CS&B - Histology - Skin Flashcards
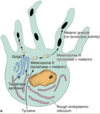
From superficial to deep, what are the layers of epidermis?
(What mnemonic might be helpful in remembering these?)
Stratum corneum,
stratum lucidum (in thick skin only),
stratum granulosum,
stratum spinosum,
stratum basale
(Come, let’s get sunburned!)
What separates the epidermis from the dermis?
The basement membrane (basal lamina + reticular lamina)
From superficial to deep, what are the two layers of the dermis?
The papillary layer;
the reticular layer
Of what type of tissue is the dermal papillary layer composed?
Loose connective tissue (areolar)
Of what type of tissue is the dermal reticular layer composed?
Dense irregular connective tissue
Of what type of tissue is the dermal papillary layer (superficial) composed?
Of what type of tissue is the dermal reticular layer (deep) composed?
Loose connective tissue (areolar);
dense irregular connective tissue
The inferiorly oriented projections of the epidermis are called:
The superiorly oriented projections of the dermis are called:
Epidermal ridges;
dermal papillae
Name all the layers of thick skin from superficial to deep.
Stratum corneum (epidermis)
Stratum lucidum (epidermis)
Stratum granulosum (epidermis)
Stratum spinosum (epidermis)
Stratum basale (epidermis)
Basal lamina (basement membrane)
Reticular lamina (basement membrane)
Dermal papillary layer (dermis)
Dermal reticular layer (dermis)
What epidermal layer is found in thick skin but not thin skin?
The stratum lucidum
Hair follicles, sudoriferous glands, sebaceous glands, nails, and mammary glands are all derived from what layer of skin?
The epidermis
(although many project into the dermis)
What are some important functions of the integument?
Protection
Sensory
Thermoregulatory
Water maintenance
Endocrine
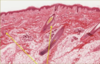
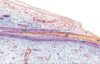
Identify the epidermis in this slide.


Identify the dermis in this slide.


Identify the subcutaneous tissue in this slide.


Identify the first deep layer in this slide that is not part of the integument.


Is the epidermal layer a part of the integument?
Is the dermal layer a part of the integument?
Is the subcutaneous layer a part of the integument?
Is the panniculus carnasus layer a part of the integument?
Yes
Yes
No
No
Which general portion of the skin is the thickest?
Which general portion of the skin is vascular and innervated?
The dermis;
the dermis
What is the primary cell of the epidermis?
The keratinocyte
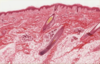
Identify the structures indicated by the letters in this slide.

Stratum corneum;
stratum granulosum;
stratum spinosum;
epidermal projection;
dermal papilla;
stratum basale;
dermis
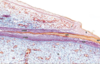
Which epidermal layer appears on histology as a dark line separating the keratinized cells from the normal, nucleated keratinocytes?
The stratum granulosum

Which epidermal layer is the primary creation point of the waterproofing layer of the skin?
The stratum granulosum
(the waterproofing layer then extending up into the stratum corneum)

What two cell junctions are especially important in the basal layer of the epidermis?
Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes
Name a few histologic appearances of the stratum basale.
Closely spaced nuclei
Basophilic
Melanin
(Note: B in image)
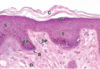
Describe the appearance of the stratum spinosum.
What cell junction is present in both the stratum spinosum and basale?
Larger and flatter cells than in the stratum basale;
desmosomes
(Note: the ‘spines’ on the cells are an artifact of slide preparation)