ability to recognise objects, faces, voices, or places despite intact elementary tactile perceptions.
Where is the primary auditory cortex (BA 41, 42) located? What is its function?
- Located in the superior temporal gyrus (Heschl’s gyrus)
- Function: Conscious perception of sound
- Perceives sound but doesn’t know meaning of sound as only a 1ary area

What part of the thalamus does the primary auditory receive input from?
From the medial geniculate nucelus (MGN)

How is the primary auditory cortex organised?
Tonotopically organised:
- Lower frequences are projected more medially into gyrus
- Higher frequences are projected more laterally/posteriorly into gyrus

what is tonotopic organisation?
Tonotopic organisation means that cells responsive to different frequencies are found in different places at each level of the central auditory system, and that there is a standard (logarithmic) relationship between this position and frequency. Each cell has a characteristic frequency (CF).
Where is the association auditory cortex (BA 22) located?
- Surrounds 1ary auditory cortex
- In the posterior section of the superior temporal gyrus
- Called Wernicke’s area (in the dominant hemisphere - typically left)
- Function: interprets and gives significance to auditory information
- I.e. decides if noise is pleasant/unpleasant etc

What is Wernicke’s area? How does it differ from Broca’s area?
- Interpretation of written or spoken word
- Wernicke’s area is the region of the brain that is important for language development. It is located in the temporal lobe on the left side of the brain and is responsible for the comprehension of speech, while Broca’s area is related to the production of speech.
Where is the primary visual area (BA 17) located?
- Area around calcarine sulcus and occipital pole
- Function: receives info from retina
- Optic nerve sends input from retina to lateral geniculate nuleus of thalamus
- Info them sent to primary visual cortex in occipital lobe

Which is the only sense that isn’t relayed in the thalamus?
Smell
Which part of the thalamus relays auditory info?
medial geniculate nucleus
Which part of the thalamus relays visual info?
lateral geniculate nucleus
How is the primary visual cortex organised?
Retinotopically

Where is the association visual cortex (BA 18, 19) located? Function?
- Surrounds 1ary visual cortex (shown in orange)
- Funcion: Interpretation of visual information
- Recognise faces, objects, trees etc

What does an injury to the association visual cortex result in?
Prosopagnosia
What is prosopagnosia?
Neurological disorder characterised by the inability to recognise faces. Prosopagnosia is also known as face blindness or facial agnosia.
Where is the taste cortex located?
Extends from inferior margin of postcentral gyrus into the insula

What are is the general association cortex?
Involved in more complex aspects of behavioural and intellectual functioning
Examples:
- Prefrontal cortex
- Parieto-temporal cortex

What is the function of the prefrontal cortex?
- Is a general association cortex
- Regulates moods and feelings
- Involved in higher order cognitive functions
- Conceptualisation, planning, judgement
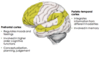
What is the function of the parieto-temporal cortex?
- Is a general association cortex
- Integrates information from different modalities (e.g. vision, hearing) and gives it meaning
- Involved in memory

What can damage to the prefrontal cortex result in?
- Tend to perform poorly on tasks that require the use of long-term strategies and the inhibition of impulses.
- Become impulsive
- Lose ability to make sound judgements
- Lose inhibition of impulsive behaviour
- Often display short-term memory deficits, which may help to explain some of their difficulties in planning.
What is cerebral dominance?
The ability of one cerebral hemisphere (left or right) to predominately control specific tasks –> i.e. lateralisation of the brain
What is the dominant hemisphere for language in most people?
The left –> two language areas are located within dominant hemisphere
What can damage to language areas result in?
Aphasia
What is aphasia?
An inability to comprehend or formulate language because of damage to specific brain regions.
What are the 2 main language areas?
- Broca’s area: inferior frontal lobe
- Wernicke’s area: superior temporal lobe

What does damage to Wernicke’s area result in?
Sensory/fluent aphasia: inability to understand language BUT words come out fluently but make no sense
(applies to written language as well as spoken language)
What can damage to Broca’s area result in?
Motor/non-fluent aphasia: inability to correctly articulate speech BUT can understand language

What is dysphasia?
Difficulty speaking
What connects the Broca’s area and the Wernicke’s area in the brain?
- The arcuate fasciculus
- A bundle of axons (white matter)
- Is an association fibre tract connecting caudal temporal cortex and inferior frontal lobe.
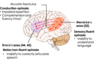
What can damage to the arcuate fasciculus result in?
Conduction aphasia:
- Impaired repetition as connection lost
- Comprehension and fluency intact
- Wernicke’s and Broca’s area intact
Cortical organisation summary:
- Some areas have precise sensory or motor function
- Other areas have progressively more associative or integrative function
- As ascends “hierarchy” of cortical function, lateralisation of some functions
- Dominant hemisphere (typically left)
- Linguistic function
- Numerical skills
- Non-dominant hemisphere
- Spatial awareness
- Dominant hemisphere (typically left)
What is the dominant hemisphere associated with?
- Linguistic function
- Numerical skills
What is the non-dominant hemisphere associated with?
Spatial awareness
Damage to secondary sensory areas leads to?
Agnosia - disorders of understanding:
- Awareness of sensation persists but significance of this sensation is lost
- E.g. eyes closed, handed scissors, can’t recognise
Damage to secondary motor areas leads to?
Apraxia - Inability to carry out purposive movements, although there is no paralysis
- Leads to inability to perform learned movements
Case Study:
- 20 year old woman fainted, unconscious for several hours.
- Once awake, unable to speak apart from saying ‘damn’ repeatedly due to frustration of loss of speech.
- Able to print words with L hand. R hand limp and paralysed.
- Months later: Loss of speech persisted, R arm and hand weak.
Locate the lesion. Structures involved? Vessel involved?
- Hemisphere: left
- Location of lesion: inferior pre-central gyrus and Broca’s area
- Vessels: Middle cerebral artery


