Cardio - Physiology - Arrhythmias; Heart Sounds Flashcards
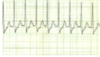
What rhythym is shown here?

Normal sinus rhythym
(P –> QRS –> T
every time)

What rhythym is shown here?

Sinus tachycardia

What is a normal PR interval?
What is a normal QRS interval?
0.12 - 0.20 sec
≤ 0.12 sec
How much time is represented by each 1 mm box on an EKG?
How much time is represented by each 5 mm box on an EKG?
How much time is represented by five 5 mm boxes on an EKG?
- 04 second
- 2 second
1 second

What is the internationally standardized speed at which EKG paper moves?
25 mm / sec
(so five large boxes = 1 sec)
If there is one large box (five 1 mm boxes) between adjacent QRS complexes, what is the heart rate?
300 BPM
(Note: divide 300 by the number of large boxes between adjacent QRS complexes to get the HR)

If there are two large boxes (each of which is five 1 mm boxes) between adjacent QRS complexes, what is the heart rate?
150 BPM
(Note: divide 300 by the number of large boxes between adjacent QRS complexes to get the HR)

If there are three large boxes (each of which is five 1 mm boxes) between adjacent QRS complexes, what is the heart rate?
100 BPM
(Note: divide 300 by the number of large boxes between adjacent QRS complexes to get the HR)

If there are four large boxes (each of which is five 1 mm boxes) between adjacent QRS complexes, what is the heart rate?
75 BPM
(Note: divide 300 by the number of large boxes between adjacent QRS complexes to get the HR)

If there are five large boxes (each of which is five 1 mm boxes) between adjacent QRS complexes, what is the heart rate?
60 BPM
(Note: divide 300 by the number of large boxes between adjacent QRS complexes to get the HR)

If there are six large boxes (each of which is five 1 mm boxes) between adjacent QRS complexes, what is the heart rate?
50 BPM
(Note: divide 300 by the number of large boxes between adjacent QRS complexes to get the HR)

If there are seven large boxes (each of which is five 1 mm boxes) between adjacent QRS complexes, what is the heart rate?
43 BPM
(Note: divide 300 by the number of large boxes between adjacent QRS complexes to get the HR)

Name the heart rate indicated by each of the following intervals of space between adjacent QRS complexes:
4 large boxes (twenty 1 mm boxes)
2 large boxes (ten 1 mm boxes)
1 large box (five 1 mm boxes)
3 large boxes (fifteen 1 mm boxes)
(Just 300 divided by the number of large boxes between adjacent QRS complexes)
75 BPM
150 BPM
300 BPM
100 BPM

Name the heart rate indicated by each of the following intervals of space between adjacent QRS complexes:
1 large box (five 1 mm boxes)
2 large boxes (ten 1 mm boxes)
3 large boxes (fifteen 1 mm boxes)
4 large boxes (twenty 1 mm boxes)
5 large boxes (twenty-five 1 mm boxes)
6 large boxes (thirty 1 mm boxes)
(Just 300 divided by the number of large boxes between adjacent QRS complexes)
300
150
100
75
60
50

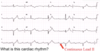
What arrythmia is shown here?

Atrial fibrillation
What arrythmia is shown here?

Atrial flutter
What arrythmia is shown here?

Third degree AV block
What arrythmia is shown here?

Premature ventricular beat
(ectopic ventricular beat –> this explains why it is opposite in polarity. It may be starting in the right ventricle)
What are some ways by which arrythmias are classified?
Origin
(SA, atrial, supraventricular, ventricular, etc.)
Pattern & rate
(tachycardia, bradycardia, fibrillation, flutter, etc.)
# of ectopic sites
(unifocal or multifocal)
How can arrhythmias be classified based on their origin?
Sinus, atrial, supraventricular, ventricular, etc.
How can arrhythmias be classified based on their pattern and rate?
Tachycardia, bradycardia;
flutter, fibrillation, etc.
How can arrhythmias be classified based on their number of ectopic sites?
Either unifocal or multifocal
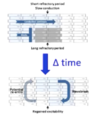
What is an example arrhythmia that could result in the following finding on EKG examination?

An ectopic site in the left atrium

(the green star in the attached diagram)
What is an example arrhythmia that could result in either of the following findings on EKG examination?

A supraventricular ectopic site firing
[either in the AV node (no P wave) or adjacent to it]
(the purple circle in the attached diagram)