Cardio - Physiology - Excitation & Contraction; EKG; Cardiac Cycle Flashcards
In a normal heart, what percentage of cardiac output comes from atrial contraction?
10%
The AV node has less of what type of channel and what type of cell junction than surrounding ventricular myocytes?
Sodium channels (those that are present are mostly inactive);
gap junctions
True/False.
Gap junctions are opened and closed based on intracellular conditions?
True
(they are regulated by intracellular pH and Ca2+ levels)
What intracellular conditions cause closure of cardiac connexons (gap junctions)?

High calcium levels;
low pH
What intracellular conditions cause opening of cardiac connexons (gap junctions)?

Low calcium;
normal pH
Describe the structure of a gap junction.
6 connexins coming together to make one connexon

In what state will cardiac gap junctions (connexons) be if the cell is at normal physiological conditions (e.g. low calcium levels, pH of 7.2)?
Open

In what state will cardiac gap junctions (connexons) be if the cell is undergoing ischemic conditions (e.g. high calcium levels, pH of ~6.4)?
Closed

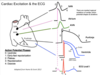
What structure is responsible for the electrocardiogram P-R interval?
The AV node
The AV node is responsible for what part of a normal EKG reading?
The P-R interval
What type of cholinergic receptor do the vagal nerves activate on the heart?
What effect does it have on ion channels?
M2 (G-protein);
activating K+ leak channels (promoting K+ efflux),
inhibiting adenylyl cyclase (and thus inhibiting Ca2+ influx)

What type of adrenergic receptor do sympathetic nerves activate on the heart?
What effect does it have on ion channels?
β1 (G-protein);
activating adenylyl cyclase (promoting Ca2+ influx)

Vagal nerves activate M2 receptors on the heart. These receptors activate what type of G-protein subunits?
Gi

Sympathetic nerves activate β1 receptors on the heart. These receptors activate what type of G-protein subunits?
Gs

The channels in the AV node are mostly:
L-type calcium channels
What is a normal time range for the PR interval?
What is the normal time value for the QRS complex?
0.12 - 0.20 sec;
< 0.12 sec

What prevents atrial depolarization from bypassing the AV node and directly leading to depolarization of the ventricles?
A fibrous ‘skeletal’ ring separating the atria from the ventricles
Why is it important that gap junctions close during ischemic conditions?
To try to isolate the ischemic tissues from the healthy
Where does repolarization occur first, the epicardium or endocardium?
Epicardium
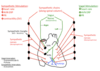
Describe the differences in action potential between the following:
SA node pacemaker cells
Atrial myocytes
AV node pacemaker cells
Purkinje fibers
Ventricular myocytes (epicardium and endocardium)
What type of cell are SA node and AV node pacemaker cells?
Modified cardiomyocytes
Arrange the following types of cell from longest to shortest action potential:
Atrial
Purkinje
Ventricular
Purkinje > Ventricular >>> Atrial
Which has more of a phase 1 ‘notch,’ the epicardium or endocardium?
Epicardium

Arrange the following types of cell from most to least unstable disatolic potential:
SA node pacemakers
AV node pacemakers
Purkinje fibers
SA node pacemakers >
AV node pacemakers >
Purkinje fibers