MSK - Histology - Nervous Tissue Flashcards
True/False.
Neurons are both irritable (responsive to stimuli) and conductive.
True.
The CNS is made up of what major portions?
Brain,
spinal cord
What are the major portions of the brainstem?
Midbrain
pons,
medulla oblongata
The peripheral nervous system is made of what major parts?
How many of each?
Cranial nerves (12);
spinal nerves (31)
The brain is made up of what major portions?
Cerebrum,
cerebellum,
brainstem
What is another term for neuronal cytoplasm?
What is another term for neuronal RER?
Perikaryon;
Nissl bodies
Neurons typically have a maximum of how many dendrites?
Neurons typically have a maximum of how many axons?
15;
1
Dendritic branches are called:
gemmules (spines)
Axons originate at the:
What happens here?
Axon hillock;
summation (temporal and spatial)
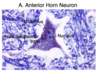
What basic neuron configuration (i.e. axonal and dendritic branching) do motor neurons have?
Multipolar
(multiple dendrites + 1 axon)
What basic neuron configuration (i.e. axonal and dendritic branching) do general sensory neurons have?
Pseudounipolar
(sensory side + laterally removed soma + transmitting side)
What basic neuron configuration (i.e. axonal and dendritic branching) do special sensory neurons have?
Bipolar
(sensory side and transmitting side bisected by soma)
What neuron type is responsible for circuit formation and creating high neuronal interconnection?
Interneurons
(typically multipolar)
Motor neurons are:
Sensory (general) neurons are:
Special sensory neurons are:
Interneurons are:
Multipolar;
pseudounipolar;
bipolar;
multipolar
Bipolar neurons are:
Multipolar neurons are:
Pseudounipolar neurons are:
Special sensory;
motor (or interneurons);
sensory (general)
Where is the most obvious location of a collection of pseudounipolar cell soma?
Any dorsal root ganglion
True/False.
Interneurons are often multipolar.
True.
Pyramidal cells and Purkinje cells receive large amounts of input from what type of neuron?
Interneurons
What type of multipolar neuron is found primarily in the cerebrum?
What type of multipolar neuron is found primarily in the cerebellum?
Pyramidal cells;
Purkinje cells
What type of cell is a pyramidal cell (e.g. multipolar, unipolar, bipolar, pseudounipolar, etc.)?
Multipolar
What type of cell is a Purkinje cell (e.g. multipolar, unipolar, bipolar, pseudounipolar, etc.)?
Multipolar
What basic neuron configuration (i.e. axonal and dendritic branching) do interneurons have?
Multipolar
Where are pyramidal cells found?
The cerebrum
Where are Purkinje cells found?
The cerebellum