Cardio - Histology - Vascular Tissue; Lymphoid Tissue Flashcards
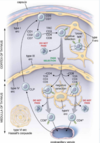
What are the three layers (tunicas) of any blood vessel?
Tunica intima
Tunica media
Tunica adventitia (externa)
The lumen is wider in which, arteries or veins of comparable size?
Veins
The wall is thicker in which, arteries or veins of comparable size?
Arteries
What fiber is found in uniquely high concentrations in the aorta and other large arteries?
Elastin
What are the three types of artery?
Elastic;
muscular;
arterioles
Which arteries are elastic?
The aorta, carotids, and subclavians
What does the elastin in the aorta do?
What does the collagen in the aorta do?
Propel blood (rebound effect);
provides strength to control distension
What transition occurs in the tissues from elastic to muscular arteries?
A shift from elastic tissue to smooth muscle
What subendothelial layer is especially prominent in muscular arteries?
The internal elastic membrane

What is a normal blood pressure?
< 120 / < 80

What blood pressure is in the elevated category?
120 - 129 / < 80

What blood pressure defines hypertension stage 1?
130 - 139 systolic OR 80 - 89 diastolic

What blood pressure defines hypertension stage 2?
≥ 140 systolic OR ≥ 90 diastolic

What structure connects arterioles and capillaries?
Metarterioles

Is capillary blood flow continuous or pulsatile?
Pulsatile
(for maximum nutrient/waste exchange)
Where are precapillary sphincters located?
What are they?
Metarterioles;
bands of smooth muscle

What intermediate filaments lend structural support to capillaries?
Desmin and vimentin
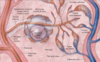
What type of tissue is shown in this micrograph?

A capillary bed
What molecule promotes tight junction leakage in capillary beds?
Histamine
How do large molecules leave capillary beds?
Transcytosis
(endocytosis and then exocytosis on the other side)
What type of well-developed mesenchymal cell surrounds capillary endothelial cells and have the ability to differentiate into smooth muscle?
Pericytes
What contractile filaments are present in pericytes?
Tropomyosin;
isomyosin
What are the three types of capillary?
Continuous;
fenestrated;
sinusoidal (discontinuous)
What types of vessel in the body contain valves?
Veins;
lymphatics