MSK - Histology - Cartilage; Bone Flashcards
What are the three main types of cartilage?
Hyaline;
elastic;
fibrous
What type of fibers are most prevalent in hyaline cartilage?
What type of fibers are most prevalent in elastic cartilage?
What type of fibers are most prevalent in fibrocartilage?
Type II collagen;
elastic fibers and type II collagen;
types I and II collagen
What type of fibers are most prevalent in hyaline cartilage?
Type II collagen
What type of fibers are most prevalent in elastic cartilage?
Elastic fibers; type II collagen
What type(s) of fibers are most prevalent in fibrocartilage?
Types I and II collagen
What are some examples of hyaline cartilage in the body?
Costal cartilage;
articular cartilage;
tracheal rings
What are some examples of elastic cartilage in the body?
Ears,
epiglottis,
part of the larynx,
auditory tubes
What are some examples of fibrocartilage in the body?
Intervertebral discs;
pubic symphysis;
menisci of the knee joint
What type of cell is most prevalent in hyaline cartilage?
What type of cell is most prevalent in elastic cartilage?
What type of cell is most prevalent in fibrocartilage?
Chondrocytes;
chondrocytes;
fibroblasts
What percentage of cartilage is typically made up by ground substance?
90 - 95%
Chondrocytes receive their nutrients via:
Diffusion
(cartilage is an avascular tissue)
The functional component of cartilage is:
the ECM
What type of cartilage is in the ear?
What type of cartilage are the menisci of the knee?
What type of cartilage is the epiglottis?
What type of cartilage are the intervertebral discs?
Elastic;
fibrocartilage;
elastic;
fibrocartilage
What two types of cartilage are found in the knee?
Articular (lining the joint);
fibrocartilage (the menisci)
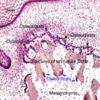
Chondrocytes sit in hollow spaces within the ground substance called:
Lacunae
Is ground substance eosinophilic or basophilic?
Basophilic (blue or dark purple)
What are the three layers of ECM in the cartilage surrounding chondroblasts?
(How strongly does each stain?)
What type of fiber predominates here?
The pericellular matrix (visible with special staining);
the territorial matrix (lightly stained);
the interterritorial (interstitial) matrix (heavily stained);
type II collagen
What two stains are used for elastic fibers?
Verhoeff’s;
orcein
What are the two types of cartilaginous growth?
Appositional (from the perichondrium);
interstitial (within the tissue by existing chondrocytes)
How many chondrocytes are typically found in each lacunae?
1 - 2
If there are two or more chondrocytes in one lacunae, these chondrocytes are termed:
Isogenous groups
What are the three types of cartilage?
Hyaline,
elastic,
fibrocartilage
Which types of cartilage have a surrounding perichondial layer?
Hyaline (excepting articular cartilage);
elastic
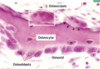
Describe the layers of hyaline cartilage from superficial to deep.
Fibrous layer (perichondrium)
Chondrogenic layer (perichondrium)
Inner chondrogenic layer (chondroblast differentiation)
Mature cartilage