Meninges and Ventricles Flashcards
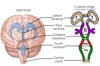
What do the meninges refer to?
the membranous coverings of the brain and spinal cord
How many layers of meninges are there? What are they called?
3 layers:
- Dura mater (outermost)
- Arachnoid mater (middle)
- Pia mater (innermost)

What are the 2 major functions of the meninges?
- Provide a supportive framework for the cerebral and cranial vasculature.
- Acting with cerebrospinal fluid to protect the CNS from mechanical damage.
How are the meninges often involved in cerebral pathology?
a common site of infection (meningitis), and intracranial bleeds.
Diagram of the meninges around the brain

Which layer of the meninges lies directly underneath the bones of the skull and vertebral column?
Dura mater
Describe the dura mater
It is thick, tough and inextensible (protective)
Describe arachnoid mater
Thin, delicate layer, spider’s web-like, vascular
Describe the pia mater
Microscopically thin, follows gyri and sulci (tightly adhered to surface of brain)

Where does the dura mater receive its blood supply from?
primarily from the middle meningeal artery and vein.
Within the cranial cavity, the dura contains two connective tissue sheets. What are these called?
- Periosteal layer
- Meningeal layer

What does the periosteal dura mater layer line?
The inner surface of the bones of the cranium (tightly adhered to)

What does the meningeal dura mater layer line?
Deep to the periosteal layer inside the cranial cavity - tightly adhered to the arachnoid mater. (It is the only layer present in the vertebral column)
Where is the only space in the layers of the meninges?
Below the arachnoid mater –> subarachnoid space

What is found in the subarachnoid space?
Cerebrospinal fluid
Function of cerebrospinal fluid?
acts to cushion the brain
Only at specific areas, the inner dural layer separates from the outer layer and protrude into the cranial cavity. What does this form?
Forming double-layered dural folds (also called partitions or septae)

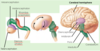
Dural infoldings diagram
These dural infoldings partition the brain, and divide the cranial cavity into several compartments.

How many dural infoldings are there? What are they called?
3 folds:
- Falx cerebri
- Tentorium cerebelli
- Falx cerebelli
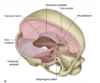
Where is the falx cerebri located?
Between the two cerebral hemispheres (forms a sickle shape from front to back)

Where is the tentorium cerebelli located?
Separates the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum below (tent over the cerebellum) –> divides the cranial cavity into supratentorial and infratentorial compartments

Where is the falx cerebelli located?
It is a small infolding of the dura in the sagittal plane over the floor of the posterior cranial fossa. Separates the two cerebellar hemispheres

What are the attachments of the falx cerebri?
Anterior: crista galli of ethmoid bone
Posterior: inner surface of occipital bone (internal occipital protuberance)

Superior view of the floor of the cranial cavity

What are the names of these 3 structures?

- Top - falx cerebri
- Left - tentorium cerebelli
- Right - tentorium cerebelli

Venous sinuses are also found between the two layers of the dura mater. How are these formed?
Spaces created at specific locations by the separation of the dural layers
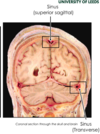
What are the dural venous sinuses responsible for?
- Venous blood from brain is collected here and then drained into the internal jugular veins
- Cerebrospinal fluid is reabsorbed

Spinal cord enclosed within dural sac

What happens regarding the meninges when the spinal nerve roots leave the spinal cord?
They take layers of meninges with them - spinal nerve roots ensheathed within dura
How do the meninges of the spinal cord differ from the brain? 2 points
- Dura mater surrounding spinal cord is only composed of one layer –> the meningeal layer only (i.e. no periosteal layer)
- Space between spinal cord and dura (epidural space) but dura mater of brain is tightly adhered to skull
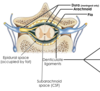
For the spinal cord, what is found between the spinal cord and the dura?
Epidural space occupied by fat

What is found below the arachnoid layer of meninges of the spinal cord?
Subarachnoid space (CSF)

What are denticulate ligaments? Function?
- Projections of the pia mater (pia ligament) that anchor the spinal cord to the arachnoid matter and to the dura mater each side
- Only found in spinal cord

Where are the denticulate ligaments found?
Interspersed between the spinal nerves

What is a potential space?
A potential space is a space between two adjacent structures that are normally pressed together (directly apposed) –> only becomes a space in pathological conditions
E.g. pleural space is a potential space
Is the epidural space in the skull (between the skull and the dura) real or potential?
Potential (normally dura should be tightly adhered)
Is the subdural space in the skull (between the dura and the arachnoid) real or potential?
Potential
Is the subarachnoid space in the skull (between the arachnoid and pia mater) real or potential?
Real - cerebrospinal fluid contained here
Diagram of cranial real vs potential

Is the spinal epidural space (between the spinal cord and dura) real or potential?
Real - filled with fat
Is the spinal subdural space (between the dura and arachnoid) real or potential?
Potential
Is the spinal subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid and pia mater) real or potential?
Real