lymphatic system-lab Flashcards
(10 cards)
No. 4 Reticular CT: Identify

Section is a lymph node prepared with a silver stain to show the reticular fibers produced by fibroblasts of the reticular connective tissue. The stroma of lymphatic tissue/organs (except thymus) is formed of this tissue, creating a spongelike, supporting framework.

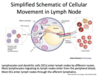
No. 63 Lymph Node: Some sections are poor, as the medulla is difficult to distinguish from cortex. The capsule is present, and the subcapsular sinus can be seen. Lymph can percolate through sinuses, and the stroma is also framework for the attachment of lymphatic cells to act on antigens in the fluid. Locate the capsule and trabeculae, the cortex with its lymphatic nodules and paracortical region, and the medulla and its medullary cords. Identify plasma cells within the medullary cords. Explore the periphery for afferent lymphatic vessels. Trace the flow of lymph through the node: afferent vessels, subcapsular sinus, cortical (trabecular) sinuses, and medullary sinuses. Efferent vessels can only be seen if your section has a well-defined hilum.


No. 37 Small Intestine: Look in the lamina propria for diffuse lymphatic tissue; look at the ileum for a Peyer’s patch, which is an aggregate of lymphatic nodules mainly in the submucosa but with some projection into the lamina propria mucosae. Scan several, observe the darker mantle, and the lighter germinal center (immature and differentiating cells) indicating activity of that nodule. Lymphoblasts and plasma cells (have an eccentric nucleus) that originate from B lymphocytes occur in the germinal center.
No. 61 Palatine Tonsil, No. 62 Lingual Tonsil: Locate lymphatic nodules, germinal centers, the mucous membrane with its stratified squamous epithelium, and deep to the tonsil, mucous glands. Identify mucous glands deep to the tonsil.

No. 64 Spleen: Locate the smooth muscle in the capsule and also scattered in trabeculae throughout the parenchyma. Red and white pulp are distinct. Trabecular arteries can be located. Identify a splenic (lymphatic) nodule and a central arteriole and the surrounding periarteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS) of T cells. The lumen of the vessel can be seen in x.s. Red pulp has so much blood in it that the sinusoids are hard to distinguish from the meshwork. Look for hemosiderin in macrophages of red pulp. Plasma cells are present.

No. 65 Thymus:

Note the capsule and the septa dividing the organ incompletely into lobules, look for the dark cortex and lighter medulla. Identify epithelioreticular cells. Thymic (Hassall’s) corpuscles are in the medulla. Developing T cells are in the cortex protected from antigenic stimulation by the blood-thymic barrier. T cells in the medulla are mature and ready to enter the vascular system to populate the various lymphatic organs.





Thymus: Thymic (Hassall’s) corpuscles are in the medulla.
Identify

Canine Spleen



