CS&B - Biochemistry - DNA Structure, Replication, Repair Flashcards
(158 cards)
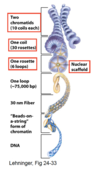
Euchromatin is known as ‘beads on a string’ due to its arrangement as nucleosomes connected by linker DNA. These fibers are commonly referred to by their width.
What width does euchromatin have?
11 nanometers
Approximately, how many basepairs (bps) are found twice-wound around the histone octamer?
And how many are found in the linker (spacer) DNA between nucleosomes?
146 bps;
90 bps
The weak forces connecting DNA to histones are primarily produced by electrical interactions between what structures?
DNA phosphate groups (-) and arginine and lysine side chains (+)
What are the proteins making up the histone octamer?
H2a (x2)
H2b (x2)
H3 (x2)
H4 (x2)
What histone protein is not part of the histone octamer?
H1
One fiber of euchromatin is ___ nm in width.
One fiber of heterochromatin is ___ nm in width.
11;
30
What portion of the nucleosome is the site of most modifications that allow for gene activation and silencing?
The histone tails
What major nucleosome modifier is responsible for decondensation (unwinding) of chromatin?
What effect will this have on the genes involved?
Acetylation;
increased gene expression
How does acetylation of the histone tails (specifically lysine residues) cause decondensation of the chromatin?
It neutralizes some histone positive charge
What enzyme is responsible for histone acetylation?
What enzyme is responsible for histone deacetylation?
Histone acetyltransferases (HATs);
histone deacetylases (HDACs)
Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) have what effect on chromatin?
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) have what effect on chromatin?
Decondensation (11 nm fibers);
condensation (30 nm fibers)
Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) have what effect on gene expression?
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) have what effect on gene expression?
Increased gene expression;
gene silencing
What effect does methylation typically have on chromatin?
Gene silencing
How does histone methylation cause gene silencing?
By preventing acetylation
What is the typical effect of histone phosphorylation?
To promote chromatin decondensation (unwinding)
Which histone modifications will typically result in chromatin decondensation (unwinding) and increased gene expression?
Acetylation (by HATs);
phosphorylation
Which histone modifications will typically result in chromatin condensation (coiling) and gene silencing?
Deactylation (by HDACs);
methylation
For what are SWI/SNF responsible in gene expression?
How?
Regulation of chromatin decondensation;
through HAT function
For what is H1 responsible in gene expression?
How?
Facilitating DNA condensation;
through HDACs
Which activators regulate HAT function and chromatin decondensation?
Which activators regulate HDAC function and chromatin condensation?
SWI/SNF;
H1
What is the function of the MECP2 protein?
To bind methylated DNA (not methylated histones)
and recruit HDACs
DNA methylation (as opposed to histone methylation) will result in activation of what protein and what effect?
The MECP2 protein;
HDAC recruitment;
chromatin condensation
What is the shortest phase of the cell cycle?
What phase is significantly shortened in rapidly dividing (e.g. tumor) cells?
M;
G1
How many chromosomal autosome pairs are there?
How many chromosomal sex pairs are there?
22;
1